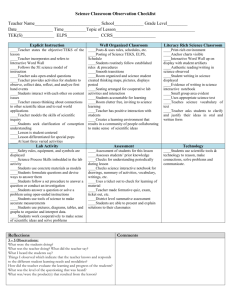
2011-2012 Year-at-a-Glance Chart for [Kindergarten/Social Studies]
advertisement
![2011-2012 Year-at-a-Glance Chart for [Kindergarten/Social Studies]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010107356_1-05b1aa66d398f78ffda270116294c622-768x994.png)
WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT 2011-2012 Year-at-a-Glance for Kindergarten/Social Studies 1st Six Weeks: August 22 – September 27 [26 days, including benchmark date: 9-23_] K.8 Government. The student understands the purpose of rules. The student is expected to: K.8a identify purposes for having rules K.8b identify rules that provide order, security, and safety in the home and school K.4 Geography. The student understands the concept of location. The student is expected to: K.4a use terms, including over, under, near, far, left and right to describe relative location. K.4b locate places on the school campus and describe their relative locations. K.3 History. The student understands the concept of chronology. The student is expected to: K.3a place events in chronological order K.3b use vocabulary related to time and chronology, including before, after, next, first, and last. K.9 Government. The student understands the role of authority figures. The student is expected to: K.9a identify authority figures in the home, school, and community K.10 Citizenship. The student understands important customs, symbols, and celebrations that represent American beliefs and principles and contribute to our national identity. The student is expected to: K.10a identify the flags of the United States and Texas K.10b recite the Pledge of Allegiance and the Texas Pledge K.16 Social studies skills. The student communicates in oral and visual forms. The student is expected to: K.16b create and interpret visuals including pictures and maps K.15 Social studies skills. The student applies criticalthinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of sources including electronic technology. The student is expected to: K.15c sequence and categorize information 2nd Six Weeks: September 28 – November 4 [27 days, including benchmark date: 11-4_] K.6 Economics. The student understands that basic human needs are met in many ways. The student is expected to: K. 6b explain how basic human needs of food, clothing, and shelter can be met 3rd Six Weeks: November 7 – December 20 [29 days, including benchmark date: 12-16_] K.5 Geography. The student understands the physical and human characteristics of the environment. The student is expected to: K.5a identify the physical characteristics of places such as landforms, bodies of water, natural resources, and weather K.7 Economics. The student understands the importance of jobs. The student is expected to: K.7a identify jobs in the home, school, and community K.7b explain why people have jobs K.6 Economics. The student understands that basic human needs are met in many ways. The student is expected to: K.6a identify basic human needs K.3 The student understands the concept of chronology. The student is expected to: K.3a place events in chronological order K.3b use vocabulary related to time and chronology, including before, after, next, first, an last K.5 Geography. The student understands the physical and human characteristics of the environment. The student is expected to: K.5b identify the human characteristics of places such as types of houses and ways of earning a living K.14 Science, technology, and society. The student understands ways in which technology has changed how people live. The student is expected to: K.14a describe how his or her life might be different without modern technology K.14b list ways in which technology helps meet people’s needs K.12 Culture. The student understands how people learn about themselves through family customs and traditions. The student is expected to: K.12a identify family customs and traditions and explain their importance K.12b compare family customs and traditions K.12c describe customs of the local community K.5 Geography. The student understands the physical and human characteristics of the environment. The student is expected to: K.5a identify the physical characteristics of places such as landforms, bodies of water, natural resources, and weather K.4 Geography. The student understands the concept of location. The student is expected to: K.4a use terms, including over, under, near, far, left, and right, to describe relative location K.5 Geography. The student understands the physical and human characteristics of the environment. The student is expected to: K.5b identify the human characteristics of places such as types of houses and ways of earning a living K.3 History. The student understands the concept of chronology. The student is expected to: K.3a place events in chronological order K.3b use vocabulary related to time and chronology, including before, after, next, first, and last K.12 Culture. The student understands how people learn about themselves through family customs and traditions. The student is expected to: K.12a identify family customs and traditions and explain their importance K.12 Culture. The student understands how people learn about themselves through family customs and traditions. K.12 Culture. The student understands how people learn about themselves through family customs and traditions. The K.6 Economics. The student understands that basic human needs are met in many ways. The student is expected to: K.6a identify basic human needs 1 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT The student is expected to: K.12a identify family customs and traditions and explain their importance K.12b compare family customs and traditions K.12c describe customs of the local community K.4 Geography. The student understands the concept of location. The student is expected to: K.4a use terms, including over, under, near, far, left and right to describe relative location. K.3 History. The student understands the concept of chronology. The student is expected to: K.3a place events in chronological order K.3b use vocabulary related to time and chronology, including before, after, next, first, and last student is expected to: K.12b compare family customs and traditions K.12 Culture. The student understands how people learn about themselves through family customs and traditions. The student is expected to: K.12c describe customs of the local community K.15 Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of sources including electronic technology. The student is expected to: K.15a obtain information about a topic using a variety of oral sources such as conversations, interviews, and music K.16 Social studies skills. The student communicates in oral and visual forms. The student is expected to: K.16a express ideas orally based on knowledge and experiences. 