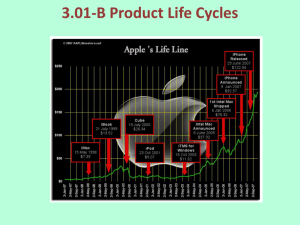
What Is a Product?
advertisement

Unit 3: The Marketing Mix Chapter 10 What Is a Product? Learning Goals Explain why product is the primary P of the marketing mix Explain the four characteristics of services that distinguish them from goods Describe the good-service continuum Describe and give an example of each of the four product element categories Summarize the purpose of product strategies Describe and draw the stages in the product life cycle Activity – Fad or Fizzle? Each of the products below - whether a good, service, or idea - was conceived as the next "big thing," but only some succeeded. Can you tell the successful fad from the fizzles? Beanie Babies McPizza Homeless American Girl doll Kardashian Kard Furby What Is a Product? The _______________ is Product the primary P in the marketing mix It is the first element of the marketing mix to be decided If you do not have a product to sell, you do not need a place, price or promotion What Is a Product? What does a customer actually buy when he or she buys a product? When you buy an automobile, are you buying just metal, cloth, plastic, and glass formed into a machine? No You are actually buying transportation, the ability to safely and easily get from one place to another You may also be buying independence and prestige What Is a Product? When you buy a ticket to a concert, are you just buying a place to sit for two hours? No You are actually buying the enjoyment of the show, the ability to tell your friends about it, and a break from the stress of your daily life What Is a Product? In Chapter 1, we learned that a product is anything that can be bought or sold A product can be … A good A service An idea Types of Products Products are usually grouped into one of two categories; 1. Consumer products Product sold to customers for personal use 2. Business products Products sold to businesses for business use Types of Products Products can also be described as ______________ or _______________ Tangible Intangible A tangible product is something that exists physically and can be touched Goods are tangible E.g. a cellphone An Intangible product is something that exists, but is not physical and cannot be touched Services and ideas are intangible E.g. a haircut or the idea to “buckle up for safety” The Service Economy Throughout the nineteenth and much of the twentieth centuries, Canada was an industrial economy The main products of an industrial economy are ___________________ Tangible Goods At this time, the majority of people in the country held jobs in manufacturing, mining, or agriculture creating tangible goods Toward the end of the twentieth century, the basis of the Canadian economy shifted from industry to knowledge The main products of a knowledge-based economy are Services _____________ The Service Economy A ______________________ is an economy Service Economy in which most of the GDP (Gross Domestic Product) comes from services and most of the workers have jobs in the services industry Today, services account for about 78 percent of GDP in the Canada Therefore, Canada is considered to be have a Service Economy Characteristics of Services Services are different from goods in four ways Services are; 1. Intangible 2. Inseparable 3. Variable 4. Perishable These characteristics of services can present special problems for marketers 1. Intangible Services are intangible, meaning they cannot be touched or tried out before purchase For example, when you shop for a car, you can kick the tires, choose a colour, and go for a test drive. However, when you buy a concert ticket, you cannot try the concert out beforehand Services are tough to represent in marketing as it can be difficult to show a picture of the service itself Examples of intangible products are; A concert Cellphone service Insurance 2. Inseparable Services are inseparable, meaning the production of the service cannot be separated from the ______ Use of the service Services also cannot be separated from the ______________ of the service Producer In other words, the service cannot be separated from the person who performs the service For example, suppose you go for a haircut. The haircut does not exist until the hairdresser cuts your hair. In addition, the haircut does not exist without the hairdresser 3. Variable Services are variable, meaning that they are _______ Unique A service only exists once and is never exactly repeated in the same way again Because services are inseparable, the customer often thinks of the service and the service provider as one in the same For example, the product of the hair salon is not just the haircut. The product is also the stylist who cuts the hair Have you ever gone to a new salon, had a bad haircut, and refused to return? Was it the salon that gave you a bad haircut or the stylist? A friend may have received an excellent cut from another stylist at the same salon 3. Variable This variability can lead to _______________ Quality Control issues It is very hard to make sure that each service provider gives the same quality service E.g. different hairdressers may give different quality haircuts For this reason, there are certification programs for doctors and other professional service providers However, even with certification, another problem that occurs is when a service provider