Chapter 4 : Cells - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
advertisement

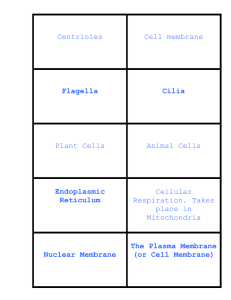
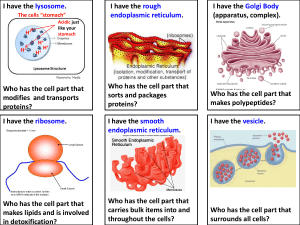
Chapter 4 : Cells A. Cell Discovery 1. Robert Hooke – 1664 – saw 1st cell and named it a cell. 2. Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow - made up cell theory. Cell Theory – says all living things are made up of cells and only cells can make cells B. Types of Cells 1. Prokaryote – cell that lacks membranebound organelles. No nucleus. Primative – ex. Bacteria 2. Eukaryote – cell that has organelles protected by membranes. More complex. *** Evidence to support the idea that prokaryote cells developed 1st and eukaryote cells resulted when prokaryotic cells ingested each other. C. Types of Eukaryotic Cells 1. Plant – has cell wall, large vacuole, plastids (ex. Chloroplast), no centrioles 2. Animal – no cell wall, small vacuole, centrioles, no plastids D. Parts of Cell --- organelle – “little organ” 1. Plasma or cell membrane – outer membrane. Phospholipid (P+O+fat) 2. Cell wall – outer membrane of plants. Made up of cellulose (we can’t digest) 3. Nucleus – control center of cell. a. nuclear membrane – outside edge of nucleus. b. nucleolus – makes proteins c. chromosomes – contains genetic material (DNA) d. nucleoplasm – fluid inside nucleus. Used to protect organelles within nucleus. 4. Cytoplasm – clear fluid inside cell. Acts as shock-absorber to protect contents of cell. 5. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) – channels used for transporting things within cell. a. smooth ER – contains no ribosomes b. rough ER – contains ribosomes. Used for transporting molecules needed in protein making. 6. Ribosomes – makes proteins 7. Golgi body or apparatus – packages proteins and lipids. 8. Vacuole – storage area for food, water and waste. Larger in plant cells. 9. Lysosome – “suicide sac” – contains enzymes used to digest foreign materials and sometimes the cell itself. 10. Mitochondria – “powerhouse of cell” – makes energy by cellular respiration. Has many folds called cristae that increases the surface area. 11. Chloroplasts – plastids that hold chlorophyll (green pigment used for making food in plants) 12. Microtubules (bigger) & microfilaments (smaller) – used for structural support – called cytoskeleton. 13. Centrioles – only in animal cells. Used during cell reproduction. 14. Cilia ( hair –like projections) & flagella (long tail-like whip) – structures some cells have for cell movement. 15. Perioxisomes- breakdown H2O2 into water and oxygen