4th Six Weeks: January 9 – February 17 [29 days, including benchmark date: 2-17_] 5th Six Weeks: February 20 – April 5 [29 days, including benchmark date: 4-5_] 6th Six Weeks: April 10 – May 30 [37 days, including benchmark date: 5-18_] K.3 History. The student understands how historical figures and ordinary people helped to shape the community, state, and nation. The student is expected to: K.3a place events in chronological order K.3b use vocabulary related to time and chronology, including before, after, next, first, and last K.2 History. The student understands how historical figures and ordinary people helped to shape the community, state, and nation. K.2a identify the contributions of historical figures such as Stephen F. Austin and George Washington who helped to shape our state and nation K.3 History. The student understands the concept of chronology. The student is expected to: K.3a place events in chronological order K.3b use vocabulary related to time and chronology including before, after, next, first, and last. K.13 Science, technology, and society. The student understands ways technology is used in the home and school. K.13a identify examples of technology used in the home and school K.4 Geography. The student understands the concept of location. The student is expected to: K.4a use terms, including over, under, near, far, left, and right, to describe relative location K.2 History. The student understands how historical figures and ordinary people helped to shape the community, state, and nation. The student is expected to: K.2a identify the contributions of historical figures such as Stephen F. Austin and George Washington who helped to shape our state and nation K.1 History. The student understands that holidays are celebrations of special events. The student is expected to: K.1a explain the reasons for national patriotic holidays such as Presidents' Day and Independence Day K.3 History. The student understands the concept of K.2 History. The student understands how historical figures and ordinary people helped to shape the community, state, and nation. K.2b identify ordinary people who have shaped the community K.9 Government. The student understands the role of authority figures. K.9a identify authority figures in the home, school, and community K.9b explain how authority figures make and enforce rules K.10 Citizenship. The student understands important customs, symbols, and celebrations that represent K.13 Science, technology, and society. The student understands ways technology is used in the home and school. K.13b describe how technology helps accomplish specific tasks K.14 Science, technology, and society. The student understands ways in which technology has changed how people live. K.14a describe how his or her life might be different without modern technology K.14 Science, technology, and society. The student understands ways in which technology has changed how people live. K.14b list ways in which technology meets people's needs K.12 Culture. The student understands how people learn about themselves through family customs and traditions. The student is expected to: K.12c describe customs of the local community 2 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT location. K.3a place events in chronological order K.3b use vocabulary related to time and chronology, including before, after, next, first, and last American beliefs and principles and contribute to our national identity. K.10c explain the use of voting as a method for group decision making K.1 History. The student understands that holidays are celebrations of special events. The student is expected to: K.1b identify customs associated with national patriotic holidays such as parades and fireworks on Independence Day K.10 Citizenship. The student understands important customs, symbols, and celebrations that represent American beliefs and principles and contribute to our national identity. K.10a identify the flags of the United States and Texas K.10b recite the Pledge of Allegiance K.10 Citizenship. The student understands important customs, symbols, and celebrations that represent American beliefs and principles and contribute to our national identity. The student is expected to: K.10a identify the flags of the United States and Texas K.10b recite the Pledge of Allegiance K.10 Citizenship. The student understands important customs, symbols, and celebrations that represent American beliefs and principles and contribute to our national identity. The student is expected to: K.10c explain the use of voting as a method for group decision making K.15 Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of sources including electronic technology. The student is expected to: K.15c sequence and categorize information K.16 Social studies skills. The student communicates in oral and visual forms. The student is expected to: K.16a express ideas orally based on knowledge and experiences K.4 Geography. The student understands the concept of location. The student is expected to: K.4a use terms including over, under, near, far, left and right to describe relative location K.3 History. The student understands the concept of chronology. The student is expected to: K.3a place events in chronological order K.3b use vocabulary related to time and chronology including before, after, next, first, and last. 3 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT Scope and Sequence Kindergarten Social Studies 1st Six Weeks: August 22 – September 23 specific to