Energy Conversion
advertisement

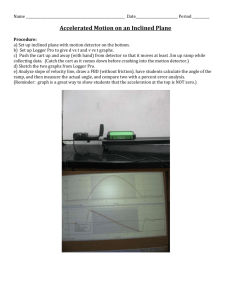
Physics 8 Name ________________________ Chapter 15.2 Lab Date Started _________ Period ___ Due date ___________ Energy Conversion and Energy Conservation Introduction: As a cart rolls down an inclined plane, the mechanical potential energy of the cart is converted to mechanical kinetic energy. Frictional forces cause a loss of kinetic energy. CONVERSION (energy changes from one form to another): During this class activity, you will take measurements to find the mechanical potential energy converted to mechanical kinetic energy by the moving cart. CONSERVATION (energy cannot be created or destroyed): You will then compare mechanical potential energy to mechanical kinetic energy to see the loss of energy due to frictional forces. Equations: 𝑃𝐸 = 𝑚𝑔ℎ 𝑣= 𝑑 𝑡 𝐾𝐸 = 1 2 𝑚 𝑣2 Distance the car traveled ______m Height = ___ Physics 8 15.2 PE KE ramp conversions 3.2013 1 Procedure for Energy Conversion: 1. Find the Potential energy of the cart at the top of the ramp. Measure the height of the ramp. Convert units to meters if needed. Record the height of the ramp = _________ m 2. Measure the mass of the cart using a triple-beam balance. Careful to zero the balance, and measure properly. Convert mass to kg if needed. Record the mass of the cart = _________ kg Calculate the potential energy of the cart at the top of the ramp. Show the E.S.A. in the box below. Have the answer to the 0.0001 place. g = 9.8 m/s2 Strategy: Measure the velocity of the cart; calculate the kinetic energy of the cart at the bottom of the ramp. 3. Measure the length of the ramp. Convert to meters if needed. Record the length of ramp = ________ m 4. Set the cart at the top of the ramp, ready the stopwatch. Measure the time for the cart to reach the bottom of the ramp in seconds to the .01s place. Record 3 trials: 1.__________ 2. _________ 3.___________ Calculate the average time. Record the average of the 3 time trials = _____s 5. Calculate the velocity of the cart. Have the answer to the 0.0001 place. Show the E.S.A. in the box below. 2 6. Calculate the kinetic energy of the cart at the bottom of the ramp. Show the E.S.A. in the box below. Have the answer to the 0.0001 place. Energy Conservation Procedure for measuring Conservation of Energy (Example) (KE + PE) beginning of action – friction = (KE + PE) end of action 100J - 5J 95J = = 95J 95J The cart was not moving at the top of the ramp, all of the mechanical energy was in the form of potential energy. Since the cart was moving the fastest and at the lowest point of the ramp, all of the resulting energy was in the form of mechanical kinetic energy. Compare (the difference) the potential energy to the kinetic energy. Using the above example, substitute and calculate the mechanical energy due to frictional forces from your lab. (PE) beginning of action – ___________ J friction _________ J = (KE) end of action _________ J 3 Summary Questions: 1. If the ramp height were doubled, what would be the new potential energy? Show the E.S.A. in the box below. 1. According to step 6, friction caused a considerable loss of energy for the cart and ramp system. Is the cart and ramp system an OPEN ENERGY SYSTEM or a CLOSED ENERGY SYSTEM? Explain using data from your lab. 2. Describe one design change for the cart which will decrease the loss of energy due to friction. Use your own wording. ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 3. Describe why the design change will decrease the loss of energy due to friction. Use your own wording. ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 4. Draw and label the design change from question 3 in the box below. 4 Brainstorm Design Options: Car Body: Shape Size Construction Materials Wheels: Number of Wheels Diameter Width Composition(what materials make-up the wheels) 5