Causes of Revolution - Nutley Public School District

Stamp Act (1765)
Problem: Sugar Act is not raising enough money – British need increased revenue to alleviate their debt
Solution:
Direct tax on all public documents – had to be on British stamped paper.
Stamped paper was more expensive than non-stamped paper.
Non-stamped paper was illegal.
Tax was a couple of cents (shillings) for each page of paper
Colonial Reaction:
Protests Against Stamp Act o 1. Sons of Liberty- coordinated street protests of the Act
Harass tax collectors and burn stamps
Objective: use confrontation to get Stamp Act removed o 2. Stamp Act Congress
Politicians from various colonies meet to discuss the response to the Stamp Act
Objective: use petition to get Stamp Act removed o 3. As a result of protests Parliament repealed the Stamp Act
Townshend Acts (1767)
Indirect tax on imports rather than a direct tax on a product’s sale o Shipments of glass, lead, paper, paint and tea
Import tax results in higher prices
Protests reach their highest point with destruction of government property (tax collectors home) in Boston
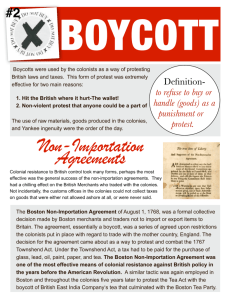
NON-Importation Agreement o Signed by multiple colonies to collectively boycott imports from
Britain o OBJECTIVE: to force decrease in profits to cause removal of the
Townshend Acts
In order for it to be successful ALL colonists had to agree to stop buying British goods
Colonial women were important to this cause because they were the major household consumers
HOMESPUN MOVEMENT: women begin making clothes in order to boycott o Also made tea- brewed on roots & herbs o In response to colonial protests the British Crown sends 4,000 soldiers to Boston
16,000 citizens in Boston
1 to 4 soldier to citizen ratio
Boston Tea Party
Tea Act (1773) o British Problem: #1 Colonists are boycotting British tea because of the tea tax o British Problem: #2 Because of non-importation the British East
India Company was struggling to sell tea in the colonies
The future of the E. India CO. was important to the health of the
British economy o ACT:
lowered the existing tax on tea (makes the tea cheaper) to end the colonial boycott
Gives the East India Co. exclusive rights to sell tea in the colonies (monopoly)
Cuts colonial merchants out of the equation o Colonial merchants enraged by Parliament’s actions
REACTION:
Sons of Liberty threaten to riot if the East India
Company shipments are unloaded after being shipped in December of 1774 o Most colonial governors send the tea back to
England --- MA governor refuses to send tea back
Result: Colonists dump close to $1 million into Boston Harbor
Coercive Acts: 1774 o Boston Harbor will be blockaded by British war ships until the $$ lost is repaid o Martial Law: civilian government is suspended – more troops sent to
Boston and military given control of the government o Quartering Act: Parliament forced colonists to house British soldiers in their homes if necessary