Cellular Respiration
advertisement

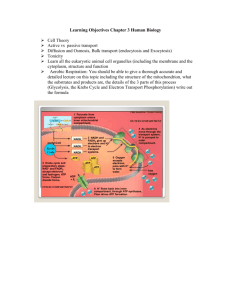
Cellular Respiration Glycolysis Preparatory reaction Citric acid (krebs) cycle Electron transport chain Glycolysis Occurs outside mitochondria Breaks down glucose into two pyruvate molecules Evolutionary speaking, glycolysis occurs in all organisms, meaning it probably evolved before the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain Steps in Glycolysis 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Begins when glucose is activated with two ATP molecules, the glucose splits into two C molecules known as G3P. G3P is then oxidized, removing electrons and H ions. The lost electrons and H ions are then accepted by NAD+ resulting in two NADH. G3P oxidation results in the production of 4 high-energy phosphate groups which make 4 ATP molecules, called substrate-level phosphorylation. There is a net gain of only 2 ATP molecules in glycolysis because 2 of the ATP molecules are used in supplying energy for the reaction What happens next depends on if O2 is available or not. If it is available, pyruvate enters and C.R. ensues. If not, fermentation occurs, and pyruvate is reduced. Preparatory Reaction Connects glycolysis to the citric acid cycle converts pyruvate to a 2-carbon acetyl group and attaches it to coenzyme A resulting in acetly-CoA through a redox reaction. The reaction occurs twice for each glucose molecule Citric Acid (krebs) cycle Occurs in the matrix of the mitochondia Sometimes called the krebs cycle because it was named for sir Hans Krebs who described the reaction in the 1930s. Begins by the addition of a 2-carbon acetyl group to a 4-carbon molecule forming a 6-carbon citric acid molecule In the reactions that follow, at three different times, two electrons and one H ion are accepted by NAD+ , forming NADH At one time in the cycle, two electrons and one H ion are accepted by FAD, forming FADH2 Some energy is released and is used to make ATP by substratelevel phosphorylation, One high-energy metabolite accepts a phosphate group and ADP to ATP in the reaction. For each glucose molecule that goes in, the citric acid cycle turns twice. The products of the cycle are 4 CO2, 2 ATP, 6 NADH and 2 FADH2 The electron transport chain Takes place in the cristae of the mitochondria, in which electrons are passed from carrier to carrier Some carriers are cytochrome molecules(complex carbon rings with iron in the center) NADH and FADH2 carry the electrons through the system Each time the electrons are passed on, NADH gives up its electrons and becomes NAD+ then picks up electrons, therefore they are reduced. ATP is released at each redox (reduction) reaction Oxygen must be present for this to work, therefore this process is also called oxidative phosphorylation Oxygen accepts electrons in the reaction and combines with hydrogen ions to form water. The electrons are being delivered to the system by FADH2, at this time two ATP molecules are formed Coenzymes and ATP in the system undergo recycling. For Monday Nov. 10 Study for a 20-point quiz (credit) Beginning lab on CR Study session after school TH 11/13 TEST will be on Monday 11/17 Lab Report for CR will also be due on that day Homework: complete/review the rest of the notes online at kauscience.k12.hi.us