Executive ppt.
advertisement

December 7, 1941, a
day
which will live in
infamy.
First Fireside Chat
FDR inaugural
address 2:12
Dirty Politics?
Obama caught Osama
Videos
Tear Down This Wall
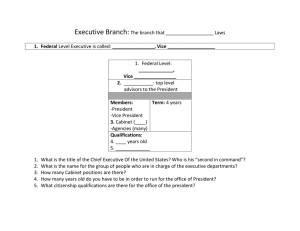
3 Qualifications:
1. Native-born U.S. Citizen
2. 35 years old
3. Resident of the U.S. for at least 14 years
$400,000 plus a
$50,000
nontaxable
allowance for
travel costs.
Are there any unofficial qualifications?
•Has a four year term.
•The Constitution did not originally specify a term limit. George Washington set a twoterm limit. It was not broken until Franklin Roosevelt.
•In 1951, the twenty-second amendment set a two-term limit to the presidency.
•One very important responsibility is to serve as president if
the president dies, leaves office, or is unable to fulfill his/her
duties.
oEight presidents have died and one has resigned while in
office
•The vice president also serves a four year term and must meet
the same constitutional qualifications as the president.
•Salary – $208,100 a year, plus a $10,000 taxable expense
allowance.
•The vice president has only one other job stated in the
Constitution – to preside over the Senate. The VP is not a
member of the senate, can not take part in Senate debates and
may vote only in the case of a tie.
Rules of Succession
{
The vice president takes his/her place.
The 25th amendment allows the new president to
nominate a new vice president.
The nomination must be approved by a majority vote of both houses.
If both the president & vice president die or leave
office, the 20th amendment gives Congress the
power to set the order of presidential succession.
1.
2.
3.
The Speaker of the House
President pro tempore of the Senate
The members of the president’s cabinet in the order in which their
departments were created.
Who takes the president’s place if
his/her position is vacated?
1. What is one qualification to become
President or Vice President?
2. What is one responsibility of the Vice
President that is stated in the Constitution?
3. What is the line of succession to the
Presidency?
Exit Ticket
{
“The executive power shall be vested in [given to] a
President of the United States of America”
-- U.S. Constitution, Article II,
Section 1
1.
2.
3.
Legislative Leader
Commander in Chief
Foreign Policy
Leader
Every year, the president recommends new laws
to Congress by delivering his State of the
Union Address.
State of the Union is given late every January.
The president sends Congress a budget.
He also influences Congress by what laws he does
not want.
Veto power is his most powerful tactic in influencing
laws.
Congress can override a veto by 2/3rds vote.
By this role he is the head of the military.
All military officers answer to him/her.
Under the Constitution only the Congress can declare war;
however, the president may send forces anywhere in the world.
The actions of the United States affect nations
everywhere and the actions of many other countries may
also strongly impact the U.S.
Our government’s plan for interacting with the other
countries of the world is called foreign policy.
Our president appoints diplomats to represent our
government in foreign countries.
Diplomats help the president secure friendships with other
countries throughout our world
The act of interacting with foreign governments is called
diplomacy.
The U.S. government also makes written agreements or
treaties with other countries.
The president has the power to make treaties but all treaties must
be approved with a 2/3rd’s vote by the Senate.
The president has the power to appoint
Supreme Court justices & other federal judges.
All appointments have to be approved by the
Senate
The president has the power to do 3 things to
those who have committed a federal crime:
1.
2.
3.
Reprieve – Postpones the carrying out of a
person’s sentence.
Pardon – Forgives a person for his/her crime &
eliminates punishment.
Commutation – Reduces a person’s sentence.
Tom Vilsack
Hillary Clinton
Hilda Solis
Eric Holder Jr.
{
President Obama’s Cabinet
The President has a group of close advisers & aides
known as the Executive Office of the President.
Because of current issues, the President needs many
advisers who are specialists in certain areas.
For example, the National Security Council (NSC)
is the president’s top ranking group of advisers on
defense & security.
The White House Office falls under the Executive
Office of the President.
The White House Office includes: the president’s
close personal & political advisers, the press
secretary, researchers, clerical staff, secretaries,
and other assistants.
The cabinet is a group of advisers to the President.
The president appoints the members of his cabinet
but his appointments must be approved by 2/3’s vote
in the Senate.
The title of most cabinet members is secretary. For
example, the head of the Department of State is the
Secretary of State. The Attorney General, however, is the
head of the Department of Justice.
George Washington had five cabinet departments.
Today we have fifteen departments.
Foreign policy is the special responsibility of the Department of State.
The Secretary of State heads a staff of officials who represent the U.S.
in countries around the world.
Ambassadors are the highest ranking U.S. representatives in foreign
countries.
An embassy is the official residence & offices of an ambassador in a
foreign country.
A consul represents U.S. commercial interests in a foreign country.
A consulate (a U.S. consul’s office) can be found in most large
countries.
At home the Department of State’s duties include keeping up with
passports and visas.
Passports – formal documents that allow U.S. citizens to travel abroad
Visas – allow foreigners to come to the U.S.
The Department of Defense is in charge of the nation’s
armed forces & operates hundreds of military bases in
the U.S. & in other nations.
The Secretary of Defense is always a civilian.
This ensures nonmilitary control over the armed forces.
The Secretary of Defense has military officers as
assistants.
The Joints Chiefs of Staff is made up of high ranking
officers from each of the armed forces.
They advise the president on military affairs.
{
The executive branch has many duties that do not fit
any of the 15 executive departments. Independent
agencies & regulatory commissions have been
created to cover such areas.
A regulatory commission is a type of independent agency
that has the power to make rules & bring violators to court.
Their decisions often have the force of law.
Regulatory commissions are created because of a specific
need.
Examples of regulatory commissions:
Federal Election Commissions (FEC) – enforces election laws, provides financial
information for campaigns, & controls public funding of presidential elections.
Consumer Product Safety Commission – enforces safety standards for consumer
products & conducts safety research.
National Labor Relations Board – enforces federal relations laws, prevents unfair
labor practices among businesses.
Bureaucracy – the many departments and agencies at all
levels of government.
Federal bureaucracy is large & involved in many areas of daily
life.
It makes many rules & regulations.
Some people complain that the regulations are confusing.
People sometimes have to fill out several forms & stand in
long lines to see a government representative.
Freedom Project