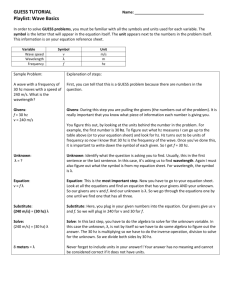
Unit 1: Science Safety
Welcome to Science
Mrs. Goins’s Room
Are you in the correct
class?
Listen carefully to role
Syllabus
Must Have Supplies
Pencils
Binder
12 Dividers
Tutorials
Late Work
Redo Work
Class Website
PowerPoint's
Assignments
Etc.
Newsletter
Remind 101
Basic Rules for Mrs. Goins
Class
QUIET Signal
No Food
Drinks in a closed containers, NO CANS
Tardies
Be Respectful
Teachers
Students
Inanimate Objects
Follow Directions
Board SEs
Clean Up after Yourself
Come to class prepared
Consequences
Contacting Home
Contacting Coaches
Write up
Grades
Grades are 50% daily grades and 50% test grades
You will have a minimum of 4 test grade each 6 weeks
which will normally consist of 1 project grade, 1 journal
grade, and 2 test grades
You will have a minimum of 10 daily grade each 6 weeks
Expected Assignments
Warm Up Logs completed daily
Test at the end of each Unit
Journal Grade
Extra
Talk to me
Storage
Supplies
My Website
Current Events for PreAP
The Rabbit
Contract
Must Turn in Signed Safety Contract and Signed
Syllabus before you can participate in labs
You will receive a 100 daily grade if turned in by
THURSDAY/FRIDAY
Seating Arrangements
You will sit in groups of 4
Groups will change every six weeks
Shoulder Partner vs. Face Partner
Think-Pair-Share
Think- On Your Own
Pair- Share Ideas or Information with you partner
Share- Share Ideas or Information with you group
First Assignment
Take a post it and write
1) Your Name
2) The state you were born
3) One fun fact about your self
4) The best part about your summer
vacation
Stand Up, Pair Up and
Share
This is an activity we will do throughout the year so remember the directions
Stand Up (with your notecard) and raise your hand
Walk around the room until you find a person with their hand up. Give them a high
five, put your hand down and wait for further instructions
Share the information on the card with your partner (listen close you will be tested)
The person who has the largest number of siblings talk first
You have 1 minute
Now say hello to your new shoulder partner
Go sit at the table group that corresponds with the number I handed you, take you
stuff and make sure you sit next to your partner
Now you will introduce your shoulder partner to the class
Enrichment
This is STUDY HALL
Your are expected to READ
I will not issue a seating chart unless I have too
You will not leave without an email from a teacher
If you can not find something I will find something for you
On Fridays you will have the opportunity to do homework
We will check grades during this time
THIS IS QUIET TIME
Warm Up
Science Safety
With your shoulder partner look around the room
and write (be prepared to share)
2 things that are SAFE
2 things that are NOT SAFE (or could potentially be
not safe)
Using Emergency Safety
Equipment
Fire Extinguisher
Remember the acronym PASS - PULL, AIM,
SQUEEZE, and SWEEP.
Step 1- PULL the pin on the handle. This
will allow the handle to work. Stand 8’ to 10’
from the fire.
Step 2- AIM the nozzle at the base of the fire.
Hit the fuel. It will not do any good to aim at
the flame tops because the chemical from
the extinguisher will pass right through
them.
Step 3- SQUEEZE the top lever or handle.
This will allow you to release the contents of
the extinguisher.
Step 4- SWEEP the nozzle from side to side
Using Emergency Safety
Equipment
http://www.youtube.com
/watch?v=ZCSms-jyOao
Are everyday substances and
chemicals dangerous?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JmjSUlKoMX
E
So what should you do if you are in that situation?
Using Emergency Safety
Equipment
Fire Blanket
Step 1- Remove fire blanket from its container.
Step 2- Shield your face, arms and hands with the
blanket by wrapping the outside of the blanket
around your arms.
Step 3- PLACE, do not throw, the fire blanket on the
burning material. No air should be getting to the
flames.
Step 4- If it is safe, turn off the heat source causing the
fire.
Step 5- Leave the blanket on the burning material at
least 30 minutes. Do not remove the blanket until it is
cool.
Note: If you are smothering a clothing fire you
should tightly wrap the blanket around the person
whose clothes are burning and roll that person on the
floor in the blanket.
Using Emergency Safety
Equipment
Face/Eyewash
Step 1- Guide injured student to the
eyewash station. Because the first few
seconds after exposure to a chemical
are critical, eyewash/face wash must
be within 10 or fewer seconds of
anywhere in the room.
Step 2- Use your hands to hold the
eyes open while using the eyewash to
be sure water reaches the eyes.
Step 3- Flush skin or eyes with tepid
water (60- 90 F) for at least 15 minutes.
DONOT RUB!
Step 4- Get medical assistance
immediately.
Science Safety
With your shoulder partner draw this thinking map
PARAPHASE how to operate the equipment in the blue
blanks
Fire Blanket
Eye Wash
Emergency Safety
Equipment
Fire Extinguisher
Science Safety
One the back create a T-chart
Emergency Safety Equipment Preventative Safety Equipment
1)
1)
2)
2)
3)
3)
Homework
On a piece of computer paper make a cartoon giving an
example of how to act safely in a science classroom and
how to act unsafely in a science classroom.
colors
-the cartoon must have a minimum of four
-there must be at least one sentence
describing the scenario on each box
-label the science safety equipment
-drawings must show effort
Warm Up Log
What is the difference between Emergency Safety
Equipment and Preventative Safety Equipment?
Emergency Safety Equipment is used in an
emergency and preventative safety equipment helps
prevent (or stop) the emergency from happening.
