Chapter 9 Vocabulary Chart
advertisement
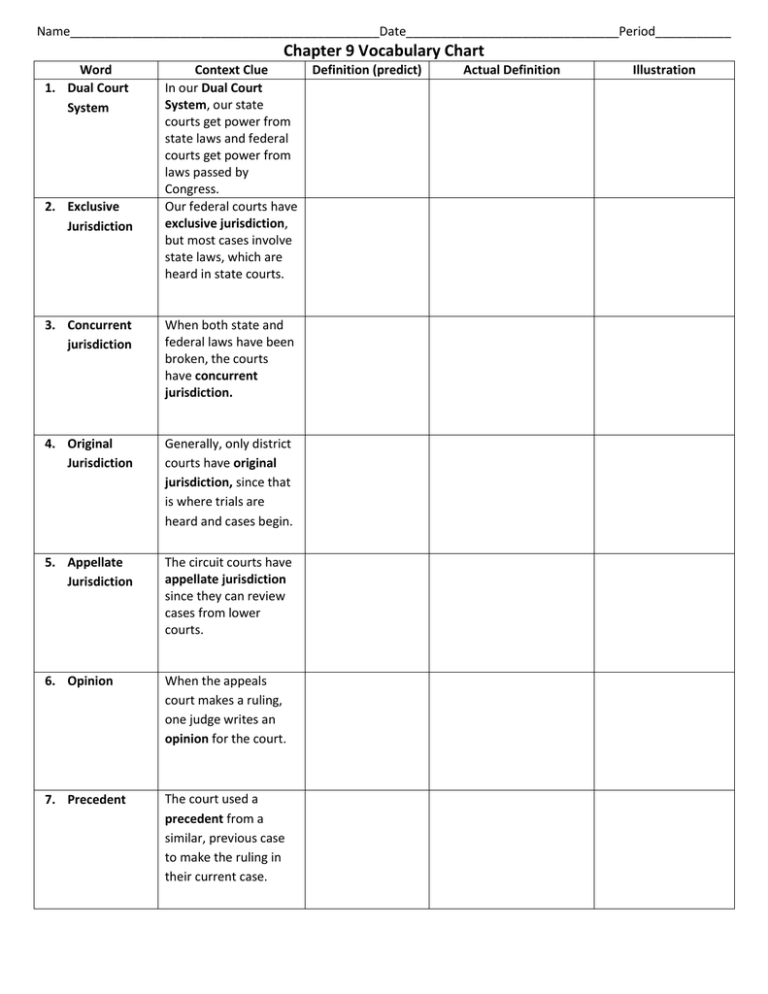
Name_____________________________________________Date_______________________________Period___________ Chapter 9 Vocabulary Chart Word 1. Dual Court System 2. Exclusive Jurisdiction Context Clue In our Dual Court System, our state courts get power from state laws and federal courts get power from laws passed by Congress. Our federal courts have exclusive jurisdiction, but most cases involve state laws, which are heard in state courts. 3. Concurrent jurisdiction When both state and federal laws have been broken, the courts have concurrent jurisdiction. 4. Original Jurisdiction Generally, only district courts have original jurisdiction, since that is where trials are heard and cases begin. 5. Appellate Jurisdiction The circuit courts have appellate jurisdiction since they can review cases from lower courts. 6. Opinion When the appeals court makes a ruling, one judge writes an opinion for the court. 7. Precedent The court used a precedent from a similar, previous case to make the ruling in their current case. Definition (predict) Actual Definition Illustration Word 8. Litigants Context Clue The litigants came to court to have the judges hear their civil case. 9. Judicial Review The Supreme Court has the power of judicial review. 10. Constitutional Supreme Court justices check to make sure laws are constitutional. 11. Docket Next up on the Supreme Court’s docket is Stewart vs. Florida. 12. Brief The lawyer presented his brief to the justices, in hopes they would agree with his side. 13. Nullify The law was unconstitutional, so it was nullified by the Supreme Court. 14. Tenure Federal judges have tenure, so they can be free from public or political pressures when hearing a case. 15. Subpoena The person received a subpoena to appear in court in February. Definition (predict) Actual Definition Illustration