grade/course (ex: insert unit # and title) 8.17 (B) Explain constitutional issues arising over the issue of states’ rights, including the Nullification Crisis and the Civil War. 8.10 (B) Compare places and regions of the United States in terms of physical and human characteristics CCRS: If applicable, insert relevant CCRS statement(s) here Insert formative assessment and/or WISD Benchmark date Reporting Category 3: Government and Citizenship Reporting Category 2: Geography and Culture For K.8 (a), (b) : “What would our classroom be like without rules?” •Creating order, security •Fairness, equality •Safety •Identify specific rules in the classroom (as well as at home or in the community: option) Extend the learning by talking about how our communities (school, home, local) depend on their members obeying the rules even when no one is watching. Order: (such as) •Home – clean up room, take out trash, wash dishes, be polite in words and actions (please, thank you, etc.) •School – clean up after self, push in chairs, pick up trash (library, bathroom, hallways, and playgrounds), be polite in words and actions (please, thank you, etc.) Security/Safety: (such as) Home – lock doors & windows, don’t play with weapons or matches, poison awareness School – walk inside, keep hands, feet & objects to self (library, bathroom, hallways, and playgrounds); only be on the computer when an adult is in the room; stay with class line, be where you are supposed to be; stay on direct path on way home… Emergency situations at school—procedures for lock downs, bad weather drills and fire drills Rest Room Safety – water, paper towels off of floor, direct walking path to and from Stranger danger awareness (regardless of location) RESOURCES http://www.texaslre.org/downloads/lessons/092004_lp_k-2.pdf “Humpty Dumpty: An Example of Why We Need Rules” by Texas Law-Related Education (Helps teach TEKS K.8, K.15BD, K.16 and ELA TEKS K.1A-D, K.15C) http://www.texaslre.org/downloads/lessons/082006_lp_k-2.pdf “Draw and Talk about the Need for Rules” lesson plan from Texas Law-Related Education (Helps teach TEKS K.8, K.9, K.16A) For K.4 (a), (b): Be sure to have the students describe or draw the campus and the following locations in relation to each other: Office, nurse, library, cafeteria, gym, playground, counselor, art, music K.11 (a): Including: body parts, head, eyes, ears, nose, mouth, teeth, tongue, hair, skin, legs / arms, feet / hands, toes / fingers, knees, wrists, elbows, ankles, shoulders, hips, heart, brain, lungs, bones, muscles (not naming specific bones or muscles), emotions, need for community / communication, acceptance 5 senses Seeing (eyes), touching (skin), hearing (ears), tasting (mouth / tongue), smelling (nose) 4 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT NOTE: Be sure to emphasize our similarities. Even though everyone looks different, we all still need love and acceptance. RESOURCES http://www.texaslre.org/downloads/lessons/012006_lp_k-2.pdf “Appreciating Likenesses and Differences” lesson plan by Texas Law-Related Education (Helps teach TEKS K.11, K.15B, K.16) http://www.texaslre.org/downloads/lessons/012006_lp_k-2.pdf “My Name is Special” lesson plan from Texas Law-Related Education (Helps teach TEKS K.11AB, K.15ABD, K.16) http://www.happalmer.com/ - songs about “ME” “Head Shoulders Knees and Toes” http://www.kellyskindergarten.com/ ELPS: Insert logical/related ELPS standard(s) here 1C; 1E; 2E; 3D; 4G; 5B 8.1(B) apply absolute and relative chronology through the sequencing of significant individuals, events, and time periods Reporting Category 1: History CCRS: If applicable, insert relevant CCRS statement(s) here K.3 (a), (b): Such as: before first after next last then yesterday today tomorrow Chronology (as related to a kindergartner’s experience) THESE CAN EASILY BE INCORPORATED INTO THE ON-GOING CALENDAR TIME. MENTION EVENTS WHEN RELEVANT. Events of a school day Events from days of the week 5 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT Events from months of the year Holidays throughout the year (if you include Christian religious holidays, such as Christmas and Easter, include religious holidays from other traditions such as Ramadan, Yom Kippur, etc.) NOTE: Use events for days of the week as examples: Mondays we go to art, etc… K.9 (a) Authority figures: set standards, enforce the law, maintain social order if there are no laws Examples: Home: parents/guardians, grandparents, adult relatives School: teachers, principals, and other school personnel Community: mayor, police, judges RESOURCES United Streaming “Going to School is your Job” (13:04min) “Community Rules & Laws” (15:00min) Invite community helpers to the classroom for discussion in their job http://www.texaslre.org/downloads/lessons/082006_lp_k-2.pdf Draw and Talk about the Need for Rules from Texas Law-Related Education (meets 9B, 8 and 16A as well) K.10 (a), (b): Introduce Pledge of Allegiance and Pledge to the Texas Flag NOTE: Be sure to teach them pledge etiquette (ex: stand at attention, right hand over heart, eyes on the appropriate flag, pausing other activities during reciting of pledge). Ask them some questions about patriotism to see how much they understand about pride and loyalty to their country. Why do we say the pledge? Why do we face the flag? RESOURCES http://www.usa-flag-site.org/kids-resources.shtml Teach Your Kids about Patriotism -flag/patriotism information http://www.texaslre.org/downloads/lessons/082003_lp_k-2_txpledge.pdf “Learning the Pledge to the Texas Flag” lesson plan from Texas Law-Related Education (Helps teach TEKS K.10A, K.16) IDEA: Have flags in different locations / levels so that students need to turn “left” or “right”, etc. to face appropriate flag Texas State Code: Sec. 3100.104 6 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT Reciting Pledge: If the pledge to the state flag is recited, each person who is present and not in uniform should: a. face the flag and stand at attention with the person’s right hand over the heart; b. if wearing a head covering that is easy to remove, remove the head covering with the right hand and hold it at the person’s left shoulder with