14.1 PPT - Mr. Gray's History Classes
advertisement

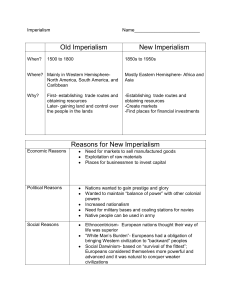
BELL RINGER 1) Who was Albert Einstein? 2) What is Anti-Semitism? 3) What is Social Darwinism? 3/23/2016 1 Ch .14 The Height of Imperialism 3/23/2016 2 Sec.1 Colonial Rule in Southeast Asia European nations began to view Asian and African societies as a source of Industrial raw materials and market for western Manufactured goods. **Imperialism**- the takeover of a country or territory by a stronger nation with the intent of dominating the economic, political, and social life 3 of the people of that nation 3/23/2016 Imperialism -Mostly for economic purposes. (markets and raw materials) -Spread Christianity Colonies were sources of National Prestige (competition) -Social Darwinism (racism) 3/23/2016 4 3/23/2016 5 Colonial takeover in Southeast Asia 3/23/2016 Great Britain- Burma and Singapore France- Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia U.S.- Philippines French made Vietnam a protectorate- (a political unit that depended on another government for it protection) 6 3/23/2016 7 3/23/2016 8 Philippines 3/23/2016 Philippines- once under Spanish control, then under the U.S after Spanish American War. Commodore George Dewey defeated the Spanish navy in Manila Bay Philippines wanted freedom (Emilio Aguinaldo was their leader) U.S. later grants it after defeating the guerrilla forces. 9 Emilio Aguinaldo 3/23/2016 10 Indirect rule and Direct rule Indirect rule- Local rulers were allowed to maintain their positions of authority and status in new colonial setting. Direct rule- Local elites were removed and Europeans ruled in their place 3/23/2016 11 New Imperialism 3/23/2016 This “new imperialism” as some historians have called it, was not content to have trading posts and agreements as the old imperialism was, but wanted direct control over territories. 12 Colonial Takeover in Southeast Asia 3/23/2016 By 1900 almost all of Southeast Asia was under Western rule. Great Britain founded a colony on a small island called Singapore (city of the lion). Singapore soon became a major port for traffic to and from China. 13 Colonial Takeover in Southeast Asia Western powers often justified their conquests by arguing they brought civilization and development. The same powers, however often feared the indigenous peoples gaining political rights. 3/23/2016 14 Colonial Regimes in Southeast Asia Colonial powers did not want their colonists to develop their own industries. Thus, the parent countries stressed exporting raw materials such as wood, rubber, tin, spices, tea, coffee and sugar. 3/23/2016 15 Colonial Regimes in Southeast Asia Colonial rule did bring benefits to Southeast Asia. It began a modern economic system and improved infrastructure. Expanded exports developed an entrepreneurial class in rural areas. 3/23/2016 16 Resistance to Colonial Rule Initial resistance to colonial rule came from the ruling classes among the subject peoples. Some resistance took the form of peasant revolts. Early resistance was overcome by Western Powers but a new kind of resistance in the form of nationalism proved to be too much for the Western Powers. 3/23/2016 17 Review 1) What is Imperialism? 2) What were the reasons for imperialism? 3) What was a protectorate? 4) What is indirect rule? 3/23/2016 18 GROUP WORK 3/23/2016 Why do you think imperialism changed from administering territories for trade purposes to actual governing the territories? 19