What does each Safety symbol
stand for?
1
2
3
4
What does each Safety symbol
stand for?
Flammable
Explosive
Corrosive
Images from http://www.cpsc.gov/CPSCPUB/PUBS/NIOSH2007107.pdf
Poison
What does each Safety symbol
stand for?
1
2
3
4
What does each Safety symbol
stand for?
Biohazard
Radioactivity
Oxidizing
Images from http://chemistry.about.com/od/healthsafety/ig/Laboratory-Safety-Signs/
Fire
Extinguisher
Science Safety Symbols
So why are safety symbols important?
As a table group you will create science safety symbol that correlates with
a scenario you will be given AND you will act out the scenario with your
group.
Requirements:
Each person must have a speaking part
Each group must act out the complete scenario in less than 60 seconds
Each group must create a safety symbol
Each group will vote if the skit is a safe lab scenario or and unsafe scenario
Jobs
A=Skit Director
B=Safety Symbol Developer
C=Cast Director
D=Time Manager and Group’s Ultimate Decision Maker
Exit Ticket
Write your name and the answer to this question on
the sticky note and hand it to me before you leave
the room.
Why is safety so important in science class?
Warm Up
List 2 important rules you must follow in science.
Science Safety Review
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xJG0ir9nDtc
Binder
Current Events
Benchmark!!!!!
Today’s
Topic:
MSDS
Sheets
LAB SAFETY AND
YOU
A STUDENT GUIDE
T. Givens / Mister Science 2013 / All Rights Reserved
WE COMMUNICATE
SAFETY IN MANY
WAYS…
CAN YOU GUESS
WHERE YOU MIGHT
SEE EACH
PICTURE?
T. Givens / Mister Science 2013 / All Rights Reserved
WHY might we need more indepth safety information?
• The Signs you just saw communicated safety
information with just a picture and perhaps a
few simple words.
• Think about the following question for 30
seconds. Why might we need more in-depth
safety information?
• After thinking quietly, pair with a neighbor and
share your thoughts.
T. Givens / Mister Science 2013 / All Rights Reserved
What is an MSDS?
MSDS stands for “Material Safety Data Sheet”.
It is intended to provide workers and emergency personnel with
procedures for handling or working with substances in a safe
manner, and includes information such as physical data (melting
point, boiling point, flash point, etc.), toxicity, health effects, first
aid, reactivity, storage, disposal, protective equipment, and spillhandling procedures. MSDS formats can vary from source to
source within a country depending on national requirements.
Have you Ever seen
these symbols?
T. Givens / Mister Science 2013 / All Rights Reserved
Examples of
Chemicals requiring
an MSDS
Chemical
Health
Fire
Reactivity
Fluorine
4
0
3
Sulfuric Acid
3
0
1
Carbon
Monoxide
2
4
0
Chloroform
2
0
0
Fluorine
•
Fluorine gas is the most reactive of all the elements and quickly attacks all
metals - steel wool bursts into flames when exposed to it !
•
In very small amounts, it is also a trace element necessary for the health of most
organisms.
•
The element and various compounds have a number of uses, ranging from the
construction of nuclear bombs to additives in dental products which are designed to
promote oral health.
T. Givens / Mister Science 2013 / All Rights Reserved
Sulfuric Acid
SULFURIC ACID IS ONE OF THE MOST IMPORTANT
INDUSTRIAL CHEMICALS. MORE OF IT IS MADE
EACH YEAR THAN IS MADE OF ANY OTHER
MANUFACTURED CHEMICAL;
IT HAS WIDELY VARIED USES AND PLAYS SOME
PART IN THE PRODUCTION OF NEARLY ALL
MANUFACTURED GOODS. THE MAJOR USE OF
SULFURIC ACID IS IN THE PRODUCTION OF
FERTILIZERS.
IT IS WIDELY USED IN THE MANUFACTURE OF
CHEMICALS, E.G., IN MAKING HYDROCHLORIC
ACID, NITRIC ACID, SULFATE SALTS, SYNTHETIC
DETERGENTS, DYES AND PIGMENTS, EXPLOSIVES,
AND DRUGS. IT IS USED IN PETROLEUM REFINING
T. Givens / Mister Science 2013 / All Rights Reserved
TO WASH IMPURITIES OUT OF GASOLINE AND
Carbon Monoxide
• A colorless, odorless, toxic flammable gas, CO, formed
by incomplete combustion, burning of fuel, of carbon. In
high concentrations, carbon monoxide can be deadly to
humans.
• Carbon monoxide has uses in the chemical industry,
medical industry, Carbon monoxide is also used in
packaged meat to keep it looking fresh.
T. Givens / Mister Science 2013 / All Rights Reserved
Chloroform
•
Chloroform is a clear liquid with an ether-like
odor and a slightly sweet taste.
•
It is a naturally-occurring chemical, but most
of the chloroform in the environment is manmade.
•
It is used to make coolants and as a dry
cleaning spot remover.
•
May be found in small amounts in
chlorinated drinking or swimming pool water.
Chlorine treatment of drinking water is often
necessary to prevent diseases that can be a
major cause of illness.
T. Givens / Mister Science 2013 / All Rights Reserved
What does a MSDS look
like?
T. Givens / Mister Science 2013 / All Rights Reserved
MSDS Scavenger Hunt
1) Scribe (You must write in complete sentences)
2) Question Reader, Time Manager and Group
Leader
3) Researcher
4) Researcher
Warm Up
Why are safety SYMBOLS important?
They are universally understood
What is the purpose of a MSDS sheet?
It gives information about a certain chemical
Equipment Stations
Today you will rotate through stations with your
group.
Make sure you are filling out the paper as you go,
you are each responsible for your own lab paper.
Remember your science safety rules
You will have 4 minutes per station