the person’s hand over the heart; and c. recite the pledge; or in uniform should remain silent, face the flag, and make the military salute. K.11(b): Including: skin color, eye color, hair color, size (including height), language spoken / accent, personalities / interests, where and when they were born RESOURCES www.unitedstreaming.com (Be sure to view clips in advance) - “Respecting Differences (A Sun burst Title)” (16:00min) - “How Customs and Heritage Shape our Community” (16:00min) http://www.harcourtschool.com/activity/sense/sense.htm Five Senses interactive website http://www.harcourtschool.com/activity/smiling/smiling.htm Brushing teeth interactive website K.4 (a): Explore the fact that their bodies and body parts, such as arms, are capable of various movement patterns and that they can change their location and position by making these movements. ELPS: Insert logical/related ELPS standard(s) here 1C; 1E; 2E; 3D; 4G; 5B If applicable and necessary, insert Student Expectations that are not assessed on STAAR but that are part of the required curriculum for the grade/course. CCRS: If applicable, insert relevant CCRS statement(s) here Clarification: List statement(s) here that clarify what should be taught to fully teach the Student Expectation listed above. ELPS: Insert logical/related ELPS standard(s) here 7 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT Scope and Sequence Kindergarten Social Studies 2nd Six Weeks: September 28 – November 4 specific to grade/course (ex: insert unit # and title) 8.27 (A) explain the effects of technological and scientific innovations such as the steamboat, the cotton gin, and interchangeable parts 8.10 (B) compare places and regions of the United States in terms of physical and human characteristics Insert formative assessment and/or WISD Benchmark date Reporting Category 4: Economics, Science, Technology and Society Reporting Category 2: Geography and Culture CCRS: If applicable, insert relevant CCRS statement(s) here K. 5 (b): Types of HOMES for people: (As related to a kindergartener’s experience) • house: Science/social studies connection: Houses in the past and present are made out of materials available in that environment as well as materials best suited to the purpose • apartment • mobile home • townhome/condo • duplex • other homes relating to other environments or circumstances (houseboat, tents, RVs, etc.) Specifics will come from student input. Ways of earning a living: (As related to a five-year-old’s experience) Wampanoag Pilgrim Today Farming women men farmers (men or women) Hunting men men hunters, butchers Political leader sachem governor mayor Pilgrims or those traveling west in later times, built homes and earned a living in comparison to the homes and jobs available today in the United States. RESOURCES United Streaming “Everybody Needs Shelter” (13:00min) Information on Wampanoag from Wikipedia for the teacher ELPS: Insert logical/related ELPS standard(s) here 1C, 1E; 2E; 3D; 4G; 5B 8.12 (A) identify economic differences among different regions of the United States 8.23 (B) explain the relationship between urbanization and conflicts resulting from differences in religion, social class, and political beliefs 8.1 (B) apply absolute and relative chronology through the sequencing of significant Reporting Category 4: Economics, Science, Technology and Society Reporting Category 2: Geography and Culture Report Category 1: History 8 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT individuals, events, and time periods CCRS: If applicable, insert relevant CCRS statement(s) here K.6(b): • Food: growing, processing, buying, trading, selling • Clothing: making, buying, selling • Safety: wear protective gear, know 911, know address, phone numbers, etc. • Love/belonging: kind words, caring for others, family, and sense of community (including classroom and home family) NOTE: Make connections to food and nutrition and/or introduce food/ nutrition or farm jobs unit. Pumpkin or other fall fruit uses: Including Food: • Such as: pie, seeds, bread, cake, soup, pancakes, and other methods Including: Need vs Want: Such as: pumpkin or other fall fruit as decoration, jack-o-lantern RESOURCES United Streaming “The Difference between Wants and Needs” (16:00min) The National Council for Economic Education has lessons to help teach Economics concepts. Many of their lessons are online http://www.econedlink.org/economic-standards/pick-state.php K.7 (a): NOTE: Make some instructional integration connections by looking at jobs that involve pumpkins or other fall fruit Such as: farmers, pumpkin picker, produce manager, pumpkin canner, baker (pumpkin pie, bread, empanadas), pumpkin seed roaster, pumpkin carver, person who makes compost, agriculturalist… RESOURCES United Streaming “Going to School is your Job” (13:04min) “Community Rules & Laws” (15:00min) “Community Helpers and the Tools of Their Trade” lesson plan by Texas Law-Related Education (Helps teach TEKS K.7, K.15B, K.16) http://www.texaslre.org/downloads/lessons/102006_lp_k-2.pdf Invite school authority figures to visit classroom and discuss his/her job Reading Rainbow - Bea and Mr. Jones (Amy Schwartz); Kindergartener and Dad change places; Dad to kinder, kinder to office K.7(b): Including: • to earn money to meet basic needs for themselves and others o purchase food, clothes, shelter, etc • to be productive and learn new skills • to feel successful and satisfied to give back to the community/society (ex: volunteering, food drives, charitable fundraisers) NOTE: This is a great place for oral interviews and integration with ELA as well. Have students ask their parents and adults in the school what are their reasons for having their particular job. How does their job meet their wants and needs? 