CHAPTER 8 chem hw
advertisement

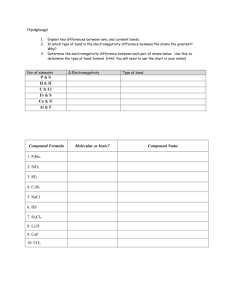
CHAPTER 8: BONDING GENERAL CONCEPTS 1. Using only the periodic table, predict the most stable ion for Na, Mg, Al, S, Cl, K, Ca, and Ga. Arrange these from largest to smallest radius, and explain hwy the radius varies as it does. Compare your predictions to the values on the periodic table. Why is radius an important factor when bonding occurs? 2. Predict the order of increasing electronegativity in each of the following groups of elements. a. Na, K, Rb b. B, O, Ga c. F, Cl, Br d. S, O, F 3. Predict which bond in each of the following groups will be the most polar. a. C—F , Si—F, Ge—F b. P—Cl, S—Cl c. S—F, S—Cl, S—Br d. Ti—Cl , Si—Cl, Ge—Cl 4. Repeat exercise 3, this time using the values for the electronegativites of the elements given on the periodic table. Are there differences in your answers? 5. Write the electron configurations for a. The cations Mg+2, K+, and Al+3 b. The anions N-3, O-2, F-, and Te-2 6. For each of the following groups, place the atoms and/or ions in order of decreasing size. a. V, V+2, V+3, V+5 b. Na+,K+,Rb+, Cs+ c. Te-2, I-, Cs+, Ba+2 d. P,P-, P-2, P-3 e. O-2,S-2, Se-2, Te-2 7. Predict the empirical formulas of the ionic compounds formed from the following pairs of elements. Name each compound. a. Li and N b. Ga and O c. Rb and Cl d. Ba and S 8. Some plant fertilizer compounds are (NH4)2SO4, Ca3(PO4)2, K2O, P2O5, and KCl. Which of these compounds contain both ionic and covalent bonds? Which would have the strongest bond? Cite evidence for your reasoning. 9. Which compound in each of the following pairs of ionic substances has the most exothermic lattice energy? Justify your answers using an appropriate formula. a. NaCl, KCl b. LiF, LiCl c. d. e. f. Mg(OH)2, MgO Fe(OH)2, Fe(OH)3 NaCl, Na2O MgO, BaS 10. Use the following data to estimate ∆H°f for magnesium fluoride. Mg(s) + F2(g) MgF2(s) Lattice energy First ionization energy of Mg Second ionization energy of Mg Electron affinity of F Bond energy of F2 Enthalpy of sublimation of Mg -3916kJ/mol -735 kJ/mol 1445kJ/mol -328 kJ/mol 145 kJ/mol 150. kJ/mol Write reactions for the stepwise production of MgF2 and quantify the energy needed/ produced in each step. Answer: -2088 kJ/mol 11. Rationalize the following lattice energy values: Compound CaSe CaTe ` Na2Se Na2Te Lattice Energy(kJ/mol) -2862 -2721 -2130 -2095 12. Use bond energy values to estimate ∆H for each of the following reaction sin the gas phase. a. H2 + Cl2 2HCl Answer: -183 kJ b. N N + 3H2(g) 2NH3 Answer: -109kJ 13. Acetic acid is responsible for the sour taste of vinegar. It can be manufactured using the following reaction: (g) + (g) + 2H2 (g) Use the tabulated values of bond energies to estimate ∆H for this reaction. Set up a clear accounting of bonds broken and bonds made. Answer: -20. Kj 14. This problem should be spread over multiple pages in your homework book. Write Lewis structures that obey the octet rule for each of the following molecules and ions. (In each case the first atom listed is the central atom.) Predict the molecular structure and bond angles for each molecule or ion in the table above and write it under your lewis dot structure. Sketch the molecule showing the proper dimensions BH3 SO4-2 XeO4 PO4-3 ClO4SO3-2 XeCl4 PO3-3 ClO3-1 SCl2 BeH2 POCl3 ClO2-1 SeF4 PF5 ClF5 S2O3-1 PCl2- ICl5 NF3 Br3- C2H2 C2H5OH SF4 SF6 Now, answer the following in relation to the molecules you just sketched. A. What conclusion scan you draw concerning the structures of species containing the same number of atoms and the same number of valence electrons? B. List the atoms/ ions are exceptions to the octet rule. C. List the atoms / ions exceed the octet rule? How is this possible? 15. Write Lewis structures for the following. Show all resonance structures where applicable. a. NO2-, NO3-, N2O4 (N2O4 exists as O2N – NO2) b. OCN-, SCN-, N3- (Carbon is the central atom in OCN- and SCN-.) 16. Benzene (C6H6) consists of a sex membered ring of carbon atoms with one hydrogen bonded to each carbon. Write the Lewis structures for benzene, including resonance structures. Keep this structure in mind when you read chapter 9 about MO theory. 17. Order the following species with respect to carbon-oxygen bond length. (longest to shortest) What is the order from the weakest to the strongest carbon-oxygen bond? (CH3OH exists as H3C—OH.) Explain your reasoning. CO, CO2, CO3-2, CH3OH 18. Which of the molecules in Exercise 14 have dipole moments (are polar)? Sketch them and show the overall direction of electron shift within the molecule using either arrow notation +---> or δ+ and δ-. 19. Two different compounds have the formula XeF2Cl2. Write Lewis structures for these two compounds, and describe how measurement of dipole moments might be used to distinguish between them. 20. Research: How is the amount of dipole moment in a molecule determined experimentally? What are the units associated with dipole moment? Include 5 lines of explanation and site your source. 21. Research: Define % ionic character. How is % ionic character calculated? a. Are HF and HCl ionic or covalent compounds? How do you know? b. Calculate and compare the percent ionic character of HF and HCl. c. Disuss how you think % ionic character and acid strength may be related. 22. Which of the following molecules have dipole moments? For the molecules that are polar, indicate the polarity of each bond and the direction of the net dipole moment of the molecule. a. CH2Cl2, CHCl3, CCl4 b. CO2, N2O c. BH3, NH3 Research: See CH 8 and CH 10 23. Find and define each of the following and rank them in order of increasing attraction between molecules and/ or atoms. Intramolecular forces: A. Metallic bonding i. While you’re researching about metallic bonding find the following: What properties of metallic bonds lead to the following metal characteristics: high mp/ bp, conductivity, malleability/ ductility? ii. Sketch the “electron sea” model for Na, Mg, and K B. Ionic bonds C. Covalent bonds i. Pure ii. Polar 24. The stronger the intramolecular force, the more energy required when the bond is broken. Compare the bond energy or lattice energy of the following compounds and suggest what the values tell about the strength of the intramolecular force. Na, Mg, K, NaCl, H2O, CO2 25. Find and define each of the following and rank them in order of increasing attraction between molecules and/ or atoms. Intermolecular forces a. Hydrogen bond – use your textbook definition, not the newly defined H-bond of 2014. b. Dipole-dipole interaction c. London dispersion force 26. Higher IMF’s lead to higher mp and higher bp. The heat of fusion and the heat of vaporization of the compound increases when the IMF is higher. Find the heat of fusion and the heat of vaporization for Na, Mg, K, NaCl, H2O, CO2. What do the values suggest about the strength of the IMF between the atoms/ molecules of Na, Mg, K, NaCl, H2O, an CO2?