Investment Risk Return How It Works
advertisement
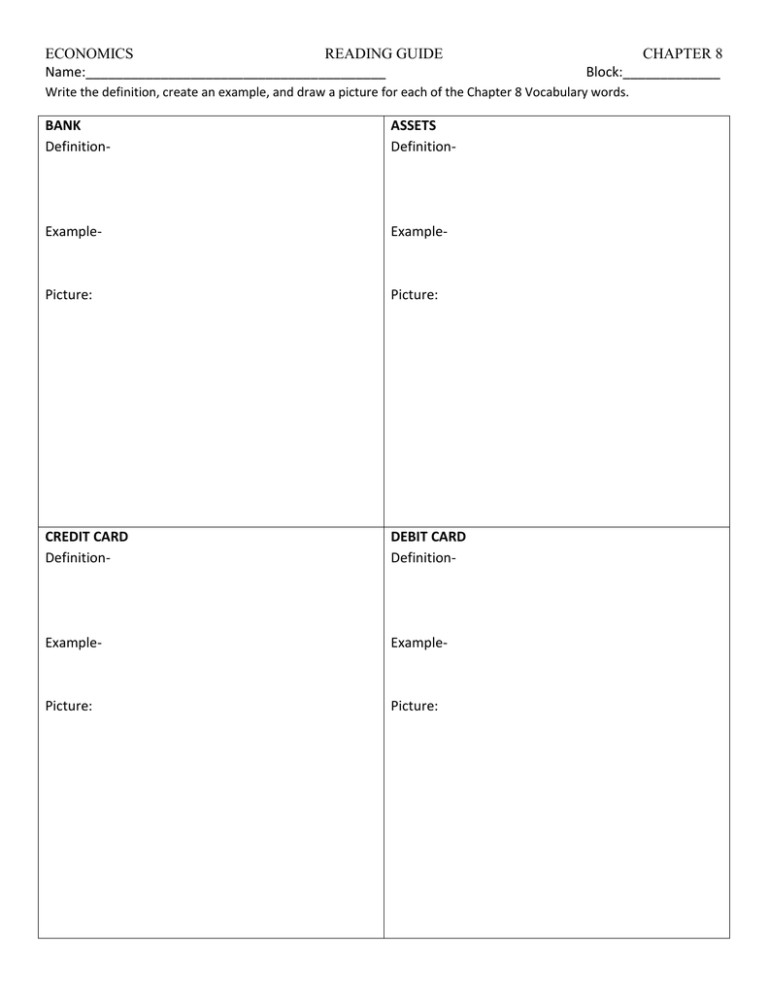
ECONOMICS READING GUIDE Name:________________________________________ CHAPTER 8 Block:_____________ Write the definition, create an example, and draw a picture for each of the Chapter 8 Vocabulary words. BANK Definition- ASSETS Definition- Example- Example- Picture: Picture: CREDIT CARD Definition- DEBIT CARD Definition- Example- Example- Picture: Picture: ECONOMICS SAVING Definition- READING GUIDE INTEREST Definition- Example- Example- Picture: Picture: PRINCIPAL Definition- DIVERSIFICATION Definition- Example- Example- Picture: Picture: CHAPTER 8 ECONOMICS READING GUIDE CHAPTER 8 NAME:________________________________________________ As you read Chapter 8, answer the following questions. 1. Suppose a generous relative gave you a gift of $1,000 for your high school graduation. In a short paragraph, outline what you would do with the money and the reasoning behind your decision. 2. Complete the following diagram, adding appropriate bubbles of information to each of the four categories that surround the center. Characteristics of Money Functions of Money What makes money…money? Historical types of money (include examples of each) Money today: What counts and what doesn’t? 3. What is the main function of banks? How do banks execute that function? ECONOMICS READING GUIDE CHAPTER 8 4. Rank the three types of deposits that savers make at banks from “most liquid” to “least liquid.” Also rank them from the “highest return” to “lowest return.” 5. If you wanted to save money at your bank for a purchase you plan to make one year from now, which type of deposit would you make? Why? 6. Complete this simile: The Fed is to the nation’s banks as a ________________ is to a _____________. Give two reasons why your simile makes sense. 7. List three reasons why you should save money. 8. Calculate your personal saving rate (or that of a family member if you have no income) by using the formulas below. Is your personal savings rate closer to 1% or 10%? Why do you save so much or so little? Monthly income – monthly expenses = monthly savings Monthly savings ÷ monthly income = personal savings rate (percentage) 9. Create a simple diagram to represent the three sources of money that most people use to fund retirement. Annotate your diagram by recording at least two details about each type of retirement plan. ECONOMICS READING GUIDE 10. When creating a budget, what can you do to make sure you are a successful saver? CHAPTER 8 11. In your own words, explain how compounding works. According to the rule of 72, if you deposit $100 in an account that pays 9% compound interest, how long will it take that initial deposit to reach $200? 12. Using the matrix of various investments below, record the following information: Is the risk high, moderate, or low? Is the return high, moderate, or low? How does this type of investment work? Explain in one or two sentences. Investment Government Bonds Corporate Bonds Stocks Mutual Funds Risk Return How It Works ECONOMICS READING GUIDE 13. What are the 6 main characteristics of money? List AND define the six characteristics. CHAPTER 8 14. Design a trifold financial advising brochure that you, as a financial advisor, might distribute to prospective clients. Fold a sheet of paper in thirds just as you would fold a letter to fit into an envelope. Then create a brochure that includes: A front cover with an appropriate title, picture, and your name. An explanation of why spending, saving, and investing are important. At least three tips on spending. At least two tips on saving and a brief explanation of available savings options. Any other creative touches or information that might be of value to your clients. ECONOMICS READING GUIDE CHAPTER 8 NAME:________________________________________________ As you read Chapter 8, answer the following questions. 1. What are the 3 basic functions of money? List AND define the three functions. Medium of Exchange- eliminates coincidence of wants Standard of Value- one scale to measure things against each other Store of Value- holds its value(purchasing power) over time. (ex. won't spoil) 2. What are the 6 main characteristics of money? List AND define the six characteristics. Acceptability- willing to take as a payment Scarcity- limited amount makes it valued Portability- must be easily carried Durability- withstand physical wear and tear Divisibility- easily divided (make change) Uniformity- needs to be exactly same...size, etc. 3. What is the difference between "commodity money" & "fiat money”? Which one do we use? Commodity money is backed by gold or silver (or another commodity). Fiat money is backed only by government decree. Our system is a fiat system. 4. What are M1 and M2? What is included in each? M1- liquid assests that can be easily converted to cash. (currency, checking accounts, travelers checks) M2- M1 + near money (savings accounts, larger deposits in CD's etc.) 5. Why do banks make loans? How do banks make a profit? Banks use deposits to create loans, which they then gain interest on. The difference between the interest paid to depositors and paid on loans is the bank's profit. 6. What does the FED do? Serves as the "Banker's Bank" and lender of last resort. The nation's central bank holds reserves from commercial banks and manages the banking system.