COURSE TITLE (COURSE CODE)
advertisement
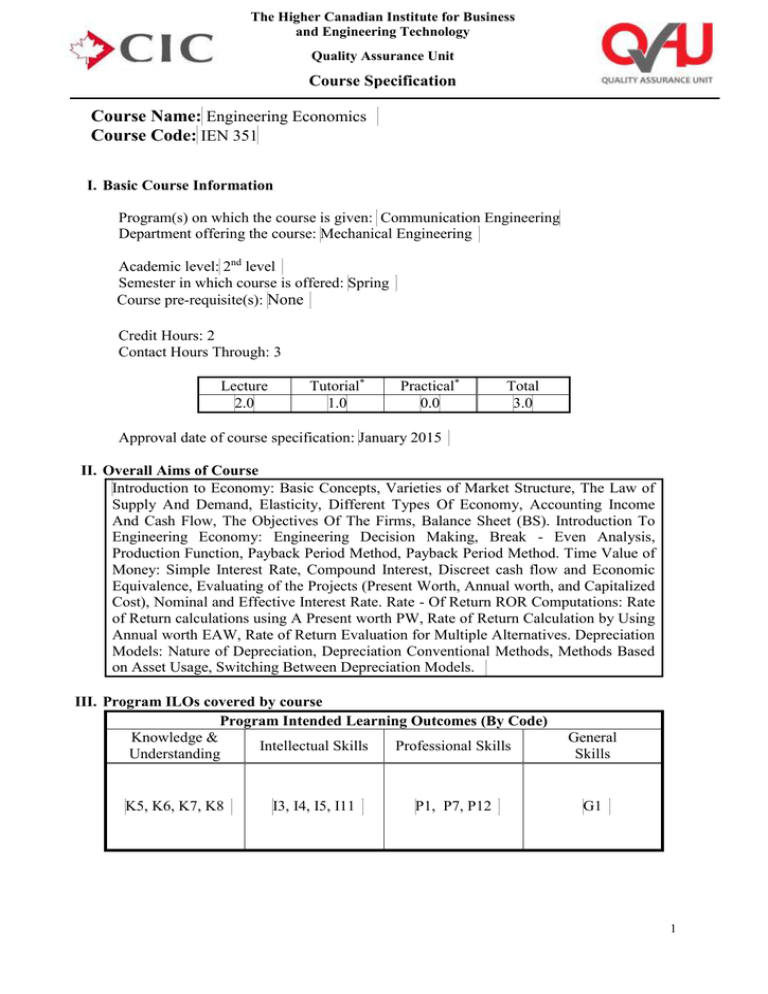
The Higher Canadian Institute for Business and Engineering Technology Quality Assurance Unit Course Specification Course Name: Engineering Economics Course Code: IEN 351 I. Basic Course Information Program(s) on which the course is given: Communication Engineering Department offering the course: Mechanical Engineering Academic level: 2nd level Semester in which course is offered: Spring Course pre-requisite(s): None Credit Hours: 2 Contact Hours Through: 3 Lecture 2.0 Tutorial* 1.0 Practical* 0.0 Total 3.0 Approval date of course specification: January 2015 II. Overall Aims of Course Introduction to Economy: Basic Concepts, Varieties of Market Structure, The Law of Supply And Demand, Elasticity, Different Types Of Economy, Accounting Income And Cash Flow, The Objectives Of The Firms, Balance Sheet (BS). Introduction To Engineering Economy: Engineering Decision Making, Break - Even Analysis, Production Function, Payback Period Method, Payback Period Method. Time Value of Money: Simple Interest Rate, Compound Interest, Discreet cash flow and Economic Equivalence, Evaluating of the Projects (Present Worth, Annual worth, and Capitalized Cost), Nominal and Effective Interest Rate. Rate - Of Return ROR Computations: Rate of Return calculations using A Present worth PW, Rate of Return Calculation by Using Annual worth EAW, Rate of Return Evaluation for Multiple Alternatives. Depreciation Models: Nature of Depreciation, Depreciation Conventional Methods, Methods Based on Asset Usage, Switching Between Depreciation Models. III. Program ILOs covered by course Program Intended Learning Outcomes (By Code) Knowledge & Intellectual Skills Professional Skills Understanding K5, K6, K7, K8 I3, I4, I5, I11 P1, P7, P12 General Skills G1 1 The Higher Canadian Institute for Business and Engineering Technology Quality Assurance Unit Course Specification IV. Intended Learning Outcomes of Course (ILOs) a. Knowledge and Understanding On completing the course, students should be able to: k.1 Identify and demonstrate competence in university level mathematics, natural sciences, engineering fundamentals, and specialized engineering knowledge appropriate to the program. k.2 Recognize the Economics in communications technologies. k.3 Identify the Business and management principles relevant to engineering. k.4 Identify and analysis of communication systems economics b. Intellectual/Cognitive Skills On completing the course, students should be able to: i.1. Use brainstorming and innovation techniques to deal with problems and to develop new ideas. i.2. Demonstrate and organize tasks into a structured economical form. i.3 Apply the economic theories in the engineering systems. i.4 Identify the numerical models for economic theroies. c. Practical/Professional Skills On completing the course, students should be able to: p.1. Formulate and use the appropriate mathematical methods for modeling and analyzing