Consciousness, Dreams, and Past Lives
advertisement

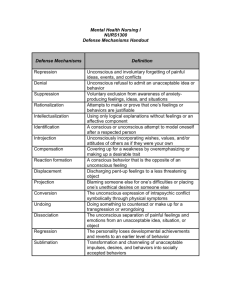
Psychology Chapter 2 & 6 Consciousness is awareness, experiencing reality, your normal walking state Unconscious: The memories and feelings that are stored in your brain that you are not aware of, but still effect your thoughts and behaviors Altered states of consciousness (ASCs) reached through dreams, hypnosis, or drugs Create a world where senses and perceptions are no longer restricted by reality Dream research: Electroencephalograph (EEG) records brain wave patterns Do past lives exist? Can we connect to them through our dreams? Do you have any irrational and unexplained phobias? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=25aeYRUSGU http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=21sJme48HV g http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eijor1bL8z0& feature=relmfu Body shuts down various functions, less sensitive to stimuli REM sleep (rapid eye movement): stage I where most dreaming occurs, closest to consciousness 75% of time spent in deep sleep (stages II,III,IV) Cycles about every 90 minutes Everyone dreams: they occupy 18-33% of sleep time Essential to your physical and mental well-being Allows body/brain to repair cells, sort and store memories, waste cleared out, restore nerve systems, and process info learned during the day Allows unconscious an outlet so that it doesn’t affect waking hours in form of hallucinations Some believe these are the only functions, others believe interpretations allow for insights into your life and issues Stories your brain makes up, based on things you have seen/experienced, everyday life Hormone levels change like experiencing actual waking emotion, but muscles turned off Dreams more often about anxiety or anger, something that needs to be processed and dealt with in your life Dream meaning: Interpretation through symbols Manifest Content: what happens in the dream Latent Content: the meaning behind what happens in the dream Falling: Fall from grace, fall out of favor or out of touch, failing Flying: Success and freedom or escaping something Nudity: Usually in public, means anxiety Exams: feeling unprepared, test in life Losing money: warning about valuables or suggestion of other type of loss Finding money: Go ahead with plan/purchase, or reminder that you are a person of value Lucid Dreaming: You are aware you are dreaming and take control of the content of the dream Sleep talking: During transitions between sleep cycles, vocalizing dreams Sleep Walking: Caused by illness, stress, emotional issues or sleep deprivation Not in relation to dream content because it happens during deep cycles of sleep Reflex actions of routines from daily life, such as driving, eating, bathing, etc. http://www.world-of-lucid-dreaming.com/sleepwalking.html http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tuNzubLTI_A&safe=active http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iPdgog3afTI&safe=active Ancient people saw them as messages from God Freud calls them “the royal road to knowledge of the unconscious activities of the mind” During sleep: unconscious calls attention to your deepest needs, allows you “wish fulfillment” Filled with imagery and symbols that can tell us about various issues and the root cause of them Attachment issues with parents, discover hidden desires, sexual imagery and jealousy http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lig53eW2 ptg http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x1CJCAv QsjQ http://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&feat ure=endscreen&v=_TJUjZpUYbE http://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&feat ure=endscreen&v=R_L1lCyK5ek Do you believe in hypnosis and the power of suggestion? ASC where subject enters into state of increased suggestibility, total concentration on hypnotist creates trance 9 out of 10 can be hypnotized: Best candidates are cooperative, have good reason to do it, and are creative and intelligent http://app.discoveryeducation.com/search?Ntt=h ypnosis http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7mW2YU3X 3kg Medical Use: To control/reduce/block-out pain during surgery, dentistry, childbirth, etc. Psychological Use: Discuss and deal with issues to hard to talk about normally, as well as childhood and past life regression Overcome addictions: posthypnotic suggestion Legal Use: Crime evidence and courtroom testimonies (controversial) Subjects are eager to please hypnotist so though they will tell the truth, they may create info to fill in gaps The unique pattern of thought, feelings and behavior by which each person reacts to the external world Grows from a complex system of conscious thought, unconscious drives, and life experiences Creates the personal values and goals that help you set priorities Everyone’s personality is unique An individual will generally behave consistently from one situation to another Modern General Consensus: Environment has the most influence on personality development proper childhood nurturing, good diet, available