9 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT RESOURCES Use classroom parents and community helpers as examples (connect to child experience) for resources “Community Helpers and the Tools of Their Trade” lesson plan by Texas Law-Related Education (Helps teach TEKS K.7, K.15B, K.16) http://www.texaslre.org/downloads/lessons/102006_lp_k-2.pdf K.14 (a), (b): Connection TEKs: During the conversation regarding the fall fruit: • Tractors and other modern farm equipment (vs hand planting and harvesting) • Transportation trucks, etc • Grocery store scales to weigh produce • Ordering products on-line K.6 (a): • Food • Clothing • Shelter/homes • Safety • Love/belonging NOTE: To use Thanksgiving to teach these TEKS and specificities, try having the students explain how these basic human needs are represented in the first Thanksgiving and in Thanksgiving as it is celebrated by different families today. The story of Squanto and how he helped the Pilgrims could also illustrate basic human needs well. Also include: • Methods of Travel (Science/social studies connection: water is a natural resource that has many functions) • Common Animals • Other Interesting Facts/dates • Questions RESOURCES United Streaming “The Difference between Wants and Needs” (16:00min) The National Council for Economic Education has lessons to help teach Economics concepts. Many of their lessons are online http://www.econedlink.org/economic-standards/pick-state.php K.3 (a), (b): Chronological Events Related to the First Thanksgiving: • First Americans (Focus on Wampanoag Nation and Squanto) • Pilgrims Come to America • 1st Thanksgiving Use the vocabulary before, after, next, first, and last when discussing the chronological events related to the First Thanksgiving, especially in terms of the cycle of the harvest. Why would Thanksgiving be in November and not in March, for example? 10 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT ELPS: Insert logical/related ELPS standard(s) here 1C; 1E; 2C; 2E; 3D; 4G; 5B If applicable and necessary, insert Student Expectations that are not assessed on STAAR but that are part of the required curriculum for the grade/course. CCRS: If applicable, insert relevant CCRS statement(s) here Clarification: List statement(s) here that clarify what should be taught to fully teach the Student Expectation listed above. ELPS: Insert logical/related ELPS standard(s) here 11 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT Scope and Sequence Kindergarten Social Studies 3rd Six Weeks: November 7 – December 20 specific to grade/course (ex: insert unit # and title) 8.10 (B) compare places and regions of the United States in terms of physical and human characteristics Insert formative assessment and/or WISD Benchmark date Reporting Category 2: Geography and Culture CCRS: If applicable, insert relevant CCRS statement(s) here K.5(b): Types of HOMES for people: (As related to a kindergartener’s experience) • house: Science/social studies connection: Houses in the past and present are made out of materials available in that environment as well as materials best suited to the purpose • apartment • mobile home • townhome/condo • duplex • other homes relating to other environments or circumstances (houseboat, tents, RVs, etc.) Specifics will come from student input. Ways of earning a living: (As related to a five-year-old’s experience) Wampanoag Pilgrim Today Farming women men farmers (men or women) Hunting men men hunters, butchers Political leader sachem governor mayor NOTE: Make connections to other cultures in different times such as Native Americans (cliff dwellers, long houses, tipis, Caddo grass houses), Americans moving west (covered wagons, sod houses), etc. NOTE: To use Thanksgiving to teach these TEKS and specificities, try using similarities and differences to show how Native Americans and early settlers, such as the Pilgrims or those traveling west in later times, built homes and earned a living in comparison to the homes and jobs available today in the United States. RESOURCES United Streaming “Everybody Needs Shelter” (13:00min) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wampanoag From Wikipedia for the teacher Information on Wampanoag K.12 (a), (b), (c): • Customs are routine practices and habits of a family which become tradition; perhaps family holiday and birthday celebrations • Traditions come from transmitting knowledge and practices through generations without written instructions: like celebrations, cultural traditions, ethnic foods, etc. • Specifics will come from student input • Holiday, birthday, other customs 12 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT • How do our family’s customs and traditions make us who we are? • Specifics will come from student input Customs of local community • Deutschenfest • Football games (high school or UT) • Cinco de Mayo NOTE: You may revisit cultures discussed throughout the year. Other customs you might want to teach or discuss include Chinese New Year, Juneteenth, Capitol 10,000, etc RESOURCES NOTE: Consider using clips from www.storycorps.net to look at other peoples’ customs. (Be sure to listen to clips in advance of sharing with class—not all are appropriate for kindergarten.) Students can then interview their own relatives. United Streaming - “How Customs and Heritage Shape Communities” (16:00min) Reading Rainbow - “Borrequita and the Coyote” (Verna Aardema); Mexican American Culture - “Knots on a Counting Rope” (Bill Martin Jr.); Native American - “Rechenka’s Eggs” (Patrcicia Polocco); Ukrainian art of egg painting - “Galimoto” (Karen Lynn Williams); African boy in search for a wire - “Gift of the Sacred Dog” (Paul Goble) Native American story http://www.texaslre.org/downloads/lessons/122004_lp_k-2.pdf “December Holiday Celebrations” from Texas Law-Related Education (Helps teach TEKS K.12A-C, K.15AB, K.16A) For background information on community customs, http://www.wikipedia.org/ “December Holiday Celebrations” from Texas Law-Related Education (Helps teach TEKS K.12A-C, K.15AB, K.16A ) ELPS: Insert logical/related ELPS standard(s) here 1C; 1E; 2C; 2E; 3D; 4G; 5B 8.12 (A) identify economic differences among different regions of the United States 8.23 (B) explain the relationship between urbanization and conflicts resulting from differences in religion, social class, and political beliefs 8.1 (B) apply absolute and relative chronology through the sequencing of significant individuals, events, and time periods Report Category 4: Economics, Science, Technology and Society Reporting Category 2: Geography