luluhawa
advertisement

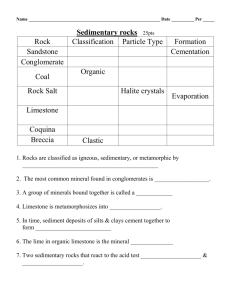
Luluhawa batuan mendak Learning objectives 6 hasil 1 Apa itu 2 Bagaimana terjadi 5 Impak/kesan 7 kepentingan luluhawa 3 Jenis2 luluhawa 4 Faktor2 yg mempengaruhi luluhawa Luluhawa – suatu proses yang berlaku di permukaan bumi untuk memecah dan menguraikan batuan (break and decompose rocks) Enviromen: terhad kepada sejauh mana air tanah (groundwater) boleh menusuk masuk (penetrate) ke dalam permukaan bumi luluhawa Boleh dilihat sebagai destructive forces - yang memecah, mengurai, mengubah bentuk dan keadaan fizikal dan kimia batuan Boleh dilihat sebagai constructive forces – yang menghasilkan sedimen, membentuk batuan mendak, mineral, mendapan mineral, landform baru Fakta asas luluhawa Berlaku perlahan sepanjang masa Mengambil masa yang lama Semua jenis luluhawa berlaku kadang2 serentak dan tak terpisah satu sama lain. Dipisahkan untuk memudahkan pemahaman sahaja Keadaan di keliling menentukan segalanya Jenis2 luluhawa 1. Luluhawa fizikal 2. Luluhawa kimia 3. Luluhawa biologi 1. Luluhawa fizikal Memecahkan batuan yang bersaiz besar kepada bahagian yang lebih kecil contoh: wedging (pembajian), exfoliation (pengelupasan), thermal expansion (kembang haba), lelasan (abrasion), (wetting and drying (esp in shales), pressure release by erosion of overburden Luluhawa fizikal 1 Frost wedging (pembajian ibun) – water expands when it freezes, breaking rocks into angular fragments; lazim berlaku dalam iklim temperat (ada ais) Nota: apabila air menjadi ais, isipadu meningkat sebanyak 10% => mebungkah (pries) batuan talus – terdapat di kaki bukit Luluhawa fizikal 2 Exfoliation (pengelupasan) – bedrocks (batuan hampar) breaks into flat sheets along joints (kekar) which parallel the ground surface. This phenomenon is caused by expansion of rock when the pressure of overlying rock is removed by erosion => sometimes called unloading Apa itu kekar? Exfoliation Stone Mt exfoliation exfoliation Active exfoliation Stone Mt goblin Mt Kinabalu Mt Kinabalu Mt Kinabalu Luluhawa fizikal 3 Thermal expansion (kembang haba) – heat causes action; cooling causes contraction => expand and contract at different rate causes stresses along mineral boundaries. Repeated heating and cooling => batuan pecah 4 Lelasan (abrasion) Batuan menjadi lebih kecil hasi drpd pergeseran dan pelanggaran semasa terangkut, contohnya di dasar sungai Glasial, ombak dan angin juga boleh menjadi agen lelasan Kelebihan kimia fizikal Luluhawa fizikal memecahkan batuan ke saiz yg lebih kecil => menyediakan lebih banyak luas permukaan batuan bersaiz kecil untuk tindakbalas kimia berlaku 2. Luluhawa kimia Memecahkan batuan secara kimia dgn menambah atau menanggalkan (removing) unsur2 kimia, mengubah unsur2 tersebut menjadi bahan2 baru contoh: dissolution (pelarutan), hydrolysis (hidrolisis), oxidation (pengoksidaan) Luluhawa kimia 1 Dissollution (pelarutan) – alters rocks by removing soluble minerals => soluble ions and insoluble ions => precipitate and crystallize (dalam tasik atau laut) Ex: pembentukan garam, batu kapur, travertine Batuan => ion larut/ tak larut => pemendakan Luluhawa kimia 2 Hydrolisis – proses di mana feldspar are weathered to form clay Note: clay make up half of sedimentary rocks on Earth (Berapa jenis feldspar kita ada? Apakah komposisinya?) Weathering of feldspar Beberapa contoh t/b kimia A. Solution of carbon dioxide in water to form acid CO2 + H2O H2CO3 H+ + HCO3B. Solution of calcite CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O C. CaCO3 + H+ HCO3- Ca2+ + 2HCO3- Ca2+ + 2HCO3- D. Chemical weathering of feldspar to form clay mineral 2KAlSi3O8 + 2H+ + 2HCO3- + H2O K feldspar Al2Si2O5(OH)4 + 2K+ + 2HCO3- + 4SiO2 clay mineral Silica