leaves a business, customers often follow the service provider E.g. When a popular hairdresser leaves a salon, many customers will follow the hairdresser and leave the salon 4. Perishable Services are perishable, meaning services cannot be __________ Stored for later use Some goods are perishable, such as milk and seafood, however most can be stored until needed, such as jeans which can be stored in a warehouse until needed by retail stores For example, unsold concert tickets cannot be stored and sold at a later time, because once the concert is over, the tickets are worthless Overcoming Service Obstacles Service providers need to be creative in developing strategies to overcome these obstacles See example below The Good-Service Continuum Many products are combinations of good and service E.g. a restaurant meal is a combination of a good and a service The food itself is a good The preparation and serving of the food is a service Products can be visualized as being on a good-service ______________ Continuum On the left end, the products are purely tangible goods, for example, soap On the right end, the products are purely services, for example, tutoring In between are the products with varying combinations of goods and services The Good-Service Continuum Pure Goods Soap Books Pure Services Restaurant Meal Cellphone Legend Amount of goods Amount of services Tutoring Concert Day 1 Assigned Work Students please complete the following; K & U Questions #1 & 5 on page 153 Thinking Questions #1 & 2 on pages 153 & 154 Product Characteristics Worksheet Hardcopy provided ***Save As Ch 10 Day 1 in your Unit 3 folder*** Day 2 Response Journal What is the purpose of packaging? List all the functions packaging performs. ***Save As Nov 27 in your Response Journal Folder*** Product Elements Products have many elements that can be changed to meet customer’s needs The elements of a product can be grouped into four categories 1. Basic product 2. Usage 3. Protection 4. Name 1. Basic Product Once you know what product you will sell, you can then begin to make basic product decisions about … A. Quality B. Features C. Options A. Quality During product development, the company must decide on the quality of the product While keeping the target market in mind ____________ is the level of excellence in something Quality Customers have different ideas of what good quality is A product that meets the quality needs of one target market might not meet the quality needs of a different target market For example, a chocolate bar from a vending machine might be the right quality level for a quick snack. It might not be the right quality level for a Valentine's Day gift for your boyfriend or girlfriend A. Quality The level of quality will affect the cost to produce the product and therefore its price There are 3 general quality levels; i. Premium quality Highest quality materials and therefore highest price ii. Moderate quality Good quality materials and therefore moderate price iii. Value quality Usually an adequate level of quality Combines the lowest price with the best possible quality at that price B. Features Both goods and service have features For a good … A physical characteristic • For example, the physical features of a cellphone include its size and colour For a service … One of the tasks that will be done as part of the service • For example, the service features of a cellphone include voice mail and call waiting C. Options An __________ Option is a feature that can be added to a product at the customer’s request For example, options on an automobile might include a sunroof, leather seats, and a high-end stereo system Options enable the customer to customize the product to his or her specific needs and wants 2. Usage Many products are designed to be assembled, installed, or used in some way Part of the product decision is how to help the customer make the best use of the product If customers do not know how to properly use a product, they are likely to get frustrated and become dissatisfied They may then return the product or just never buy from you again 2. Usage Aspects of usage include; A. Instructions Clear instructions are an essential part of many products Some companies provide videos, classes, or seminars to help customers use their products B. Installation Installation is the process of placing a good where it will be used and making the good ready for use C. Technical support Complex products have a tendency to develop problems from time to time Many companies that sell complex products offer technical support Technical support consists of people who are available to help customers with problems 3. Protection Protection consists of product elements that protect the product from harm, both before and after purchase Protection includes; A. Grades and standards B. Packaging C. Warranties and guarantees D. Maintenance and repair services A. Grades and Standards Measurable Grades and standards are _______________ attributes that describe the value and utility of a product For example, when buying certain food products, such as butter or eggs, consumers may look for the "Canada Grade A" symbol on the packaging Likewise, Transport Canada has mandatory safety standards that automobile manufacturers must meet As a point of customer assurance, marketers will promote these attributes