1.3.5 Marketing strategy student version1
advertisement

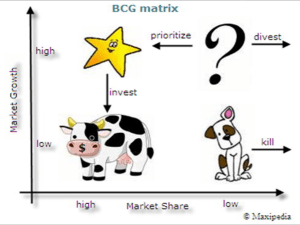
1.3.5 Marketing strategy - cartoon 1.3.5 Marketing strategy - syllabus Candidates should be able to: • Define the marketing mix • Define the product life cycle • Analyse extension strategies • Assess the Boston Matrix & product portfolio • Evaluate marketing strategies for different types of market (mass and niche; B2B and B2C marketing) • Evaluate consumer behaviour – how firms develop customer loyalty Definitions: the marketing mix What is the marketing mix? • The integration of ________________ _________________________ designed to achieve the marketing objectives of the business • It is also known as the ______ Definitions: product What does the ‘product’ include? What is the aim? Definitions: place What does ‘place’ include? In general the more places there are to buy a product from the better, unless…? Where could chocolate be sold? Definitions: price What does ‘pricing’ include? Definition: promotion What does ‘promotion’ refer to? E.g. It is NOT just advertising How do market conditions affect the marketing mix? If this was an exam question, how would you answer? The Product Life Cycle The product life cycle is the path of a product from its introduction onto the market, to its eventual disappearance The product life cycle: five stages Development stage: Introduction stage: Growth stage Maturity stage Decline stage Extension strategies Extension strategies occur at the end of the maturity stage when a product is improved or changed in order to increase sales and prevent it falling into decline. How useful is the product life cycle? Product Portfolio What is a product portfolio? Product Portfolio Analysis – The Boston Matrix What is product portfolio analysis? • Assessing the existing products to help develop a ___________ range of goods and services What is the Boston Matrix? • A way of analysing a firm’s products based on market share and market growth Product Portfolio Analysis – The Boston Matrix • Large firms with a wide range of products are most likely to use the Boston Matrix e.g. Unilever • It is used to try and spread the risk • It can help a business focus on products with the most potential The Boston Matrix: the question mark Question mark: The Boston Matrix: the dog The Dog: The Boston Matrix: the cash cow The Cash Cow: The Boston Matrix: the star The Star: What can the Boston Matrix be used for? It can be used to ensure that a firm has a suitably balanced product portfolio: Question marks are needed to they may grow into Stars are needed to they may bring in new customers Cash cows can be ‘milked’ for __________ to pay for question marks and stars Dogs are not very __________ although inevitable! Drawbacks of the Boston Matrix? The Boston Matrix and the product life cycle Consumer marketing and B2B marketing What is consumer marketing? •E.g. •It is aimed at the general public • Typically there are lots of potential buyers and lots of sellers What is business to business marketing? •Typically there are fewer buyers and many fewer sellers How do firms develop customer loyalty?