International Relations
advertisement

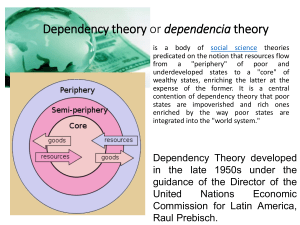
Dependency critique Chilcote, Smith, Evans Back to Weber & Marx • • • • Marx: state monolithic Weber: plurality & legitimate state coercion Marx theory dynamic Weber: focus on bureaucratic order Political economy • Back to Smith, Ricardo, Marx • Study comparative politics – state & class at national level – imperialism & dependency international • Economic base and political superstructure Economic base • Mode of production (mix of productive forces) • Relations of production (division of labour) • Forces of production (productive CAPACITY) • Means of production (tools, land, buildings etc.) Political superstructure • State (legal forms and instruments maintaining class rule) • class (groups of people classified according to relation to means of prod) • ideology (false consciousness – legal, political, religious and philosophical) Theory of state and class – View system as capitalist Pluralist conception of state challenged (Mosca, Pareto, Dahl, etc.) Dahl extended pluralism to socialist economies Raised issue of socialist democracy Theory of state and class 2 – Domhof and Miliband see capitalist class using state as instrument of rule of unified corporate elite – Structuralist view (Poulantzas) sees state serving capitalism best when members do not participate actively in state apparatus Underdevelopment • Gunder Frank et al challenged the possibility of development. • Paul Baran focused on extraction of surplus • Prebisch divided centre-periphery Underdevelopment 2 • Dos Santos on need for change in internal structure and external relations • Emmanuel stressed inequities in international exchange • Amin uneven development because unable to challenge foreign “monopolies” criticisms – No unified theory – Emphasis on underconsumption [externalising dynamic] – Few practical solutions – Incompatibility with Marxist theory Smith: Dependency Approach • • • • [not a theory!] Marxist roots, but many debates Latin American origins global division of labour chief force shaping history of the South Capitalism • global economy • dependency a subset Dependency premise • “one must see [change] as a function of the power of economic imperialism generated by the capitalist “core” of world affairs…” [119] Approach • Studies effects of imperialism • Focus is on the part not the whole • explaining “logic of capitalist expansion on the periphery” Tools of analysis • dual economy • export oriented modern sector – econ & politically part of international – dependent • traditional sector – disintegrates – marginalized land Class formation • modern sector symbiotic with international capitalism • intermediaries • “compradors” • parasites!! Summary • • • • Division of labour prime social reality political activity class based bias against ethnicity problems of 3W arise from form of growth pursued in the North Clarifications • Dual economy not rigid – some genuine industrial base – dependent development possible (Evans) • Role of the state – more than auxiliary – backward and forward links • diversity Fight with developmentalism • easy to criticise • no economic perspective (even in Political Order) • dual economy seen as transitional • task of pol dev to back up diffusion – speed up disappearance of traditional Future of dependency • Rivalry • Focus on DFI – ignore aggregate data • leave periphery but can’t join core • [takes care of Taiwan/Brazil arguments] • “Piddling criticism is a waste of time” !! Effective criticism • Challenge economic determinism • Challenge imperialist theory • Merely a corrective to the developmentalist school? – Marxism does have its own assumed development path