because they often impact customer-buying decisions B. Packaging Packaging serves many functions; Protect a product from damage Appropriate packaging is necessary to keep foods fresh and healthful Also, many fragile products such as computers and lamps are carefully packaged to prevent damage Promotion The “face” of the product Often is the first thing that attracts a customer Part of the product’s identity B. Packaging Make products easier to stack or display in stores Protect the customer For example, using plastic bottles instead of glass for beverages and child safety caps for medicines Discourage theft Provides product information Content labelling, nutritional information, weight, etc. May provide product instructions B. Packaging - Canadian Labelling Requirements In Canada packaging and labelling must follow specific requirements as set by the government The purpose of these regulations is to protect consumers and help them make the best choices when shopping B. Packaging - Canadian Labelling Requirements Some of these requirements are; False or misleading packaging is against the law Most packaged foods require an ingredient list Labelling must appear in English and French Product must be clearly identified Quantity of product must be expressed In units of volume, weight or quantity E.g. 1L, 200 g, 25 pieces Product must include the manufacturer and dealer’s name and address B. Packaging - Canadian Labelling Requirements C. Warranties and Guarantees To convince customers of the quality and reliability of their products, marketers often provide a … Warranty A written document which states the quality of a product and promises to correct certain problems, should they occur E.g. most new automobiles have a warranty Guarantee A promise that the product has a certain quality or will provide satisfaction Usually used in promotions E.g. some pizza delivery services guarantee pizza in half an hour or it is free D. Maintenance and Repair Services Complex machines often require regular maintenance E.g. cars May also need periodic repairs Maintenance and repair services should be planned when the product is developed The availability of these services may affect the customer’s buying decision E.g. when you purchase a car, you have a choice of dealers. Some consumers might choose to buy from the dealer with the most convenient service department 4. Name The name includes; Product name Brand name Product’s “personality” Choosing the right name for a product is a critical part of the marketing mix You will learn more about names and branding in chapter 11 Product Elements Overview Product Elements Basic Product • Quality • Features • Options Usage • Instructions • Installation • Technical support Protection • Grades and standards • Packaging • Warranties and guarantees • Maintenance and repair services Name • Product Name • Brand Name • Personality Day 2 Assigned Work Students please complete the following; K & U Questions #7 & 8 on page 153 Product Elements Worksheet Hardcopy provided ***Save As Ch 10 Day 2 in your Unit 3 folder*** Day 3 Response Journal Like humans, products go through a life cycle of their own. As a marketer, how might I be able to tell if a product is reaching the end of its “life”? ***Save As Dec 1 in your Response Journal Folder*** Product Strategy A __________________ Product Strategy consists of all of the decisions made about a product It starts with the decision about which product to offer • It then proceeds to decisions about product elements, keeping the target market in mind A product strategy can help distinguish your product from the competitors Must balance meeting customers’ needs and beating competition with the costs of production and marketing Product Life Cycle Products go through a life cycle similar to the human life cycle As humans, we are born, grow, reach maturity, then age and eventually die Product Life Cycle A _____________________ consists of the stages that a product or a product category goes through from beginning to end The product life cycle has four stages; 1. 2. 3. 4. Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Product Life Cycle The stage in the life cycle of a product is based on _______ Sales of that product, including all brands and generics All sales of a product are often referred to as _________________ Industry Sales For example, to determine the life cycle of cellphones, you would gather industry sales information for cellphones from the time they were introduced to the present Product Life Cycle The product life cycle is often shown on a graph The graph plots _______ Sales on the y-axis and ______ Time on the x-axis Sales are expressed in dollars Time is expressed in months or years Product Life Cycle The curve on the graph shows the rise and fall of industry sales for a product (in dollars) over time The stages of the product’s life cycle are based on the shape of the curve, which represents changes in the number of sales __________ can be made at each stage of a Profit product’s life cycle, but the marketer has to know how to market the product at each stage Profits over the Product Life Cycle Industry profits change over the life cycle of a product. Notice that during the introductory stage, no profit is being made. Product Life Cycle The length of each stage varies, depending on the product