in solution or as fine solid particles Cara jurutera bahan mengungkap formula untuk memudahkan kefahaman 2KAlSi3O8 Al2Si2O5(OH)4 K2O Al2O3 6SiO2 Al2O3 2SiO2 2H2O Luluhawa kimia 3 oxidation – the process by which ironbearing minerals (pyroxene, amphibole, biotite) weather to produce iron oxides Di kawasan tropik iron bearing aluminosilicate => lateritic soils, red clayey soils Oxidation reaction 4FeSiO3 + O2 +10H2O Fe pyroxene 4FeO.OH + Goetite 4H4SiO4 2Fe2SiO4 + 2O2 + 4H2O 4FeO.OH + 2H4SiO4 Fe olivine 3. Luluhawa biologi Pemecahan batuan disebabkan oleh tindakan organisma hidup spt tumbuh2an, haiwan dalam tanah dan lichen (kulat? yang hidup di atas batuan dan kayu) Pengaruh => minimum Hasil luluhawa Weathering products Malaysia Average daily temperatures range from a minimum of 25o C to a maximum of 33o C. has an average annual rainfall of more than 2500 mm Hujan dan suhu wettest driest Mineral stability in the weathering environment Mineral didapati tak stabil dalam enviromen tertentu Minerals which formed at high temperature and pressures are least stable in the weathering environment and weather most quickly Minerals which formed at lower temperatures and pressures are most stable under weathering conditions Rates of weathering Soil profile D horizon Fresh rocks Soil profile Eluviation illuviation leaching Leaching/larutlesap: proses kimia yang menghasilkan unsur larut dan tak larut. Yang larut akan lesap ke bawah dalam profil tanah sementara yang tak larut akan terkumpul di bahagian atas profil tanah => warna membezakan lapisan tanah Eluviation: removal of materials dissolved or suspended in water Illuviation: horizon of maximum accumulation of suspended material or clay Chelation: pembentukan kompleks kimia Laterite profile Acid run-off at gold mine bryce Oxidation effect Oxidation effects Staglatite-staglamite sinkholes Gred luluhawa (weathering grade), kekuatan ekapaksi dan rock-soil ratio UCS(MPa) RSR Gred VI Gred V Gred IV Gred III Gred II Gred I tanah/soil completely weathered highly weathered moderately weathered slightly weathered Fresh rock <0.15 0.2-0.15 0.4-0.2 0.9-0.4 0-30 30-60 60-90 90-95 95-100 Tengok transparensi lain Sinkholes (tanah benam) Bagaimana terjadi? Enviromental problem? Jenis2 tanah Residual soil - laterit, iklim tropik Transported soil – till, loess, iklim temperat Tanih - pelbagai jenis tanah contoh: laterit, pedalfer, latosol, paleosol Wentworth scale Particle name Boulders Cobbles Pebbles Granules Sand Very coarse sand Coarse sand Medium sand Fine sand Very fine sand Silt Clay - grain size scale Particle diameter Gravel > 256 mm 64 - 256 mm 2 - 64 mm 2 - 4 mm 1 - 2 mm 0.5 - 1 mm 0.25 - 0.5 mm 0.125 - 0.25 mm 0.0625 - 0.125 mm 1/256 - 1/16 mm (or 0.004 - 0.0625 mm) < 1/256 mm (or < 0.004 mm) sesetengah buku guna takrif <2 mikron Kitar batuan (Rock cycle) Hakisan (erosion) The movement of weathered material from the site of weathering. Primary agent is gravity, but gravity acts in concert with running water pergerakan bahan terluluhawa dari tempat luluhawa berlaku ke tempat ia ditemui Sedimentary cycle Malaysia bagaimana? Faktor yang mempengaruhi pembentukan tanah 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Iklim (climate) Batuan induk (parent material) Relief (keadaan permukaan bumi) Vegetation (tumbuhan) Masa (time) Sambung => batuan mendak (lihat beberapa transparensi mengenai luluhawa) Apa kesudahannya? kepentingan jenis2 Ciri2 utama apa Batuan mendak Bagaimana terjadi Di mana Perubahan sebelum, semasa dan selepas pembentukan Hasil drpd luluhawa ialah sedimen Sediment = loose particulate material (clay, sand, silt, gravel, etc.) Sediment becomes sedimentary rock through lithification, which involves: Compaction