and Culture Report Category 1: History CCRS: If applicable, insert relevant CCRS statement(s) here K.6 (a): • Food 13 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT • Clothing • Shelter/homes • Safety • Love/belonging NOTE: To use Thanksgiving to teach these TEKS and specificities, try having the students explain how these basic human needs are represented in the first Thanksgiving and in Thanksgiving as it is celebrated by different families today. The story of Squanto and how he helped the Pilgrims could also illustrate basic human needs well. Also include: • Methods of Travel (Science/social studies connection: water is a natural resource that has many functions) • Common Animals • Other Interesting Facts/dates • Questions RESOURCES United Streaming “The Difference between Wants and Needs” (16:00min) The National Council for Economic Education has lessons to help teach Economics concepts. Many of their lessons are online http://www.econedlink.org/standards/ There is also a green CD available in each campus library titled “Virtual Economics.” It contains even more lessons from NCEE (1200 economics lessons, K-12). How to search: Choose “Browse Economics Lessons” then “Search by Standard” then “Texas.” Lessons will be displayed by individual TEKS. K.3 (a), (b): Chronological Events Related to the First Thanksgiving: • Pilgrims Come to America • 1st Thanksgiving Use the vocabulary before, after, next, first, and last when discussing the chronological events related to the First Thanksgiving, especially in terms of the cycle of the harvest. Why would Thanksgiving be in November and not in March, for example? ELPS: Insert logical/related ELPS standard(s) here 1C; 1E; 2C; 2E; 2F; 3D; 4G; 5B If applicable and necessary, insert Student Expectations that are not assessed on STAAR but that are part of the required curriculum for the grade/course. CCRS: If applicable, insert relevant CCRS statement(s) here Clarification: List statement(s) here that clarify what should be taught to fully teach the Student Expectation listed above. ELPS: Insert logical/related ELPS standard(s) here 14 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT Scope and Sequence Kindergarten Social Studies 4th Six Weeks: January 9 – February 17 specific to grade/course (ex: insert unit # and title) Insert formative assessment and/or WISD Benchmark date CCRS: If applicable, insert relevant CCRS statement(s) here Clarification: List statement(s) here that clarify what should be taught to fully teach the Student Expectation listed above. ELPS: Insert logical/related ELPS standard(s) here 8.1 (B) apply absolute and relative chronology through the sequencing of significant individuals, events, and time periods 8.1 (C) explain the significance of the following dates: 1607, founding of Jamestown; 1620, arrival of the Pilgrims and signing of the Mayflower Compact; 1776, adoption of the Declaration of Independence; 1787, writing of the U.S. Constitution; 1803, Louisiana Purchase; and 1861–1865, Civil War. 8.19 (D) identify examples of responsible citizenship, including obeying rules and laws, staying informed on public issues, voting, and serving on juries Reporting Category 1: History Reporting Category 3: Government and Citizenship CCRS: If applicable, insert relevant CCRS statement(s) here K.2(a): Including: • Washington: -Including: first president, “Father of Our Country,” -Such As: Commander-in-Chief, his image can be found on the quarter and the dollar bill, Mount Rushmore, led the Continental Army which defeated England and won the American Revolution, ran the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia in 1787. (The U.S. Constitution establishes the rules for how our 15 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT government works.) Washington put the needs of his country above his own needs. • Lincoln: -Including: 16th US President, “Honest Abe”, freed the slaves -Such As: his image can be found on the penny(backside of penny), the five-dollar bill, Mount Rushmore, Lincoln Memorial Including: • President’s Day: celebration of presidents; to show pride and to the people who have made positive contributions and dedicated their lives to our country • Independence Day: celebrated on July 4th, the signing of the Declaration of Independence which gave us our freedom from England NOTE: July 4th will be revisited in Bundle 12 as it pertains to summer. This introduces AS a national holiday. NOTE: Use folktale of Washington and cutting down the cherry tree to teach honesty as a good character trait: “he could not tell a lie.” NOTE: Stephen F. Austin will be studied in Bundle #10. During Bundle #8, national heroes can be studied. You can also discuss heroes as related to a kindergartner’s experience such as real life people (mom, dad, grandma, etc.) RESOURCES “George Washington: A Great Leader” lesson plan on p. 8 in Ordinary People, Extraordinary Citizens by Aldridge and Wray. This resource is located in your campus library. (Also helps teach TEKS SS K.15B, C and ELA K.1A-E, K.9) “Celebrate Freedom Week: What is Freedom?” lesson plan from Texas Law-Related Education (Helps teach TEKS K.1A, K.2A, K.15BD, K.16) http://www.texaslre.org/downloads/lessons/112004_lp_k-2.pdf “Facts about George Washington” lesson plan from Texas Law-Related Education (Helps teach TEKS K.1A, K.2A, K.15B, K.16A) http://www.texaslre.org/downloads/lessons/Feb_08-Facts_About_George_Washington.pdf K.1(a): Including: • traditions of parades, picnics, and fireworks are established as a way to celebrate patriotic holidays • other patriotic traditions include wearing patriotic colors (red, white, and blue) • displaying the US flag, patriotic community parades, and watching fireworks with family and friends • Federal holiday (banks, schools, post office are closed in recognition of the holiday) RESOURCES Biographies and Facts about Presidents from White House 101 http://www.whitehouse.gov/about/white-house-101/ “Facts about George Washington” lesson plan from Texas Law-Related Education (Helps teach TEKS K.1A, K.2A, K.15B, K.16A) http://www.texaslre.org/downloads/lessons/Feb_08-Facts_About_George_Washington.pdf Suggested Books: - A