E.g. Ivory Soap was first sold in 1879, and it is still a strong seller, therefore Ivory Soap has a long life cycle E.g. the Pet Rock sold only during the gift-giving season of 1975, therefore the Pet Rock had a very short product life cycle A product with a very short life cycle is called a ______ Fad Product Life Cycle In the same time period, different products are in different stages of their life cycles For example, electric automobiles are in the introduction stage, cellular phones are in the growth stage, in-line skates are in the maturity stage and CD players are in the decline stage 1. Introduction _______________ Introduction is the stage during which a new product is presented to the market Typically, profit is not being made at this stage because money spent on product development has not yet been earned back Goals of marketing at this stage include; Get publicity Explain product benefits Persuade customers to buy 1. Introduction A good example is in-line skates Before 1984, few people knew about in-line skates Then the Rollerblade Company began marketing in-line skating as a new and cool sport To gain customer notice and get customers to try the new skates, free Rollerblade in-line skates were given to the rental shops along trendy Venice Beach in California What products do you believe are in the introduction stage today? 2. Growth It takes a while for a new product to "catch on“ Some products catch on quickly, others take more time, and some products never get off the ground The __________ Growth stage of a product occurs when sales and profits rise rapidly Goals of marketing at this stage include; Distinguish their brand from the competition Build brand loyalty 2. Growth As the product becomes more successful, competitors enter the market, and now there are many companies competing for customers At this stage, marketers may add new features and benefits to make their product stand out from the rest In the life cycle of a product category, one producer usually takes the lead in introducing, marketing, and selling the new product For the in-line skate category, that leader was Rollerblade. Once Rollerblade made in-line skates popular, competitors started entering the market, and now there are several competitors What products do you believe are in the growth stage today? 3. Maturity A product or product category reaches the ___________ Maturity stage when sales start to level off Goals of marketing at this stage include; Continue to distinguish their brand from others and build brand loyalty Improve the product Find new ways to keep the product fresh and exciting Find new markets for your product 3. Maturity An example of a product that found a new way to keep it fresh and exciting is … Old El Paso Tacos An example of a product that found new markets to enter is … Arm & Hammer Baking Soda 3. Maturity Why do sales stop rising at the maturity stage? Because the market is ______________ Saturated A saturated market is one in which everyone who needs, wants, and can afford the product has already bought it No more people will buy in a saturated market unless their current product wears out, or new customers are born and enter the market In the in-line skate category, once all the people who want to skate have bought their first skates, they do not need new ones for quite a while What products do you believe are in the maturity stage today? 4. Decline A product or product category reaches the ___________ Decline stage when sales begin to fall Decline often occurs when a new technology begins to grow E.g. the product category of music CDs started declining when the MP3 player technology started growing Goals of marketing at this stage include; Develop new marketing strategies to boost sales OR Discontinue the product to prevent financial losses 4. Decline Deciding whether a product is at the end of its life cycle can be particularly tricky Why do products decline? New technology makes the product obsolete Fashions change Trends change Non-product related factor A decline in sales may not indicate that the product is in the declining stage of its life cycle E.g. if there is a recession in the economy, car sales go down. However, that does not mean that cars are at the end of their life cycle Crocs Article 4. Decline When a product category starts declining, marketers have to decide what to do about it They can … Develop marketing strategies to boost sales OR They can discontinue the product Some marketers specialize in selling products in the decline stage. They … Buy large quantities at very low prices Sell them at low prices, but still make a profit • E.g. XS Cargo, KW Surplus, K & K Liquidation, etc. 4. Decline Knowing the life cycle stage of the product and product category helps marketers develop effective marketing strategies Often, different markets are targeted at different stages of the life cycle Different marketing mixes work better at different stages of a product or product category's life cycle For example, High During introduction prices are often ________ Lower During maturity, the price is _________ During decline, the price is often ___________ Lowest Day 3 Assigned Work Students please complete the following; K & U Questions #14, 15, 16 & 17 on page 153 Application Questions #3 & 5 on page 154 ***Save As Ch 10 Day 3 in your Unit 3 folder***