health care, freedom from worry, and feelings shared with family/friends Hard to study, widely debated, various theories Studied to determine what is normal/abnormal, learn about social/cultural differences, explain morals and values Ancient beliefs about influences of gods, demons, spirits, and astrology Gall’s Phrenology: Feeling bumps on the head to determine traits of personality (1800s) Sociobiology: Genes programmed to determine behavior based on survival instinct Studied twins separated at birth Humors: Created by Hippocrates in 400 BC, determine health and behavior due to excess or deficiency of bodily fluids Phlegm: passive, careful, slow-moving Black bile: Melancholic, anxious Yellow bile: Irritable, angry Blood: Easygoing, optimistic Altered in 1960s to this form: http://similarminds.com/eysenck.html Body type determines personality and behavior Pioneer in mental testing to determine range of personality characteristics Freud forms first major personality theory Combination of hereditary and environment shapes personality developments, as well as contributions of unconscious = Freud’s unique contribution Controversial: Changed mindset of psychology Theory grew from Freud’s treatments of mentally ill His discoveries lead to proper treatment Many controversial studies for time period; not given recognition until 1920s Your mind is an iceberg: conscious, preconscious and unconscious Freudian slip: indicator of unconscious issues http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hpu_iEsISuI& safe=active Life and Death forces in all of us: Eros: Life-survival instincts, fueled by psychic energy of libido which allows us to love Thanatos: Death wish-can lead to suicide, crime, genocide and war if unchecked Humans are caught between their own needs and the needs of society Three forces to help resolve conflict Id: Goal is to maximize pleasure and minimize pain = selfish needs and desires Wants immediate satisfaction, whether it’s right or wrong Allows us to find joy in experiences Buried in the unconscious Moderating force between demands of Id and the world around you Measures risk and analyzes consequences before allowing Id to take action Wants to provide pleasure with least amount of pain Helps suppress desires that conflict with society but ultimately wants to satisfy Id Superego absorbs social morals/values taught to us by our parents/society Demands you behave morally, do what’s right In conflict with Id’s desire for pleasure Saves you from temptation Punishes with feelings of guilt when you do something wrong (conscience) Rewards with good feelings when you do something right (ego ideal) Repression: block out painful memories to protect yourself, but still effect your life Displacement: Take your emotions out on someone else more vulnerable Sublimation: Turn powerful negative feelings into positive socially accepted expression of emotion Projection: Displace hard to deal with internal stress and project it onto outside target to cope with your own inadequacies/insecurities Regression: Return to infantile state of behavior when faced with stress/anxiety, overuse can lead to pattern of nonproductive behavior Reaction Formation: converts forbidden feelings into positive feelings/motivation, with underlying resentment Rationalization: Justifying excuses when you feel guilty for not living up to your own expectations, issues with never taking responsibility for your own actions Procrastination: Avoid completing unpleasant task to avoid stress or fear of failure, usually causes more stress Children formerly thought to be “pure and innocent angels” Freud “murdered childhood” saying we all have sexual feelings/desire from birth We are taught these natural feelings are “abnormal” and attempt to repress them Sexual feelings surface in dreams, Freudian slips, jokes, etc. Freud believes sex is the single most powerful force in determining our feelings, thoughts and actions Oral Stage: First year of life; eating Explore with mouth Oral fixation later in life is not resolved Anal Stage: Age 2-3; potty training Child needs to feel pride and learn in their own time Develop a rebellious or anal retentive (controlling) personality later in life if forced Phallic Stage: Age 4-6; Oedipus complex Children learn relationship skills from opposite sex parent Develop issues is that parent isn’t present/attentive Daddy issues or Mama’s boy Latency Period: Age 6-puberty Spend time with same sex groups Opposite sex “has cooties” Genital Stage: Puberty into adult life Explore love relationships and sexuality If some stage is unresolved then it prevents normal development and healthy intimacy Penis envy and sexism issues Use couch; therapist is mostly silent until personal progress is made, then make observations and suggestions Free association: Speak freely about anything that comes to mind without guilt Use insights about past to overcome present barriers to happiness Transference: Attach feelings about important people to analyst, rely on them, love/hate relationship, then ask yourself what you want from analyst and from life