File - mba 671 distribution management
advertisement

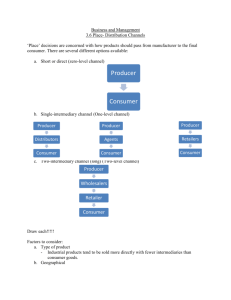
LECTURE 3 DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS Distribution Management M Wahidul Islam Spring 2015 Planning, Forecasting & Budgeting Warehousing and Logistics Channel Information Systems Sales Force Management Elements of Distribution Management Distribution Channels Product Pricing and Promotion Product Visibility WHAT IS A DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL? A group of people and firms involves in the transfer of title or ownership as the product moves from the producer to the ultimate consumer “the structure of intra company organization units and extra company agents, dealers, wholesalers and retailers through which a commodity, product or service is marketed” – American Marketing Association KEY QUESTIONS FOR DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL Who will be the Channel Members? Who is driving the Channel? What What is the Channel Format? would be the Patter of Distribution? DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL MEMBERS Company Owned Distribution Center Distributors/ Dealers / Stockiest Carrying and Forwarding Agents Owned or Contracted Consignment Selling Agents or General Selling Agents Exclusive / Shared Value Added Resellers Wholesalers Direct Marketing Sales force Retailers Franchises DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL MEMBERS C&FA Consignment Selling Agents (CSAs) or General Selling Agents (GSAs) Facilitators Do not pay for the product or hold physical possession of the goods. Merely stores in a central location and then pass it on to the distributor Example: Edible Oil Industries Sales the goods on behalf of the company and transfer amount to the producer Example: Shipping Companies, Airlines Companies Value Added Resellers Purchases incomplete product or kit and add value to assembling it and then selling to customers Example: Personal Computers, Bicycles, Producer CSAs / GSAs Direct Marketing Team Central Distributor Regional / Market Specific Distributor Wholesalers Retailers Customers Authorized Reseller Own Branded Store PATTERS OF DISTRIBUTION It represents the service level that the organization provides to its customers Intensive Distribution • The strategy is to make the product available to as many customer as possible • Example: Unilever, GP, BATB, FMCG Products Selective Distribution • Few carefully selected outlets are permitted to keep company’s products • Example: QUBEE, HP, Nikon Exclusive Distribution • Only one or two outlets in a market may keep the company’s product • Example: Franchises, BATA, Transcom, KFC DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL MEMBERS Company Owned Distribution Center Distributors/ Dealers / Stockiest Carrying and Forwarding Agents Owned or Contracted Consignment Selling Agents or General Selling Agents Exclusive / Shared Value Added Resellers Wholesalers Direct Marketing Sales force Retailers Franchises CHANNEL FORMATS Who plays the major / dominant role in the distribution channel is also a big deciding factor Producer Driven Seller Driven Company Owned Retail Outlets Existing Retailers Service Driven Others Couriers Multilevel marketing Wholesalers Licensed Outlets Kiosks Modern Store Formats Consignment Selling Agents Credit Card Companies TV home shopping networks Specialty Stores Factory / Discount Stores Financial Institutions Franchisers Catalogue shopping Agents / Dealers Distributors D2D Sales People 3P Logistic service providers Internet based sellers HOW TO DECIDE WHICH DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS TO USE? Product type Industrial / Textile / Chemicals and Fertilizers Automotive FMCG Pharmaceutical Telecommunication IT hardware Services Consultancy Requirement of after-sales service?? Who is driving the channel? Ability to influence consumer’s buying decision Producer CSAs / GSAs Direct Marketing Team Central Distributor Regional / Market Specific Distributor Wholesalers Retailers Customers Authorized Reseller Own Branded Store INDUSTRIAL PRODUCTS General natures Technical Mostly B2B Need of more personal interaction with the customer Relationship management very important Examples: Production Raw Materials, Steel Mills Producer Agent Industrial Distributor Customers Critical Question: How do you manage the relationship with the Customer? PHARMACEUTICAL PRODUCTS Highly technical Doctors one of the key stakeholders End Users / Customers virtually have no communication with the manufacturer Examples: Medicine Companies Producer Distributor Wholesaler Retailer / Chemist Customers Critical Question: Can the producer influence Customers buying decision? Doctors CONSUMER PRODUCTS Target is to reach as many customers as possible Every possible route is selected Most evolved distribution flow / channels format Producer Distributor Wholesaler Different forms of Retail Examples: Lux, Clear, Low Cost Ball Pen, Mineral Water etc. FMCG Products Customers / Consumers Critical Question: Which distribution flow is right for my product? Is my Consumer buying my product? CONSUMER DURABLES Similar to Consumer Products But needs to be maintained / serviced Targeted Customer / End Users based Usually high-end Examples: Samsung, NOKIA, Sony, Mercedes Benz, QUBEE Producer Market Specific Distributor Different forms of Retail Customers / End Users Critical Question: Which is more important? Distribution Flow or Service? After Sales Service?? Product Service Team SERVICES Customer Experience is the most important factor, leading to high coordination of Sales and After Sales Customer Service The customer interaction is directly with Company Representative, usually Usually customer goes through a process of service experience Service Provider Different Forms of Service Outlets Purchase > Experience > Post Evaluation Franchises / Agents are carefully chosen, and are closely controlled Customers Examples: DHL, Hospitals, Airlines’ Telecommunication?? GP?? Critical Question: Does a distribution flow exist as there is no physical movement of services? NEW FORM OF DISTRIBUTION FLOWS Mixture of Service and Physical Distribution Online Marketing Tele-shopping Catalogue Marketing (New or Old) Kiosks Others???? ONLINE MARKETING TELE-SHOPPING CATALOGUE MARKETING CATALOGUE MARKETING KIOSK / VENDING MACHINE KIOSK / VENDING MACHINE The Google Vending Machine The Facebook Vending Machine REFERENCES Chapter 8 – Distribution Management and the Marketing Mix Havaldar K. and Cavale V. M. (2011) Sales and Distribution Management – Text and Cases (2nd Edition) Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill Education Private Limited Chapter 9 – Marketing Channels Havaldar K. and Cavale V. M. (2011) Sales and Distribution Management – Text and Cases (2nd Edition) Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill Education Private Limited END