CRITERIA FOR CAUSE AND CONSEQUENCE
advertisement
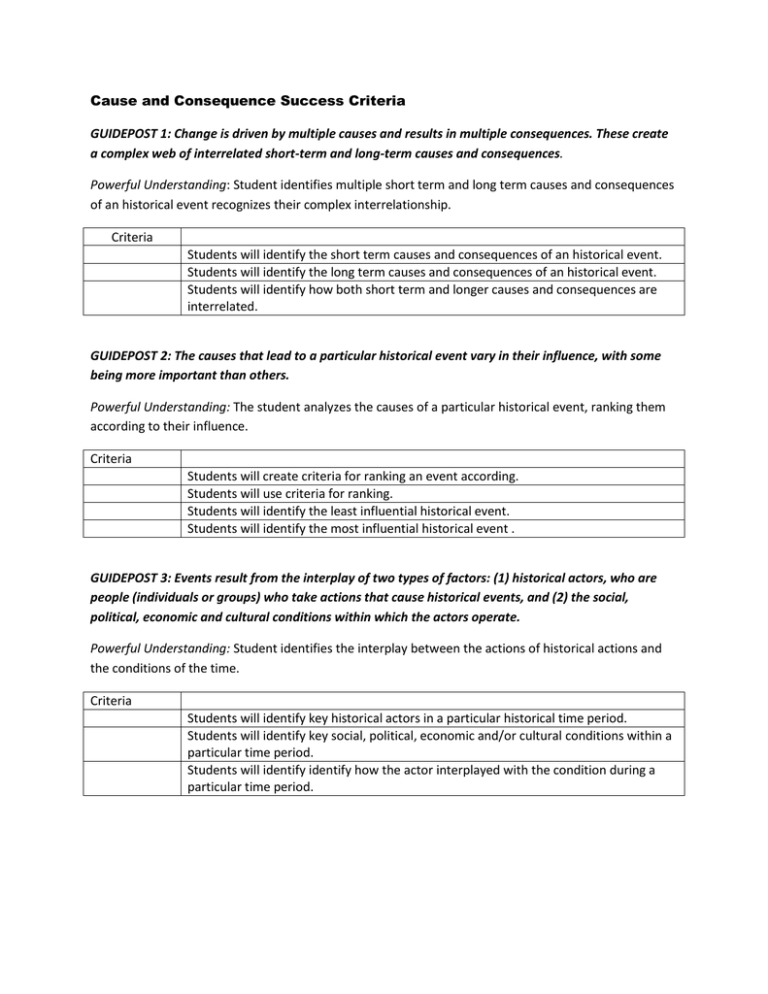
Cause and Consequence Success Criteria GUIDEPOST 1: Change is driven by multiple causes and results in multiple consequences. These create a complex web of interrelated short-term and long-term causes and consequences. Powerful Understanding: Student identifies multiple short term and long term causes and consequences of an historical event recognizes their complex interrelationship. Criteria Students will identify the short term causes and consequences of an historical event. Students will identify the long term causes and consequences of an historical event. Students will identify how both short term and longer causes and consequences are interrelated. GUIDEPOST 2: The causes that lead to a particular historical event vary in their influence, with some being more important than others. Powerful Understanding: The student analyzes the causes of a particular historical event, ranking them according to their influence. Criteria Students will create criteria for ranking an event according. Students will use criteria for ranking. Students will identify the least influential historical event. Students will identify the most influential historical event . GUIDEPOST 3: Events result from the interplay of two types of factors: (1) historical actors, who are people (individuals or groups) who take actions that cause historical events, and (2) the social, political, economic and cultural conditions within which the actors operate. Powerful Understanding: Student identifies the interplay between the actions of historical actions and the conditions of the time. Criteria Students will identify key historical actors in a particular historical time period. Students will identify key social, political, economic and/or cultural conditions within a particular time period. Students will identify identify how the actor interplayed with the condition during a particular time period. GUIDEPOST 4: Historical actors cannot always predict the effects of conditions, opposing actions, and unforeseen reactions. These have the effect of generating unintended consequences. Powerful Understanding: Student differentiates between intended and unintended consequences. Criteria Students will identify intended actions and reactions of historical actors. Students will identify unintended actions and reactions of historical actors. Students will identify how intended actions can cause intended results Students will identify how unintended actions can cause unintended results Students will identify how intended actions can cause unintended results GUIDEPOST 5: The events of history were not inevitable, any more than those of the future are. Alter a single action or condition, and an event might have turned out differently.. Powerful Understanding: Students demonstrates that an event in history was not inevitable. Criteria Students will identify a particular action that could have been altered to change an event. Students will identify a particular condition that could have been altered to change an event. THE BIG SIX, HISTORICAL THINKING CONCEPTS. PETER SEIXAS AND TOM MORTON.




