Quadratics Day 2 Vertex Form
advertisement

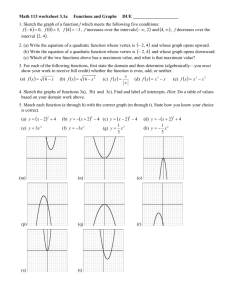
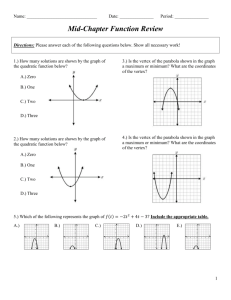
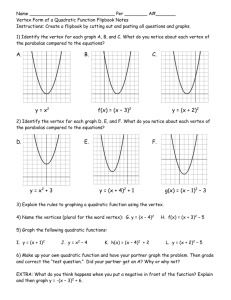
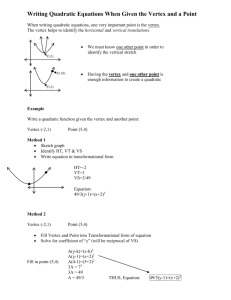
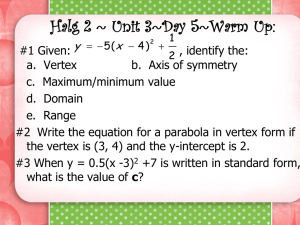
Quadratics Day 2! VERTEX FORM Unit 6 Quadratic Functions Math II VERTEX FORM! y = a(x – 2 h) +k -Where a is the same a from Standard Form -The Vertex of the quadratic is at (h, k) -We can easily graph a quadratic when it is in vertex form Converting from Vertex to Standard Form Example: y = -2(x – 4)2 + 5 Vertex Form: Square the binomial Distribute the coefficient of the trinomial…. = -2(x2 – 8x + 16) + 5 Combine “like” terms = -2x2 + 16x – 32 + 5 = -2x2 + 16x – 27 Standard Form! Example: Convert each quadratic to Standard Form. 1. y = 5(x + 2)2 – 9 1. y = -3(x – 4)2 + 7 1. (x – 2)2 + 6 Review Example: Find the Axis of Symmetry of Vertex. 1. y = -2x2 + 4x – 9 1. y = x2 – 10 a = ____, b = ____, c = ____ a = ____, b = ____, c = ____ 1. y = x2 + 4x – 1 1. y = -2x2 + 8x – 8 a = ____, b = ____, c = ____ a = ____, b = ____, c = ____ Converting Standard Form to Vertex Form • Step 1: Determine the a value from standard form • Step 2: Find the vertex. – Use x = -b/2a to find the x coordinate – Substitute x in for the original equation to find y • Step 3: Substitute vertex and a to vertex form. Example: Convert the quadratic to Vertex Form. y= a=8 2 8x – 16x + 27 b = -16, c = 27 (16) 16 1 2(8) 16 y 8(1) 2 16(1) 27 (y-coordinate) y 19 Vertex: (x-coordinate) x Vertex: (1, 19) Vertex Form: y= 8(x – 1)2 + 19 Example: Convert the quadratic to Vertex Form. y= 2 5x – 40x + 67 Your turn!: Convert the quadratic to Vertex Form. 1. y = x2 – 9 1. y = 7x2 + 28x + 19 1. y = -2x2 – 24x – 75 Writing the equation of a Quadratic given the vertex and a point.. Example: Find the equation of the quadratic with vertex (0, 0) and passes through the point (-2, 8) y = a(x – 0)2 + 0 Substitute vertex in for h and k 8 = a(-2 – 0)2 + 0 Substitute x and y values in 8 = a(-2)2 8 = 4a 2=a Simplify and solve for a Vertex Form: y = 2(x – 0)2 + 0 OR y = 2x2 Example: Find each quadratic function with the given vertex that passes through the given point. Write in Standard Form. 1. Vertex (2, 0) passing through (1, 3) 1. Vertex (-3, 0) passing through (-5, -4) 1. Vertex (2, 5) passing through (3, 7) 1. Vertex (-3, 4) passing through (0, 0)