Cementation Recrystallization (of carbonate sediment) Wentworth scale Particle name Boulders Cobbles Pebbles Granules Sand Very coarse sand Coarse sand Medium sand Fine sand Very fine sand Silt Clay - grain size scale Particle diameter Gravel > 256 mm 64 - 256 mm 2 - 64 mm 2 - 4 mm 1 - 2 mm 0.5 - 1 mm 0.25 - 0.5 mm 0.125 - 0.25 mm 0.0625 - 0.125 mm 1/256 - 1/16 mm (or 0.004 - 0.0625 mm) < 1/256 mm (or < 0.004 mm) sesetengah buku guna takrif <2 mikron Ternary diagram Sand-Silt-Clay Kitar batuan (Rock cycle) Pengelasan batuan mendak 1 Terrigenous (detrital or clastic) – bumi/benua – – – – Conglomerate or Breccia Sandstone Siltstone Shale 2 Chemical/biochemical – Evaporites – Carbonate sedimentary rocks (limestones and dolostone) – Siliceous sedimentary rocks 3 Organic (coals) – Other - ironstones Classification of sedimentary rocks Hjulstrom Curve Menghubungkait vel-size dgn proses (1939) A. Terrigenous (also called detrital or clastic) Terrigenous sedimentary rocks are derived from the weathering of pre-existing rocks, which have been transported to the depositional basin. They have a clastic (broken or fragmental) texture consisting of: 1. Clasts (larger pieces, such as sand or gravel) 2. Matrix (mud or fine-grained sediment surrounding the clasts) 3. Cement (the glue that holds it all together), such as: 1.calcite 2.iron oxide 3.silica Clasts and matrix (labelled), and iron oxide cement (reddish brown color) Sand: Grain size 1/16 to 2 mm Sandstone If dominated by quartz grains = quartz sandstone (also called quartz arenite) If dominated by feldspar grains = arkose If dominated by sand-sized rock fragment grains = lithic sandstone (also called litharenite or graywacke) conglomerate breccia Quartz sandstone Arkose (mengandungi banyak feldspar) Greywacke (sand-sized rock fragments) Silt: Grain size 1/256 to 1/16 mm (gritty) Siltstone Clay: Grain size less than 1/256 mm (smooth) (< 2 micron) Shale (if fissile) Claystone (if massive) Note: Mud is technically a mixture of silt and clay. It forms a rock called mudstone (or mudshale if fissile). shale kaolin B. Chemical/biochemical Sedimentary Rocks This group includes the evaporites, the carbonates (limestones and dolostone), and the siliceous rocks. These rocks form within the depositional basin from chemical components dissolved in the seawater Evaporites - The evaporites form from the evaporation of water (usually seawater). Rock salt - composed of halite (NaCl). Rock gypsum - composed of gypsum (CaSO4.2H20) Travertine - composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), and therefore, also technically a carbonate rock; travertine forms in caves and around hot springs. Bonneville Salt Flats of the Great Salt Lake, Utah. The lake bed is covered with rock salt which gives it the white color. The salt is mined by the Morton Salt Company. gypsum Gypsum crystals, Marion lake, Australia Carbonates - The carbonate sedimentary rocks are formed through both chemical and biochemical processes. They include the limestones (many types) and dolostones. Two minerals are dominant in carbonate rocks: – Calcite (CaCO3) (batu kapur)-mudah berbuih dgn asid lemah – Dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) – perlu digores jadi serbuk, baru bertindakbalas dgn asid Carbonate rock names: Micrite (microcrystalline limestone) - very finegrained; may be light gray or tan to nearly black in color. Made of lime mud, which is also called calcilutite. Oolitic limestone (look for the sand-sized oolites) Fossiliferous limestone (look for various types of fossils in a limestone matrix) Coquina (fossil hash cemented together; may resemble granola) Chalk (made of microscopic planktonic organisms such as coccolithophores; fizzes