presentation here
advertisement

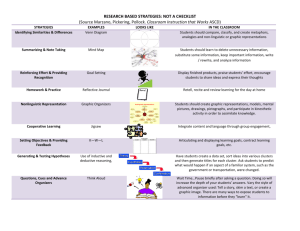
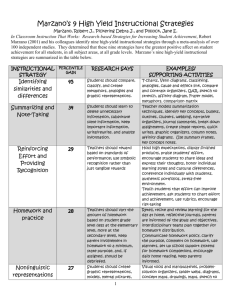
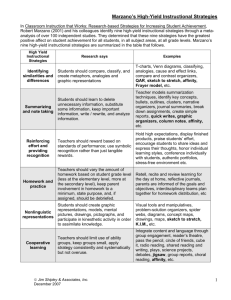
Best-Practice Instruction in Birdville ISD Crysten Caviness Curriculum Management Specialist Birdville ISD Best-Practice Instruction Objectives Explore BISD’s Learning Platform Identify, analyze, and apply Marzano’s 9 bestpractice strategies Make connections between the work we have been doing in BISD and the next steps we need to take Brainstorm classroom applications for the strategies we apply to our own learning today Explanation Game BISD Alignment Model BISD Learning Platform BISD Learning Platform STUDENT- COGNITIVE CENTERED Standards INTERACTIVE Student-Centered The focus is on what STUDENTS do, not what the teacher is doing. It is about the LEARNING. Students will be involved in more authentic tasks that are challenging and provide experiences that lead to holistic learning. Cognitive This is about the RIGOR higher-order, conceptual learning. This represents the THINKING required by the standards. Learning causes students to construct their thinking according to their developmental stage. When they can reflect upon and express this, their thinking is made visible and teachers can better assess their levels of cognition to determine necessary scaffolding. Interactive This is about the dynamics and structures of the class, as well as the locus of control. Teachers empower students to be more accountable for their own learning and provide opportunities for sociable collaboration that allows students to interact not only with each other, but with their own learning. Learning expectations for students Teachers deeply understand the content, context, and cognitive requirements of the standards Teachers explicitly communicate learning expectations so students clearly understand and can take ownership over their own learning Teachers design learning tasks that closely align to the content, context, and cognitive requirements of the standards Teachers and students monitor learning toward achievement of standards Feedback based on student performance Mostly formative and reflective Triangulation of data: numerical, descriptive, observational feedback Timing and efficiency of assessments Feedback from teacher, peers, and selfreflection throughout the learning cycle Authentic Student Tasks and Products The focus is on what students are actually doing each day The work students do causes them to engage in the content, context, and cognitive rigor of the standards Students are able to demonstrate understanding of the connection between the standards and their work tasks and products Best-practice strategies and structures Robert Marzano and John Hattie have both done extensive work in determining what effect certain teaching strategies and structures have on learning. How much do we know about these best-practice strategies and structures? Best Practices Average Percentile Point Gains on Student Achievement Tests Advance Organizer How did this strategy push my thinking? What processes did I go through in my brain throughout the activity? How could I use this to advance student learning in my classroom? 5 Out of 9 We have already. . . Used analogies to find similarities between concepts and practices Set objectives Incorporated Cooperative Learning Generated and tested hypotheses Begun an advance organizer that also serves as a guide for note-taking Setting Objectives & Providing Feedback Research: •Students learn more efficiently when they know the goals and objectives of a specific lesson or learning activity. Cooperative Learning Research: • Organizing students into cooperative groups yields a positive effect on overall learning if approach is systematic and consistent. Generating & Testing Hypotheses Research: •Generating and testing hypotheses involves the application of knowledge, which enhances learning. Generating & Testing Hypotheses Examples of Strategies Problem Solving Invention Investigation Experimental Inquiry DecisionMaking Questions, Cues & Advance Organizers Questions • Help students analyze what they already know Cues • Provide explicit reminders about what a student is about to experience Advance Organizers • Help students retrieve what they know about a topic and focus on the new information Questions, Cues & Advance Organizers Recommendations: Introduce new vocabulary Begin with student predictions Provide links to prior knowledge or experiences Tell students the topic of an article they are about to read Provide ways for students to organize new content Identifying Similarities and Differences Research: The ability to break a concept into its similar and dissimilar characteristics allows students to understand and solve complex problems by analyzing them in a more simple way. Identifying Similarities and Differences -Comparing -Classifying • similarities and differences • grouping things that are alike -Metaphors -Analogies • comparing two unlike things • identifying relationships between pairs of Identifying Similarities and Differences Recommendations: Give students a model for the process. Use familiar content to teach steps. Give students graphic organizers. Guide students as needed. Identifying Similarities and Differences Step 1 • Where does each Marzano category fit on the learning platform? • WHY? Step 2 • What parts of the learning platform remain? • How does it meet and go beyond Marzano? Step 3 • How are these qualities SIMILAR and/or DIFFERENT from what you already do in your classroom? How did this strategy push my thinking? What processes did I go through in my brain throughout the activity? How could I use this to advance student learning in my classroom? Valuable Homework and Practice Research: •Both homework and practice give students opportunities to deepen their understanding and proficiency with content they are learning. Increasing Value in Homework and Practice Non-Linguistic Representations Research: •Engaging students in the creation of nonlinguistic representations actually stimulates and increases activity in the brain Representations NonNon-Linguistic Linguistic Representations Recommendations: Generating mental images Drawing pictures or pictographs Constructing graphic organizers Acting out content Making physical models Making revisions to physical models, mental images, pictures, graphic organizers Representations NonNon-Linguistic Linguistic Representations Use Graphic Organizers to: Make thinking visible Activate current knowledge Present information Take notes Summarize information Assess student learning Using Non-Linguistic Representations Identifying similarities and differences Using non-linguistic representations Questions, cues and advance organizers Reinforcing effort and providing recognition Increasing value in homework and practice Generating and testing hypotheses Setting objectives and providing feedback Incorporating cooperative learning effectively Summarizing and note-taking How did this strategy push my thinking? What processes did I go through in my brain throughout the activity? How could I use this to advance student learning in my classroom? Reinforcing Effort & Providing Recognition Rewards do not necessarily have a negative effect on intrinsic motivation. Reward is most effective when it is contingent on the attainment of some standard of performance. Symbolic recognition is more effective than tangible rewards. (charts) Reinforcing Effort & Providing Recognition Recommendations: Recognize effort & progress throughout unit Specific praise Students chart effort and achievement Intermittent celebrations Students record progress toward goals Reinforcing Effort & Providing Recognition Summarizing and Note Taking - encourages powerful learning - leads to deeper understanding - facilitates long-term recall Verbatim note taking is the least effective way to take notes. Summarizing Recommendations Verbal summaries Written summaries Have students paraphrase key points Graphic organizers Revise and interact with notes during and after learning Note Taking Research • Note taking and summarizing are closely related. Both require students to identify what is most important about the knowledge they are learning and then state that knowledge in their own words. Note Taking Recommendations Explicitly teach students a variety of note-taking formats Provide an organizer for taking notes Have students revise and review their notes Provide an activity for students to use their notes Headlines Think Write Share Discuss Advance Organizer How did this strategy push my thinking? What processes did I go through in my brain throughout the activity? How could I use this to advance student learning in my classroom? Best-Practice Teaching Involves incorporating all pedagogical categories All strategies will not work all of the time Categories help us select strategies based upon their purposes Accounts for the art and science of teaching Critical for the shift to a learning platform Critical to ensuring that all students learn Best Practices We hit them all! Professional Development Website One step at a time toward a platform of learning in BISD http://schools.birdvilleschools.net/surveys