Picture Book of Abraham Lincoln (David Alder) - A Picture Book of George Washington (David Adler) K.10 (a): Including: • US Flag Compare current flag of US to historical flags of US (original 13 stars “Betsy Ross” flag); colors of flags: Red, White, Blue, Stripes, Stars, # of stripes and stars • Songs Including: “Star Spangled Banner” 16 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT Such as: “You’re a Grand Old Flag”, “My Country ‘Tis of Thee”, “America the Beautiful” NOTE: K.10b: while you have been reciting the pledge during the year, this provides the opportunity to teach the general meaning and understand what it says and why it says it. RESOURCES Meaning of the US Pledge: http://www.kyrene.org/schools/brisas/sunda/flag/flag_day/page4.htm Teach Your Kids about Patriotism - flag/patriotism information - songs http://www.usa-flag-site.org/kids-resources.shtml “Learning the Pledge to the Texas Flag” lesson plan from Texas Law-Related Education (Helps teach TEKS K.10A, K.16) http://www.texaslre.org/downloads/lessons/082003_lp_k-2_txpledge.pdf Pledge of Allegiance lesson plan from Texas Law-Related Education (Helps teach TEKS K.10AB, K.15B, K.16B) http://www.texaslre.org/downloads/lessons/Pledge%20of%20Allegiance%20Aug%2003.pdf Invite school authority figures to visit classroom (such as school principal, counselor, nurse, etc…) K.10 (c): • Introduce basic voting procedures/process for group • Decision making (secret vote, raise hand, vocal assent, etc.) • Making decisions / rules by voting (vote for authority figures, such as a president) • Country elects president by voting RESOURCES Electing a President Lesson Plan from Texas Law-Related Education http://www.texaslre.org/downloads/lessons/102004_lp_k-2.pdf Your Vote Counts lesson plan from TX LRE http://www.pflugervilleisd.net/curriculum/sstud/documents/Oct-08-Your-Vote-Counts-Aldridge.pdf Reading A-Z Election Materials http://www.readinga-z.com/theme/election08.html ELPS: Insert logical/related ELPS standard(s) here 1C; 1E; 2E; 2F; 2I; 3D; 4G; 4I; 5B If applicable and necessary, insert Student Expectations that are not assessed on STAAR but that are part of the required curriculum for the grade/course. CCRS: If applicable, insert relevant CCRS statement(s) here Clarification: List statement(s) here that clarify what should be taught to fully teach the Student Expectation listed above. ELPS: Insert logical/related ELPS standard(s) here 17 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT Scope and Sequence Kindergarten Social Studies 5th Six Weeks: February 20 – April 5 specific to grade/course (ex: insert unit # and title) Insert formative assessment and/or WISD Benchmark date CCRS: If applicable, insert relevant CCRS statement(s) here Clarification: List statement(s) here that clarify what should be taught to fully teach the Student Expectation listed above. ELPS: Insert logical/related ELPS standard(s) here 8.1 (B) apply absolute and relative chronology through the sequencing of significant individuals, events, and time periods 8.1 (C) explain the significance of the following dates: 1607, founding of Jamestown; 1620, arrival of the Pilgrims and signing of the Mayflower Compact; 1776, adoption of the Declaration of Independence; 1787, writing of the U.S. Constitution; 1803, Louisiana Purchase; and 1861–1865, Civil War. 8.19 (D) identify examples of responsible citizenship, including obeying rules and laws, staying informed on public issues, voting, and serving on juries Reporting Category 1: History Reporting Category 3: Government and Citizenship CCRS: If applicable, insert relevant CCRS statement(s) here K.2 (a): Including: • State: o Stephen F. Austin is the “Father of Texas.” Austin, the capital city of Texas, is named after him, brought first US settlers to Texas o Sam Houston – General of Texas Army, Texas President (when it was a republic), important in shaping Texas Such as: o Barbara Jordan, Lady Bird Johnson, Susanna Dickinson (survivor of Alamo) RESOURCES “Stephen F. Austin: The Father of Texas” lesson plan from Texas Law-Related Education (Helps teach TEKS K.2A, K.3, K.15B, K.16) http://www.texaslre.org/downloads/lessons/032004_lp_k-2.pdf Stephen F. Austin information from Lone Star Junction http://www.lsjunction.com/people/austin.htm 18 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT K.2(b): Historical / Ordinary: • Cowboys – took the cattle from the ranchers to railroads where they would go to cities in the north to be food • Farmers – grow crops such as corn, cotton, and soybeans • Ranchers – raise cattle and other livestock • Pioneers – went to live in new places around few other people NOTE: Please remember to emphasize the diversity within these groups. Movies and textbooks usually show us white cowboys and pioneers, but the truth is that cowboys started as vaqueros, Indian people caring for herds on Spanish missions. After the Civil War, former soldiers, African-American ex-slaves, Mexicans and Mexican Americans, and American Indians all became cowboys. Similarly, farmers, ranchers, and pioneers came from diverse backgrounds. Historical Local / Ordinary: W. E. Stewart Family Local / Ordinary: Choose several of the following and help students understand how these people are shaping their communities in positive ways: • Teacher of the Year—current or previous • Humanitarian of the Year—current or previous • School volunteers including PTO president • Principal • Lion’s Club NOTE: You could have the students interview several of the people above to help them understand how we help ourselves by helping others and that makes the world a better place. Possible questions students could ask the guests: • What do you do to help the community? • Why do you think this is important? • How does it make you feel to help other people? • What are you going to do next to help your community? After the guest(s) have left, students could also think about what character traits these people show such as honesty, responsibility, and good citizenship. RESOURCES Reading Rainbow: - Meanwhile Back @ the Ranch (Trinka Hankes Noble); ranchers & cowboys - Ox Cart Man (Donald Hall); colonial village/relationships with land animals for survival - Paul Bunyan (retold by Steven Kellog); tall tale K.9 (a)(b): CONNECTION NOTE: As it pertains to state and local Authority figures • set standards, enforce the law, maintain social order if there are no laws Examples of authority figures: • mayor, police department, judges, sheriff, principal, superintendent 19 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT RESOURCES Invite community helpers into classroom for discussion “Draw and Talk about the Need for Rules” lesson plan from Texas Law-Related Education (Helps teach TEKS K.8, K.9, K.16A) http://www.texaslre.org/downloads/lessons/082006_lp_k-2.pdf K.10 (c): CONNECTION NOTE: As it pertains to state and local Introduce basic voting procedures/process for group decision making • Introduce basic voting procedures/process for group • Decision making (secret vote, raise hand, vocal assent, etc.) • Making decisions / rules by voting (vote for authority figures, such as a president) • Country elects president by voting RESOURCES Your Vote Counts lesson plan from TX LRE http://www.pflugervilleisd.net/curriculum/sstud/documents/Oct-08-Your-Vote-Counts-Aldridge.pdf Reading A-Z Election Materials http://www.readinga-z.com/theme/election08.html K.10 (a), (b): Including: • Texas Pledge of Allegiance Established 1845, “Tejas” [Caddo for Friends] Lone Star NOTE: According to the Rules Governing the Use of the Texas Flag: “While rendering the salute to the Texas Flag, a person should stand erect, face the Texas Flag and hold their right hand over the heart. • Songs Including: “Texas, Our Texas” NOTE: K.10b: while you have been reciting the pledge during the year, this provides the opportunity to teach the general meaning and understand what it says and why it says it. RESOURCES “Texas, Our Texas” http://www.lsjunction.com/song.htm ELPS: Insert logical/related ELPS standard(s) here 1C; 1E; 2E; 2F; 2I; 3D; 3G; 4G; 4I; 5B If applicable and necessary, insert Student Expectations that are not assessed on STAAR but that are part of the required curriculum for the grade/course. CCRS: If applicable, insert relevant CCRS statement(s) here Clarification: List statement(s) here that clarify what should be taught to fully teach the Student Expectation listed above. ELPS: Insert logical/related ELPS standard(s) here 20 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT Scope and Sequence Kindergarten Social Studies 6th Six Weeks: April 10 – May 30 specific to grade/course (ex: insert unit # and title) Insert formative assessment and/or WISD Benchmark date CCRS: If applicable, insert relevant CCRS statement(s) here Clarification: List statement(s) here that clarify what should be taught to fully teach the Student Expectation listed above. ELPS: Insert logical/related ELPS standard(s) here 8.28 (A) compare the effects of scientific discoveries and technological innovations that have influenced daily life in different periods in U.S. history 8.23 (B) explain the relationship between urbanization and conflicts resulting from differences in religion, social class, and political beliefs Reporting Category: Economics, Science and Technology, Society Reporting Category: Geography and Culture CCRS: If applicable, insert relevant CCRS statement(s) here K.13 (a) Home: cell phone, computer, microwave, etc. School: computer, calculator, pencil, paper, book, etc. Student brainstorm list examples: electricity, light bulb, air conditioning, washing machine, dishwasher, vacuum cleaner, car, telephone, computer, microwave, etc. K.13(b) Home: computers allow us to access information and connect with other people from home, school, and around the world. School: computers allow us to access information and connect with other people from home, school, and around the world. Science/technology allows for an easier life style. Including light bulb allows work at night. Air conditioning keeps comfortable and allows work indoors in summer. Microwaves cook food quickly RESOURCES Suggested Book: - Mike Mulligan and the Steam Shovel (Virginia Lee Burton) K.14(a) Examples include: Television vs. no television 21 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT Computer vs. no computer Car vs. no car Video games vs. no video games Cell phone vs. no cell phone Running water vs. no running water Other specifics will come from student and adult input NOTE: This TEKS would integrate well with K.3A and K.13A. Classroom guests of various ages could tell about how their lives were different without modern technology. NOTE: You could ask adults of different ages to come into the classroom and talk about “I remember when…” and explain how they used to dial a phone, turn on a television, use a typewriter, warm up leftover food, etc RESOURCES www.unitedstreaming.com - “Long ago, Yesterday, Today” (15:00min) K.14(b) Transportation: such as with/without cars. trucks, buses, trains and airplanes, Jobs: such as with/without computers, electricity, air conditioning/heating, cell phones, and tools. Daily life: such as with/without cell phones washing machines, refrigerators, television, video games, toilets, running water. Specifics will come from student and adult input RESOURCES www.unitedstreaming.com - “Away we go, All about Transportation” (22:30min K.12(c) Customs of Local Community/School End of the year events such as: •Kindergarten Graduation/Awards •Field Day •Memory Books •Yearbooks •End of year writing to go in portfolio (pass along folder) reflecting kindergarten year RESOURCES Fourth of July – Independence Day – the day we became a country so this is the birthday of the United States of America http://www.cantonpl.org/kids/julyfour ELPS: Insert logical/related ELPS standard(s) here 1C; 1E; 2C; 2E; 3D; 4G; 5B If applicable and necessary, insert Student Expectations that are not assessed on STAAR but that are part of the required curriculum for the grade/course. CCRS: If applicable, insert relevant CCRS statement(s) here Clarification: List statement(s) here that clarify what should be taught to fully teach the Student Expectation listed above. 22 WESLACO INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT ELPS: Insert logical/related ELPS standard(s) here 23