readily in acid) Crystalline limestone Travertine (see evaporites) Others - intraclastic limestone, pelleted limestone Stromatolitic limestone Batuan karbonat di Mexico Siliceous rocks - The siliceous rocks are those which are dominated by silica (SiO2). They commonly form from silica-secreting organisms such as diatoms, radiolarians, or some types of sponges. Chert is formed through chemical reactions of silica in solution replacing limestones. Diatomite - looks like chalk, but does not fizz in acid. Made of microscopic planktonic organisms called diatoms. May also resemble kaolinite, but is much lower in density and more porous). Also referred to as Diatomaceous Earth. Chert - Massive and hard, microcrystalline quartz. May be dark or light in color. Often replaces limestone. Does not fizz in acid. . Organic Sedimentary Rocks (Coals) This group consists of rocks composed of organic matter (mainly plant fragments). Because of this, they lack minerals (which must be inorganic, be definition). These are the coals. In order of increasing depth of burial (temperature and pressure): Peat (porous mass of brownish plant fragments resembling peat moss) Lignite (crumbly and black) Bituminous coal (dull to shiny and black; sooty; layers may be visible) Anthracite coal (extremely shiny and black, may have a slight golden shine; low density; not sooty; technically a metamorphic rock due to high temperatures and pressures to which it has been subjected) others There are several other interesting sedimentary rock types: Ironstones Oolitic hematite, banded iron formations Abundance of sedimentary rocks Soalan Maklumat apakah yang boleh dicerap dari pemerhatian batuan mendak? Senaraikan… Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary structures form in the basin of deposition, as a result of the action of natural processes such as waves, currents, drying events, etc. Beds or strata Cross-bedding Graded beds Ripple marks -Current ripple marks (asymmetrical ripples) Oscillation or wave ripple marks (symmetrical ripples) Mud cracks Structures formed during deposition 1-4, after deposition 5,6 1 4 2 3 5 6 Ripple marks Graded bedding, Jurassic of New Jersey Graded bedding halus kasar halus kasar mudcracks bagaimana terjadi? ripples rounding sorting High energy enviroment Low energy enviroment varves Cross stratification (berlaku semasa transgression-regression air laut) Important note Descriptive properties => interpretive properties Geology => engineering Objective: to aid planning, design, construction, mitigation, conservation, preservation Sedimentary Environments Sedimentary environments are places where sediments accumulate and sedimentary rocks form. They can be grouped into: Terrestrial environments (non-marine) – Rivers (fluvial environment)/sungai) – Alluvial fans (kipas lanar) – Lakes (lacustrine environment)/tasik - Swamps/paya - Deserts (aeolian environment) - Glacial environments Transitional environments (at the transition between the marine and nonmarine environments) Beach and barrier islands Delta Lagoons Estuaries Marine environments Continental shelf Continental slope and rise (deep sea fans) Abyssal plain Reefs (karang) Alluvial fan Enviroment of sedimentary rx SEDIMENTARY ENVIROMENTS AGENTS & ENERGY SOURCES ALLUVIAL WIND ACTION (Eolian) Continental enviroment: fluvial layering beach Marine environment Depositional environments Model for landform development Fossils Fossils are the remains or traces of prehistoric life. Outcrop in Nova Scotia, Canada of the McCoy Brook Formation of Early Jurassic age in which a dinosaur skeleton was found (box) Drawing of the outcrop on left, emphasizing layering. Facies - the characteristics of a unit of sediments, which