problems in electrical, electronic and communications engineering. p.2. Set up, design, build and test a economic engineering systems. p.3 Create a technical reports. d. General and Transferable Skills On completing the course, students should be able to: g.1 Manipulate, sort and present the information in a variety of ways V. Course Matrix Contents Main Topics / Chapters 1- interest affect money 2- effective interest rate 3- Rate of return analysis Breakeven, sensitivity and payback analysis Estimating costs and 54- systems Net Teaching Weeks 2 2 3 Course ILOs Covered by Topic (By ILO Code) K&U I.S. P.S. G.S. k1 i1 k2 i1,i2 All i3 p1 g1 3 k3, k4 3 k2 Duration (Weeks) p2 All g1 p3 13 2 The Higher Canadian Institute for Business and Engineering Technology Quality Assurance Unit Course Specification VI. Course Weekly Detailed Topics / hours / ILOs Week No. 1 2 3 4 5 Total Hours Sub-Topics Introduction to Engineering Economics How time and interest affect money How time and interest affect money Nominal and effective interest rate Present worth analysis 2 4 4 4 4 6 Annual worth analysis 7 Midterm Exam Rate of return analysis 8 Benefit/Cost analysis and public sector projects 9 Breakeven, sensitivity and payback analysis 10 Effects of inflation 11 Effects of inflation 12 Estimating costs 13 Research Project 14 15 Final Exam Total Teaching Hours Contact Hours Theoretical Practical Hours Hours* 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 4 2 2 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 VII. Teaching and Learning Methods Teaching/Learning Method Lectures & Seminars Tutorials Computer lab Sessions Practical lab Work Reading Materials Web-site Searches Research & Reporting Problem Solving / Problem-based Learning Projects Independent Work Group Work Case Studies Presentations Simulation Analysis Course ILOs Covered by Method (By ILO Code) K&U ALL k1 Intellectual Skills All All Professional Skills P2 All General Skills g1 All g1 k3, k4 i3 p2 i3 p3 g1 Others (Specify): 3 The Higher Canadian Institute for Business and Engineering Technology Quality Assurance Unit Course Specification VIII. Assessment Methods, Schedule and Grade Distribution Course ILOs Covered by Method (By ILO Code) Assessment Method K&U I.S. P.S. G.S. Midterm Exam Final Exam Quizzes k1, k2, k3 All k1, k2, k4 Course Work Report Writing Case Study Analysis Oral Presentations Practical Group Project Individual Project i1, i2, i3 Assessment Weight / Percentage Week No. 20 % All i2, i3 10 % All i3 All p3 i2, i3 p2 g1 5% 5% 10 % Others (Specify): IX. List of References Essential Text Books Basics of Engineering Economy Textbook ISBN #: 978-0-07-128762-3Publisher : McGraw-Hill Course notes Recommended books Periodicals, Web sites, etc … Lecturers notes and slides X. Facilities required for teaching and learning Big sized lecture rooms. Computers (Personal & Notebook). Laboratory Data show. Course coordinator: Dr. Nabil Shams Head of Department: Dr. Mahmoud Mohamed Date: January 2015 4