CHAPTER 4
advertisement

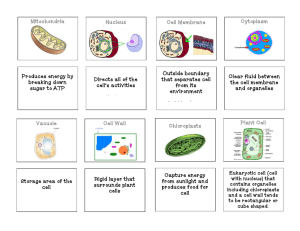
CHAPTER 4 4.1 History of Cell Biology OBJECTIVES: – Name scientists who first observed living and non living cells. – Summarize research that led to cell theory. – State 3 principles of Cell Theory – Explain why cells are basic units of life Discovery of Cells A. Hooke A. Discovered cells in cork B. 1st to observe dead cells B. Leeuwenhook A. First to observe living cells B. Described first cells as animulcules Cell Theory A. Cell Theory has 3 parts A. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. B. Cells are the basic units of structure. C. Cells come only from the reproduction of existing cells. Cellular Basis of Life A. All living things A. Have cells B. Obtain energy C. Perform chemical reactions D. Change with time E. Respond to the environment F. reproduce 4.2: Introduction to cells Objectives: – Describe 3 basic parts – Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells – Analyze relationship between cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms Cell Diversity A. Cell shape reflects the different functions of the cell. B. Cells not only differ in the shape but also the size. Two basic types of cells A. Prokaryotic Cells – Do NOT have a nucleus – Bacteria B. Eukaryotic Cells Has a nucleus Has organelles Has Nucleus Ribosomes and DNA No Nuclear Membrane Cell Organelles Animal Cell Plant Cell Cell Organelles A. Plasma Membrane A. Covers the cell and acts as a barrier between the inside and outside B. Cytoplasm A. Fluid inside the cell C. Nucleus A. Control center of cell B. Controls most functions of the cell Cell Organelles D. Nucleolus A. Site of DNA (genetic material) E. Ribosomes A. Made of protein B. Direct construction of protein F. Mitochondria A. Powerhouse of the cell B. Transfers energy Cell Organelles G. Rough endoplasmic reticulum A. System of flattened sacs B. covered with ribosomes C. produces phospholipids and proteins D. transport system H. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum A. builds lipids (cholestrol) B. Abundant in liver and kidneys C. Detox body Cell Organelles I. Golgi Apparatus A. Packages materials throughout the cell J. Lysosomes A. Contain enzymes Cytoskeleton K. A. Microtubules A. B. Provide structure Microfilaments A. Contribute to cell movement Cell Organelles L. Cilia A. many hairlike structures used for movement M. Flagella A. Tail like organelle B. Assists in movement C. Tail on human sperm cells N. Centrioles A. Organize cytoskeleton for cell division Cell Organelles N. Cell Wall A. Outside plasma membrane B. Found only in PLANT cells C. Provides structure O. Vacuole A. Storage sac P. Chloroplasts A. Used in photosynthesis (green) Cell WALL Cell MEMBRANE Nucleus: control center for the cell 4. Ribosomes: grain like bodies on the ER & in the cytoplasm 5.Endoplasmic Reticulum: (called ER) carry proteins and materials within the cell 6. Golgi Body: receives and packages proteins from ER and distributes around cell and body (mailroom) 7. Cytoplasm: clear gelatinous fluid inside a cell 8. Vacuoles: storage area of the cell Plant has one large vacuole Stores food, waste, & enzymes 9. Mitochondria = powerhouse of the cell; where cell energy comes from. 10. Chloroplasts: ONLY IN PLANTS captures sunlight and produces food for the cell 11. Flagella = used for movement 12. Cilia = used for movement; tiny hair-like structures; found on cells that need to move mucus COMPARE and CONTRAST Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cytoskeleton Plant Cell Wall Nucleus Cell Membrane Chloroplasts Large Vacuole Importance of Cell Surface Area What is surface area? – The amount of surface for a cell Why is surface area important? – When the volume of the cell increases, the surface area increases – S.A. limits cell growth because if the cell becomes to large it will not be able to take in enough food and get rid of enough waste