Study Guide Unit III – Chapter 11 Answer Key Review questions
advertisement
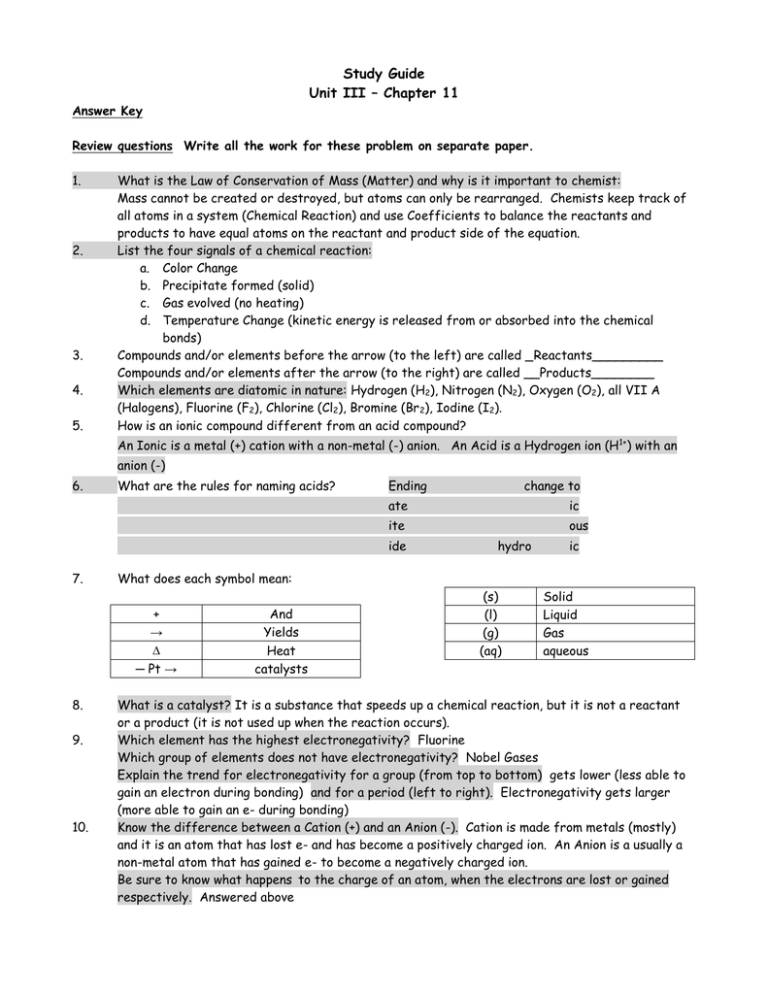
Study Guide Unit III – Chapter 11 Answer Key Review questions Write all the work for these problem on separate paper. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is the Law of Conservation of Mass (Matter) and why is it important to chemist: Mass cannot be created or destroyed, but atoms can only be rearranged. Chemists keep track of all atoms in a system (Chemical Reaction) and use Coefficients to balance the reactants and products to have equal atoms on the reactant and product side of the equation. List the four signals of a chemical reaction: a. Color Change b. Precipitate formed (solid) c. Gas evolved (no heating) d. Temperature Change (kinetic energy is released from or absorbed into the chemical bonds) Compounds and/or elements before the arrow (to the left) are called _Reactants_________ Compounds and/or elements after the arrow (to the right) are called __Products________ Which elements are diatomic in nature: Hydrogen (H2), Nitrogen (N2), Oxygen (O2), all VII A (Halogens), Fluorine (F2), Chlorine (Cl2), Bromine (Br 2), Iodine (I2). How is an ionic compound different from an acid compound? An Ionic is a metal (+) cation with a non-metal (-) anion. An Acid is a Hydrogen ion (H1+) with an anion (-) 6. What are the rules for naming acids? Ending ate ic ite ous ide 7. 9. 10. hydro ic What does each symbol mean: + → ∆ ─ Pt → 8. change to And Yields Heat catalysts (s) (l) (g) (aq) Solid Liquid Gas aqueous What is a catalyst? It is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction, but it is not a reactant or a product (it is not used up when the reaction occurs). Which element has the highest electronegativity? Fluorine Which group of elements does not have electronegativity? Nobel Gases Explain the trend for electronegativity for a group (from top to bottom) gets lower (less able to gain an electron during bonding) and for a period (left to right). Electronegativity gets larger (more able to gain an e- during bonding) Know the difference between a Cation (+) and an Anion (-). Cation is made from metals (mostly) and it is an atom that has lost e- and has become a positively charged ion. An Anion is a usually a non-metal atom that has gained e- to become a negatively charged ion. Be sure to know what happens to the charge of an atom, when the electrons are lost or gained respectively. Answered above 10. O2 HClO Fe(SO4) I2 Al2(CO3)3 Na(C2H3O2) H2SO4 CO2 K2CrO4 Ag(NO3) ZnO H 2O Name _________Oxygen_________________________ _________Hypochlorous Acid_________________ ______Iron(II) Sulfate_______________ _______________________Iodine____ _______Aluminum Carbonate_____________ _____________Sodium Acetate_______ _______Sulfuric Acid________________ _________________Carbon Dioxide___ _____Potassium Chromate______________ _______________Silver Nitrate______ _____Zinc Oxide___________________ _____________Water______________ Then you will also need to be able to write the formula from the name! 11. Thinking Formula Silver hydroxide ________________ ____Ag(OH)_ Nitrous Acid ________________ _______HNO2___ Carbonic acid ________________ ____H2CO3____ Carbon Dioxide ________________ CO2_________ Hydrochloric acid ________________ _______HCl___ Calcium carbonate ________________ __CaCO3_____ Lithium chlorate ________________ _______LiClO3_ Hydrogen gas ________________ _______H2____ Lead (II) phosphate ________________ _Pb3(PO4)2____ Barium sulfate ________________ _____BaSO4_____ 12. List all of the compounds from question #10 and #11 that would dissociate in water? [Hint: use the solubility table]:All of the following would become [aqueous (aq)] #11. HClO, Fe(SO4), Na(C2H3O2), H2SO4, K2CrO4, Ag(NO3), and for # 12. Nitrous Acid (HNO2), Carbonic Acid (H2CO3), Hydrochloric Acid (HCl), Lithium Chlorate (LiClO3), 13. From the pairs given below choose the metal that is more reactive. [Hint use the reactivity of metals table (back of periodic table or p. 333)] a. Li or Cu b. Ag or Cu c. Mg or K 14. d. Al or Zn e. Pb or Ca f. Hydrogen (H2) or Cu a. Balance the following equations, using coefficients. Also identify the type of chemical reaction it equation represents (combination, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, or combustion). __2_ H2O2 __2__ H2O + ____ O2 type: __Decompostion___ b. _3_ Zn + _2__ H3(PO4) c. __2_ Ag(NO3) + __ PbI2 d. _4__Al + _3__ O2 ___ Zn3(PO4)2 __ Pb(NO3)2 __2_ Al2O3 + _3_ H2 + _2_ AgI __Single Replacement__ _Double Replacement__ ___Combination_______ e._ Ca(OH)2 f. + _2_ HCl __ CaCl2 + _2_ H(OH) ___ Na2O + ___ H2O ——→ metal oxide and water yields (actually H2O) __Double Replacement___ __2_ Na(OH) a base t _____Decompostion_____ Practice Chemical Equations (finishing, balancing and identifying) Type: 15. Al(s) + __Combination_____ 16. Mg 17. Ca(s) + 18. Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 19. O2 (g) + Ca(NO3)2 __NO Reaction _ + Check Activity Series _ _Single Replacement___ N2O3 Mg(NO3)2(aq) ___Ca(NO3)2 (aq) + + H 2O K2CO3(s) 21. Zn 22. Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 23. 24. + __HNO2 (aq)____ ___K2O(s)_____ + HCl (aq) ___ZnCl2 (aq) + _H2 (g)_ 25. 2 NH3 (g) 26. NaCl(aq) + N2 (g) H 2O + O2 + 3 H2 (g) K(NO3)(aq) NaCl(aq) + __Double Replacement____ ___Decomposition___ _Single Replacement __ 3 Ca(OH)2(aq) _2_Al(OH)3(s) + 3 Ca(SO4)(s) ----Fe3+-- ___Single Replacement____ __Combination_______ __CO2 (g)____ C12H22O11 (s) + 12 O2(g) _12_CO2 (g)_ + H2O2 (aq) ___Mg(s)___ Na2S(aq) ___CuS (s)__ + __2_NaNO3 (aq) 20. (s) ___Al2O3 (s)_ _11_H2O (l)_ _Double Replacement___ ___Combustion __ __Decomposition___ (g) __Decompostion____ KCl(aq) No Reaction, because all the reactants and products are aqueous. Double Check – for questions 15 – 25 were there some combinations that would be No Reaction? [Hint use the Solubility Table and Activity Series of Metals Table] Word Equations: Write the reactants and the products and then balance, also list the type of reaction that each is: 27. Solid Copper, plus Oxygen gas in a flame yields – 2 Cu (s) + O2 (g) 2 CuO (s) Combination 28. Zinc metal and Sulfuric Acid yields – Zn(s) + H2(SO4) (aq) Zn(SO4) (aq) + H2 (g) Single Replacement 29. Magnesium nitrate solution and Sodium hydroxide solution placed together in a test tube yields – Mg(NO3)2(aq) + 2 Na(OH) (aq) Mg(OH)2 (s) + 2 Na(NO3) (aq) Double Replaement 30. Copper (II) Carbonate is heated and yields – Cu(CO3) (s) CuO (s) + CO2(g) Decomposition 31. Methane from the Bunsen burner is reacted with oxygen in the air and yields CH4 (g) + 2 O2 (g) CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (l) Combustion 32. Lithium metal and water yields – Li(s) + H2O (l) Think of water as H(OH) 33. 34. 35. 36. Li(OH) Hydrochloric acid and aluminum hydroxide yields – 3 HCl (aq) + Al(OH)3 3 H(OH) + Water (aq) + H2 (g) AlCl3 Sulfur dioxide gas (SO2) and water yields – SO2 (g) + H2O (l) H2SO3 (aq) Non-metal plus water makes an acid Oxide Copper Hydroxide is heated and yields – Cu(OH)2 (s) CuO (s) + H2O(l) Burning sugar (C12H22O11) produces – C12H22O11 + 12 O2(g) 11 H2O(l) + Single Replacement Double Replacment Combination Decomposition 12 CO2(g) Combustion 37. Calcium nitrate solution is mixed with sodium phosphate solution and yields 3 Ca(NO3)2 (aq) + 2 Na3(PO4) (aq) Ca3(PO4)2 (s) + 6Na(NO3) (aq) 38. Explain how to test for each of the following gases: Hydrogen (H2): Use a lit wooden splint if it pops (explodes) it is hydrogen. Oxygen (O2): Use a glowing splint if it relights it is oxygen. Carbon Dioxide (CO2): Use a lit or glowing splint if it goes out it is carbon dioxide. 39. c. Sn + 4HNO3 SnO2 + 4NO2 + 2H2O 40. a. Fluorine 41. c. helium 42. c. Pb(SO4) 43. The following reaction is balanced Sn + 4HNO3 → SnO2 + 4NO2 + 2H2O true 44. d. combination 45. d. rearranged or spread apart but can be accounted for 46. NaI (aq) + Pb(NO3)2 (aq) PbI2 (s) + Na(NO3) (aq) + 47. Correctly balance the equation below and then draw the way the particles are arranged in the provided beakers. Mg (s) + + HCl (aq) MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (g) SOLUBILITY RULES (solubility in water) All alkali metal compounds are soluble in water. All nitrates are soluble in water. All acetates are soluble in water, except when they contain Ag +1. All NH4+ compounds are soluble. All chlorates are soluble. All chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble except those containing Ag+, Hg+2, and Pb+2. All sulfates are soluble except those containing Sr +2, Ba+2, and Pb+2. All carbonates and phosphates are insoluble in water, except those containing alkali metals and NH 4+1. All hydroxides and sulfides are insoluble, except those containing alkali metals and ones containing NH 4+1, Sr+2, Ba+2, and Ca+2. PREDICTING CHEMICAL REACTIONS Metallic carbonates break into metallic oxides and carbon dioxide. Metallic chlorates break into metallic chlorides and oxygen. Cation (+) Peroxides break into Cation oxides and oxygen. A non-metal oxide and water produce an acid. Some acids break into non-metallic oxides and water (H2CO3 and H2SO3) A metal oxide and water produce a base or a hydroxide. Metallic hydroxides break into metallic oxides and water. A metal oxide and a non-metal oxide produce an ionic compound.






