GB6 Review - mrstaorminageometry
advertisement
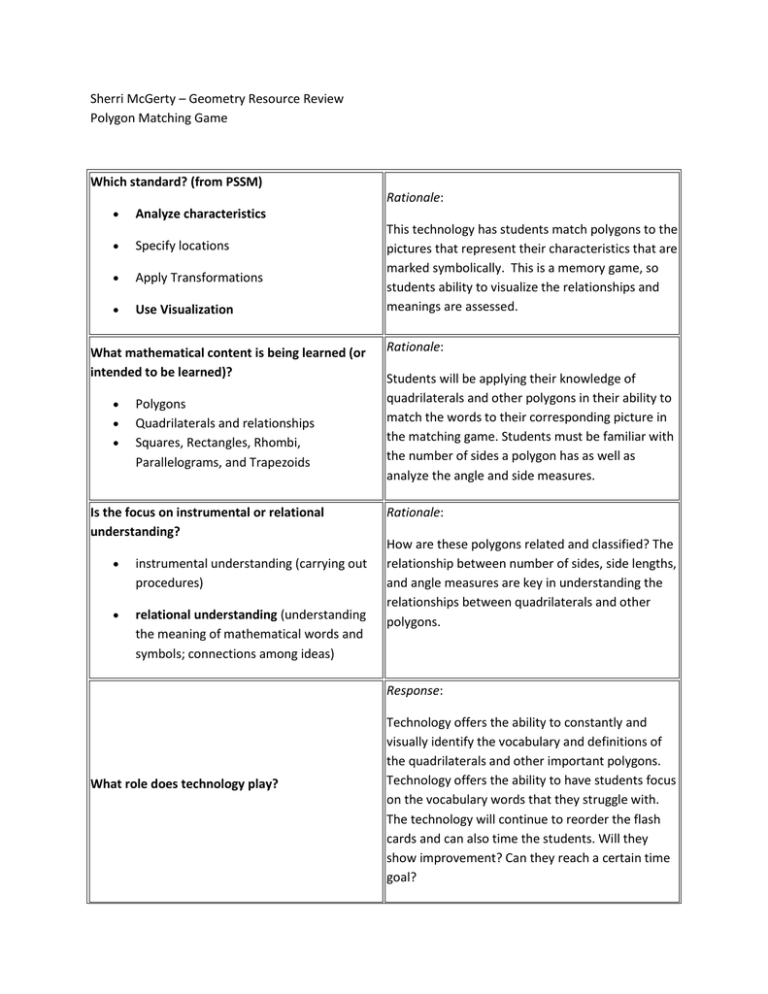
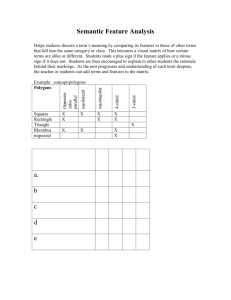
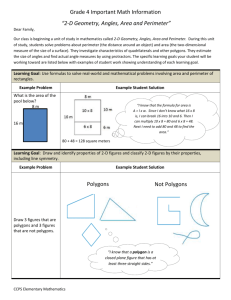
Sherri McGerty – Geometry Resource Review Polygon Matching Game Which standard? (from PSSM) Rationale: Analyze characteristics Specify locations Apply Transformations Use Visualization What mathematical content is being learned (or intended to be learned)? Polygons Quadrilaterals and relationships Squares, Rectangles, Rhombi, Parallelograms, and Trapezoids Is the focus on instrumental or relational understanding? instrumental understanding (carrying out procedures) relational understanding (understanding the meaning of mathematical words and symbols; connections among ideas) This technology has students match polygons to the pictures that represent their characteristics that are marked symbolically. This is a memory game, so students ability to visualize the relationships and meanings are assessed. Rationale: Students will be applying their knowledge of quadrilaterals and other polygons in their ability to match the words to their corresponding picture in the matching game. Students must be familiar with the number of sides a polygon has as well as analyze the angle and side measures. Rationale: How are these polygons related and classified? The relationship between number of sides, side lengths, and angle measures are key in understanding the relationships between quadrilaterals and other polygons. Response: What role does technology play? Technology offers the ability to constantly and visually identify the vocabulary and definitions of the quadrilaterals and other important polygons. Technology offers the ability to have students focus on the vocabulary words that they struggle with. The technology will continue to reorder the flash cards and can also time the students. Will they show improvement? Can they reach a certain time goal? What instructional function(s) does the resource serve? practice (i.e., practicing skills or knowledge already learned) direct instruction/explanation (i.e., explaining or presenting content to students) learning through exploration (i.e., provides context in which students can see new relationships; come to new understandings) Rationale: This is practice of basic vocabulary and relationships amongst polygons according to their angles, side lengths, and number of sides. What kinds of representations of the mathematics are used? symbolic (i.e., numerals, symbols) graphical (i.e., standard graphical notation The technology represents the vocabulary as such as Cartesian (X-Y) coordinate system, pictures instead of definitions in words, so it is bar graph, pie chart) visual in nature. Within the figures, congruence and angle measures are marked with their visual/spatial (e.g., circles or squares with corresponding and appropriate symbols, and not lines to show fractions) numbers. The figures represent the definitions and concrete or real-world objects (e.g., images are representative of graphs and could be on the coordinate plane too. of base-10 blocks, puppies, or jars) dynamic (mathematical ideas represented through motion or sound) Rationale: