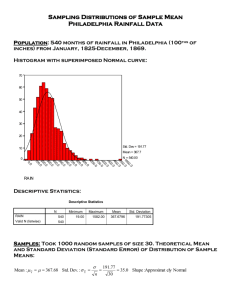
Document
advertisement

GROUP ASSIGNMENT REPORT Group One Chen Yongtao Wang Gaonan 2010.6.6 Kuang Yun Zhu Zhenxuan Cheng Yuchen AGENDA 1. Abstract 2. Structure of the Catapult 3. The Fish-bone Diagram 4. Design of the Experiment 5. Analysis of the Experimental Data 6. Optimization 7. Test of the Results and Conclusion 8. Weakness and Possible Improvement 9. References ABSTRACT Topic: Goal: Experimental Result: • A study on the factors that influence the ejection range of the catapult • Elucidate the influence of the factors and try to find the best combination of the parameters which make the ejection range closest to 2.7 m • We found 3 combinations of the parameters and chose the best combination with std.=6.4 STRUCTURE OF THE CATAPULT A是橡皮筋支点的位置,有4个level B是挡板的位置,有6个level C是投石杆发射的位置,是个连续变量 The fish-bone diagram DESIGN OF THE EXPERIMENT (1) • Detail of variables: 控制变量 (单位) control variable (units) 正常水平与 可操作范围 normal level & range 橡皮筋支点 水平4个位 置 挡杆的位置 依次6个位 置 投 石 杆 发 射 的 120— 180° 位置(角度) 测量精度 与方法 meas. precision & setting error How known? 标号记录 标号记录 刻度记录 精度:0.1° 推荐试验设置 proposed settings, based on predicted effects 对响应变量的 预期效果 predicted effects (for various responses) 1号位置,此时弹力最大 支点越高,飞得 越远 投石杆与挡杆水平位置越 挡 杆 位 置 越 靠 接近越好,但投石杆不得 前,球飞得越远 超过挡杆 投石杆与挡杆水平位置越 投石杆发射位置 接近越好,但投石杆不得 越接近水平位置, 超过挡杆 发射距离越远 DESIGN OF THE EXPERIMENT (2) • Detail of fixed variables: 期望试验设置值 固定变量(单位) 及允许变动范围 factor desired (units) experimental level & allowable range 水平放置角度 (°) ±2° 弹球/车身抛射 角(俯视)° ±2° 测量精度与方 法 measurement precision How known? 变量控制方法 how to control (in experiment) 水平仪(手机 自带) 使用胶带固定 直尺圆规 固 定 张 力 橡 皮 使用一根 无 筋(N/cm) 弹球质量(g) 弹球质量差别小 电子秤 于平均质量的5% 用力方向控制 预期效果 anticipated effects 实验过程中车 身一直保持水平 弹球飞出方向 平行于车身的朝 向 不要将橡皮筋 一直使用一根 弄裂或弄断 橡皮筋 剔除质量过重或 弹球质量基本均 者过轻的弹球 等 DESIGN OF THE EXPERIMENT (3) • Parameters. 干扰参数(单位) nuisance factor (units) 试验地风速(m/s) 测距卷尺位移(cm) 测量精度及方法 measurement precision How known? 风速计/人体感觉 另一个卷尺测量 试验应对策略 strategy (e.g., randomization, blocking, etc.) 预期效果 anticipated effects 尽 量 在 室 内 、空 避免风速对弹球的飞 气流速慢的地段进 行距离造成影响 行试验 固 定 卷 尺 起 点于 避免试验过程中卷尺 地面 的位移 DESIGN OF THE EXPERIMENT (4) • Take two levels of A, B and C, we denote: • A: The hole at the highest level is -1, and the lowest be +1. • B: The second hole is -1, and the fifth one is +1. • C: Make 150° as − 1,and 180° as +1. • Then we conduct a 23 full factorial design. • There are 8 combinations of parameters, each of which we do 5 replications, and totally we get 40 groups of data. ANALYSIS OF THE EXPERIMENTAL DATA (1) • Here are the data: Our response values are Mean and std. So totally we have 8 data. ANALYSIS OF THE EXPERIMENTAL DATA (2) • Main effects chart and interaction chart of Mean distance: Mean 主效应图 Mean 交互作用图 数据平均值 数据平均值 A B -1 1 -1 1 400 500 300 300 A 平均值 200 100 500 -1 1 C -1 1 300 B 400 100 300 200 C -1 1 A -1 1 B -1 1 ANALYSIS OF THE EXPERIMENTAL DATA (3) • Main effects chart and interaction chart of std.: Standard deviation 主效应图 Standard deviation 交互作用图 数据平均值 数据平均值 A -1 B 1 -1 1 12.5 15 10.0 10 A 7.5 平均值 A -1 1 5 15 5.0 -1 1 C 12.5 -1 1 10 B 5 10.0 7.5 C 5.0 -1 1 B -1 1 ANALYSIS OF THE EXPERIMENTAL DATA (2) • For mean distance: 标准化效应的正态图 (响应为 Mean,Alpha = .05) 99 效应类型 不显著 显著 95 90 C 80 百分比 70 60 50 40 30 20 A 10 5 1 -5.0 -2.5 0.0 2.5 标准化效应 5.0 We can obtain the following model: 7.5 10.0 因子 A B C 名称 A B C ANALYSIS OF THE EXPERIMENTAL DATA (3) • For standard deviation: 标准化效应的正态图 (响应为 Standard deviation,Alpha = .05) 99 效应类型 不显著 显著 95 90 因子 A B C C 80 百分比 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 5 1 -3 -2 The model of std.: -1 0 1 标准化效应 2 3 4 名称 A B C OPTIMIZATION(1) • As our goal is set the range closest to 2.7m and get the smallest std., we define our strategy as “setting one parameter to make the std. as small as possible, then adjust the other two parameters to get mean of 2.7m”. • Solution 1: • According to the main effect chart, we should set C to be -1, that is x3=150°. Standard deviation 主效应图 数据平均值 A B 12.5 10.0 平均值 7.5 5.0 -1 1 C 12.5 10.0 7.5 5.0 -1 1 -1 1 OPTIMIZATION(2) Mean 与 B, A 的等值线图 1.0 100 120 140 160 180 B 0.5 0.0 保持值 C -1 -0.5 -1.0 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 A 0.5 1.0 Mean < – – – – – > 100 120 140 160 180 200 200 We can see that the range never reaches 2.7m when C take the smallest value, so we should adjust A and B and try to find a combination. Set mean with 270, then To make x3 small, we can set x1=-1 and x2=1. Solution 1 is A=1,B=5,C=158°. OPTIMIZATION(3) • Solution 2: • We set A with the largest value, then follow the previous steps. Standard deviation 与 C, B 的等值线图 1.0 Standard deviation < 2 2 – 4 4 – 6 6 – 8 8 – 10 10 – 12 > 12 C 0.5 0.0 保持值 A 1 -0.5 -1.0 -1.0000 -0.3333 0.3333 B • Solution 2 is A=4,B=3,C=176.4°. 1.0000 OPTIMIZATION(4) • Solution 3: We set B with the smallest value, then follow the previous steps: Standard deviation 与 C, A 的等值线图 1.0 Standard deviation < 4 4 – 6 6 – 8 8 – 10 > 10 C 0.5 保持值 B -1 0.0 -0.5 -1.0 -1.0000 -0.3333 0.3333 A Solution 3 is A=3,B=2,C=171°. 1.0000 TEST OF THE RESULTS AND CONCLUSION(1) • Test of solution 1 • Using the model, we can obtain: • Mean distance=288.6cm, std.=12.74cm • Then we got 12 distances under this experimental condition, and here is the histogram of these data: R e s u l t 1 直方图(包含正态曲线) 均值 266.2 标准差 9.600 N 12 4 频率 3 2 1 0 250 260 270 Result1 280 TEST OF THE RESULTS AND CONCLUSION(2) • Test of solution 2 • Using the model, we can obtain: • Mean distance=270.9cm, std.=7.98cm • Then we got 10 distances under this experimental condition, and here is the histogram of these data: result2 直方图(包含正态曲线) 均值 266.2 标准差 6.529 N 10 3.0 2.5 频率 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 255 260 265 270 result2 275 280 TEST OF THE RESULTS AND CONCLUSION(3) • Test of solution 3 • Using the model, we can obtain: • Mean distance=275.7cm, std.=7.29cm • Then we got 10 distances under this experimental condition, and here is the histogram of these data: result3 直方图(包含正态曲线) 均值 262.4 标准差 7.382 N 10 3.0 2.5 频率 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 245 250 255 260 265 result3 270 275 280 TEST OF THE RESULTS AND CONCLUSION(4) • Conclusion • After compared the performance of the above three solutions, we can see the best solution is solution 2——A=4, B=3, C=176.4° WEAKNESS AND POSSIBLE IMPROVEMENTS • We didn’t consider the second-order relationship in the model. • In our analysis, we treat the mean and std. of a five-value group as the response variables, so we only have 8 response values, and we have no replications. As a result, the model we obtained has relatively large error. References • Design and Analysis of Experiments(Sixth Edition), Douglas C.Montgomery, 2005 THANK YOU! Q&A