AP Worksheet Review II 600 to 600
advertisement

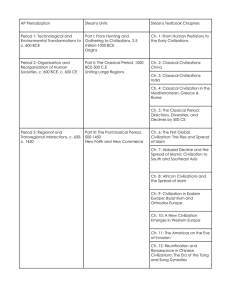
AP Worksheet Review II Classical Societies: There are 5 major Classical Societies. You’ll need to be able to differentiate between them. These are: China Classical India Persia Greece Rome Above, write the Region of each. Next, write the names of each of the Chinese and Indian dynasties and their years. Go ahead, and divide Rome into Republic and Empire - with descriptions of each. After you’ve divided the Classical civilizations - go ahead, above and write some details for each. Think PERCI II. Interactive: Match the Classical Civilization with it’s description: ______________ Zoroastrianism in this society held the belief of rewards and punishments in the afterlife. These people can trace their roots to ancient Mesopotamian civilization. These people were noted for their tolerance toward the customs of their conquered people. ______________ Beginning as an Indo-European known as Mycenaea (which later was destroyed by the Dorians) this civilization was based on fishing and trade. They adopted their alphabet from Phoenician mariners who needed it for recordkeeping and commercial transactions. ______________ There are three famous dynasties in this civilization. The emperors considered themselves “sons of Heaven”. Agriculturally, this civilization had wheat in the north and rice in the south. _____________ This society has its roots from the invasions of the Aryans about 1500 BCE. These people came from Central Asia. Much knowledge of the Aryans comes from their oral epics, called the Vedas. The Vedic Age (1500-1000 BCE) is the term applied to this early classical civilization. The Epic Age followed from (1000-600 BCE). _____________ This civilization began as a kingdom in central Italy about 800 BCE. The period of expansion in the Mediterranean world with the defeat of Carthage in North Africa in the Punic Wars (264-246 BCE). Which dynasty? Match the dynasty name with its descriptions Qin The Golden Age of India Gupta The Chinese Civil Service began Han Mauryan Zhou Chinese territory expanded to include the Yangtze River Valley A common written language was standardized The first to unify the Indian subcontinent III. Republic versus Empire Put RR (Roman Republic) or RE (Roman Empire) next to each. Government centered around the Senate Conquered people given a measure of self-rule. The Senate was composed of members of the aristocracy. The executive resided in two consuls. A lasting feature of it was its system of laws: some included: the concept that a defendant is innocent until proven guilty by a court of law. Laws written down, known as the Twelve Tables. Inhabitants in conquered provinces granted citizenship. IV. Applying knowledge: Under both the Han and the Roman empires a. imperial roads were connected to the Silk Roads. b. new territories were added to the empires. c. a time of peace settled over both emires. d. enduring cultural traditions were established. e. all of the above. Compare and Contrast Roman and Han Empires with Classical India V. Famous People Match the civilization with the names of famous people. Classical Greece Julius Caesar Classical Rome Chandragupta Gupta Confucius (Kong Fuzi) Mauryan Alexander the Great Han Cyrus the Great Qin Aristotle Zhou Shi Huangdi Persia Ashoka Vocabulary: what’s the difference between jati and sati? VI: Achievements: For each civilization write 2 examples of scientific achievement Han Classical Greece / Hellenistic Gupta India The Arts: Identify where each of the following artistic achievement took place. Be specific when possible. ___________ The manufacture of silk cloth ___________ Paper manufacturing ___________ High Towered temples in honor of the gods ___________ Stadiums were constructed to provide entertainment ___________ Ramayana and Mahabharata ___________ Arches with a keystone. ___________ The Odyssey and the Iliad VII. Religions / World Beliefs: Connect the definition of the vocabulary word and then, connect it to its religion/belief: Polytheism Hebrew scriptures Animism respect for patriarchal family / veneration of the ancestors Monotheism the moral law, serves as a guide to actions Filial Piety the person’s good or evil deeds in his or her personal life Hinduism “The Way” the belief that gods and goddesses inhabit natural features Christianity Nirvana after death the soul enters another human or an animal. Karma the soul is united with the soul of Brahma; unification of this. Dharma the worship of one god Torah male, assertive; female, submissive: concepts of balance Yin and Yang moral law of the Hebrews Moksha union with the divine essence Ten Commandments Buddhism Polytheism Daoism Judaism belief in more than 1 god. Messiah a life force which exists in nature Disciples a savior from sin reincarnation Confucianism followers VIII: Social Status Quickly Review the essay on page 89 “The Classical Mediterranean in Comparative Perspective”. Now, make a note page or graphic organizer below addressing the issue of social status (hierarchy) and the general comparisons with the classical societies. IX. Contacts with others: use the word bank below The growth of the classical civilizations with their impressive achievements and monuments, clearly had an impact on surrounding peoples. Some trade with neighboring regions was common. _______________ had the widest commercial reach, extending all the way into Southeast Asia, but ______________ also traded with parts of Africa and Asia outside its own empire. Even more widely, nomadic peoples were often attracted toward the centers of civilization as immigrants, ___________ or invaders. Some nomadic peoples facilitated __________ between civilizations. These developments were important at the time and had implications for later patterns in world history. For example, cultural and ________ contacts often prepared the way for later __________ migrations into the classical societies. WORD BANK soldiers Rome trade nomadic India Trade systems in Classical Societies - for each trading system, list the regions invovled and the goods traded. Regions involved Goods Traded Silk Road Trade Indian Ocean Trade Trans-Saharan Trade X. Things that stayed the same: For each topic, make a few notes how these continuities were different in styles: China India Mediterranean Partriarchy Iron Tools Agriculture Traditions Old Age Overall, what has been the major contributions of Classical Civilizations? Why is it significant to our study of history? Write your answer below: The lasting contributions of Classical civilization have been ____________________________ __________________, _________________________________________ and ___________ _________________________. They are important because___________________________, __________________________________ and _____________________________________.