Chapter 7 The Property System
advertisement

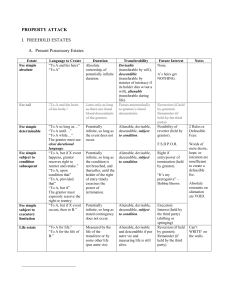
Chapter 21 Law of Property: Real, Personal, and Intellectual 13-1 Definition of real property Land and everything permanently attached to it. An item is “attached” if: removal would cause damage to the property, or it is essential to the functioning of the structure. Fixtures Personal property that is later permanently attached to the realty. Exception for trade fixtures. Extent of ownership Air space Water rights Mineral rights 13-2 Interests in real property Fee simple absolute Most complete estate one can own. Conditional estate Subject to a condition that could terminate the interest. Life estate Ownership lasts until death, then passes to another party. Holder of life estate cannot waste the property. Future interest Present ownership of right to possess land sometime in the future. 13-3 Interests in real property (continued) Leasehold estates A possessory interest. Tenant can exclude everyone else, including the landlord. Sublease. Easements Irrevocable right to use a portion of another’s land. By express agreement. By prescription. Created by open use of portion of another’s property for statutory period. By necessity: when parcel of land is landlocked. License Temporary, revocable right to be on someone else’s property. 13-4 Co-ownership Tenancy in common Joint tenancy Can own unequal shares. Can sell without consent of other owners. Interest can be attached by creditors. Heirs receive interest at death. Each owns an equal share. Can sell without consent of other owners. Interest can be attached by creditors. Other owners receive interest at death. Tenancy by the entirety Only for married couples. Need consent of other owner to sell. Creditors of only one owner cannot attach the property. Upon death, ownership passes to other owner. Upon divorce, becomes tenancy in common. 13-5 Voluntary transfer of real property A proper deed will: Deed must be Identify grantor and grantee. Express grantor’s intent to convey the property. Identify type and percentage of ownership. State price paid. Describe the physical boundaries of the property. Specify easements and restrictions, if any. Identify warranties and promises made by grantor. executed delivered accepted Recording of deed. Not required by law. But should always be done to protect grantee’s interest. 13-6 Types of Deeds General warranty deed: grantor gives covenant: of seisen: a promise she owns the title she is conveying. of right to convey: a promise she has the right to convey her interest. against encumbrances: promise there are no mortgages or other liens not stated in the deed. for quiet enjoyment: promise to defend grantee’s title against any challenges. of further assurances: promise to furnish any necessary documents grantee needs to perfect his title. Special Warranty deed : Warranties limited to time of Grantors ownership. Quitclaim deed Grantor conveys title. Grantor makes no additional covenants. 13-7 Involuntary transfer of real property Adverse possession A person can become the owner of realty that belongs to another if he: treats realty as his own openly without permission of the true owner for the statutory period of years. Condemnation Eminent domain Government acquires ownership of private property. For public purpose. Must pay just compensation. 13-8 Restrictions on land use Restrictive covenants Entered into voluntarily by parties. Agree to use or not use land in particular ways. Zoning Restriction of land use. To allow for orderly growth and development To protect health, safety, and welfare of citizens. Variance Permission to use land in a manner prohibited by the zoning laws. Other statutory restrictions on land use Historic preservation 13-9 Personal property Tangible material Intangible without and movable a physical form Voluntary transfer of personal property Title to property passes when parties so intend. Transfer by purchase. Transfer by gift. Delivery of the gift. Donative intent. Acceptance by the donee. 13-10 Personal property (continued) Involuntary transfer of personal property Abandoned property Lost property Owner has accidentally dropped or left somewhere. Mislaid property. Property discarded by original owner. Owner intentionally placed property somewhere but has forgotten where. Bailments One party (the bailor) transfers possession of personal property to another party (the bailee). Might be for benefit of: the bailor the bailee of both (mutual benefit) 13-11 Trademarks Distinctive mark, word, design, picture or arrangement used by a seller in conjunction with a product tending to cause the consumer to identify the product with the producer. Common law protection. Registration with U.S. Patent Office. Infringement. Likelihood of confusion. Remedies Damages Injunction 13-12 Trade Secrets and Patents Trade secret A process, product, method of operation, or compilation of information that gives a businessperson an advantage over her competitors. Includes inventions and designs. Protected from unlawful appropriation so long as it is kept secret. Lawful to discover the secret by reverse engineering. Patents Legal protection for a: product, process, invention, machine, or for certain plants. Must be new and useful. Cannot be used for tying arrangements cross-licensing 13-13 Copyrights Protection for expression of creative ideas. Lasts for life of creator plus 50 years. Such works as: books periodicals musical compositions motion pictures art computer programs Infringement Fair use For criticism, comment, news, teaching, research. 13-14