Chapter 26.3 Lecture Station
advertisement

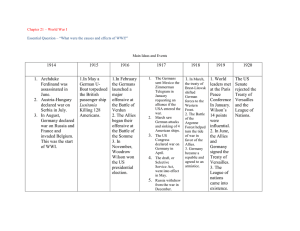
Exploring American History Unit VIII- Boom Times and Challenges Chapter 26 – Section 3 The War in Europe and Northern Africa WWII- A World Conflict Allied Goals1st- Defeat the Germans 2nd- U.S. to postpone the offensive in the Pacific and continue an active defense. War in Europe and North Africa The Big Idea After fierce fighting in North Africa and Europe, the Allies stopped the German advance and slowly began driving back German forces. Main Ideas • The Allies fought back against the Axis Powers in North Africa and Europe. • Key Allied victories halted the German advance. • In the D-Day invasion, Allied forces attacked Germancontrolled France. Main Idea 1: The Allies fought back against the Axis Powers in North Africa and Europe. Allies Join Forces • Casablanca • Priority: New Technologies • Sonar • Long-range aircraft Casablanca Conference- Jan. 1943 Jan. 14-24, 1943, World War II meeting of U.S. President Franklin Delano Roosevelt and British Prime Minister Winston Churchill at Casablanca, French Morocco. A joint declaration pledged that the war would end only with the unconditional surrender of the Axis states, and the U.S. to attack Germany 1st. The Allies Fight the Battle of the Atlantic Allied ships and aircraft •American shipyards. •Convoys. Cracking the Enigma •Enigma •Ultra How and why did the Allies fight the Battle of the Atlantic? control of the seas- safe for shipping Germany had a very powerful navy wolf pack. The entry of the United States into the war would help turn the tide in the Battle of the Atlantic. Battle for the Atlantic • German Wolf Packs- sinking thousands of tons of Allied shipping each month. • 1942-43 critical, allies need food and supplies. • Radar and Sonar were invented • Use of Ultra (code breaking), Convoys and Destroyers • U.S. Producing more ships and supplies than the Germans could sink. The Allies Fight Back • Recall – How did sonar help the Allied war effort? • Explain – Why did Stalin want the Allies to attack in Europe immediately? Main Idea 2: Key Allied victories halted the German advance. North Africa •1942– German Afrika Korps •Battle of El Alamein. •Dwight D. Eisenhower Operation Torch Italy •July 1943– Allied forces invaded Sicily •June 1944– Allied forces captured Rome. North African Theater Erwin Rommel- German 1942- Tanks and Blitzkrieg Send to Africa to help the Italians stop the British and take British Oil Fields “Desert Fox”- Outwitting opponentsGreatest German General Also planned the defense of the Atlantic Wall. Later accused of being Anti-Hitler conspirator- forced to take poison. Afrika Korps- Rommel Battle of Tobruk and El Alamein Threaten Oil Fields of Middle East and the Suez Canal North African Theater Bernard Montgomery- British El Alamein- Nov. 4, 1942 Allies defeat the Germans Germans bottled up in Tunisia. U.S. Landing in “Vichy” Algeria“Operation Torch,” November 8, 1942 entailed the largest amphibious invasion in U.S. naval history. 107,000 men. Operation Barbarosa. • • • • June 22, 1941 – Hitler makes the great blunder- he feels that all battlefields are alike and blitzkrieg always works. He invades Russia Napoleon had learned a hard lesson a hundred years before- Russia is too big, too frozen and would cause the downfall of his empire. Hitler would learn the same lesson. Germans moved quickly and went deep into Russia, but when they got to Moscow the worst winter in 30 years struck. Freezing temps stopped the german advance. Germans are stalemated at Leningrad, Stalingrad and Moscow Eastern Front • Massive German and Soviet armies battled on eastern front. • By mid-1942, Battle of Stalingrad. • In January 1943 the German commander surrendered. • Soviet victory came at an enormous cost. – More than 1 million Soviet soldiers dead – About 800,000 Axis soldiers killed Halting the German Advance • Identify – What countries did each of the three generals involved in the North African Campaign come from? • Explain – What caused the different views of Italy’s strength in 1943 and 1944? Halting the German Advance • Describe – In the Battle of Stalingrad, how did many Germans die? • Explain – What is meant by “The tide of the war in the east had turned”? • Contrast – What advantages did Soviet Troops have over the advancing German soldier. Main Idea 3: In the D-Day invasion, Allied forces attacked German-controlled France. Invasion of German-occupied France • Dwight Eisenhower • June 6, 1944– D-Day, or “designated day” – American, British, and Canadian troops – Americans landed on two beaches, codenamed Utah and Omaha. – Almost 3,000 killed or wounded at Omaha Beach alone. Amphibious Tanks (DD Tanks) These so-called Duplex Drive tanks of the 741st Armoured Battalion were launched from landing craft four kilometres from the beach. Fitted with large canvas skirts round the upper portion of the vehicle, the DD tanks were designed to float low in the water appearing to the enemy as nothing more menacing than a rubber boat. The entry of this first group into the rough seas proved disastrous. The tanks were intended to operate in seas with a one-foot swell, yet on D-Day the waves rose six feet. High waves The heavy seas swamped 27 DDs, sending them to the sea floor. The D-Day Invasion • Explain – What was the Allied mission? • Rank – Which area would prove to be the toughest fight: North Africa, France or Italy • Identify - What did the “D” in D-Day mean? The D-Day Invasion • Recall – Soldiers from which countries took part in the D-Day Invasion? • Compare – How did the D-Day invasion compare to past sea to land invasions. • Make Judgments - What is your opinion of the type of men who could wade ashore and fight on the Normandy beaches?