can be used to interpret the depositional environment. Batuan mendak Batuan hos kepada petroleum dan gas asli Mendapan mineral spt Cu, Pb, Zn, Tungsten dll a bit about Si www.webelements.com 14 Si 28.0855(3)The essentials Name: silicon Symbol: Si Atomic number: 14 Atomic weight: 28.0855 (3) r CAS Registry ID: 7440-21-3 Group number: 14 Group name: (none) Period number: 3 Block: p-block Description Here is a brief description of silicon. Standard state: solid at 298 K Colour: dark grey with a bluish tinge Classification: Semi-metallic Silicon is present in the sun and stars and is a principal component of a class of meteorites known as aerolites. Silicon makes up 25.7% of the earth's crust by weight, and is the second most abundant element, exceeded only by oxygen. It is found largely as silicon oxides such as sand (silica), quartz, rock crystal, amethyst, agate, flint, jasper and opal. Silicon is found also in minerals such as asbestos, feldspar, clay and mica. Silicon is important in plant and animal life. Diatoms in both fresh and salt water extract silica from the water to use as a component of their cell walls. Silicon is an important ingredient in steel. Silicon carbide is one of the most important abrasives. Workers in environments where silicaceous dust is breathed may develop a serious lung disease known as silicosis. Important facts Hydrolysis and condensation of substituted chlorosilanes can be used to produce a very great number of polymeric products, or silicones. These range from liquids to hard, glasslike solids with many useful properties. Elemental silicon transmits more than 95% of all wavelengths of infrared and and has been used in lasers to produce coherent light at 456 nm. Isolation Here is a brief summary of the isolation of silicon. There is normally no need to make silicon in the laboratory as it is readily available commercially. Silicon is readily available through the treatment of silica, SiO2, with pure graphite (as coke) in an electric furnace. SiO2 + 2C Si + 2CO Under these conditions, silicon carbide, SiC, can form. However, provided the amount of SiO2 is kept high, silicon carbide may be eliminated. 2SiC + SiO2 3Si + 2CO Very pure silicon can be made by the reaction of SiCl4 with hydrogen, followed by zone refining of the resultant silicon. SiCl4 + 2H2 Si + 4HCl Fakta penting mengenai Malaysia Most cities and large towns in the Peninsula are located on a thin surface alluvium over limestone and granite. Malaysia is generally formed by highland, floodplain, and coastal zones (Figure 1.2 ). In the Peninsula, the Banjaran Titiwangsa from north to south divides the West Coast and East Coast states, while in Sarawak the Banjaran Kapuas Hula and Banjaran Iran border Indonesia. All of these ranges are governed by virgin forest Malaysia is warm and humid throughout the year, as characterised by the equatorial climate, and has an average annual rainfall of more than 2500 mm with spatial variation shown in Figure 1 . 3 . In the Peninsula wettest area is Taiping in Perak whilst the driest is Kuala Pilah in Negeri Sembilan (Figure 1 . 5 ). Average daily temperatures range from a minimum of 25o C to a maximum of 33o C. Relative humidity is high, sometimes exceeding 80%. Daytime cloudy hours are also high while haze lately is a frequent occurrence that will contribute to acid rains. Urbanisation poles are formed in many different ways including; · centrally in dense arrangements such as towns, cities, ports, commercial/business centres, and new development areas · linearly along road, highway, railway, river, estuary, and coastal areas · randomly located, including villages and high class residential areas Next lecture on metamorphic rocks