Lab Equipment - Ms Kim's Biology Class
advertisement

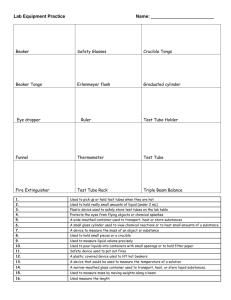
Lab Equipment Goggles • Most important piece of lab equipment) • Protects eyes from broken glass, chemicals and flames. Length and Volume • Meter Stick, Ruler used to measure Length. • Graduated Cylinder, Flask, Beaker used to measure Volume. Mass • Balance –Digital –Triple beam Digital Scale • You must ZERO/TARE the scale before measuring mass. TARE the balance with the container first, then add material to be measured (liquid/granules) You do not want the mass of the container in your reading. Measuring Mass We will be using triple-beam balances to find the mass of various objects. The objects are placed on the scale and then you move the weights on the beams until you get the lines on the right-side of the scale to match up. Once you have balanced the scale, you add up the amounts on each beam to find the total mass. What would be the mass of the object measured in the picture? 70 300 + _______ 3.4 373.4 g _______ + ______ = ________ Top Image: http://www.southwestscales.com/Ohaus_Triple_Beam_750-SO.jpg Bottom Image: http://www.regentsprep.org/Regents/biology/units/laboratory/graphics/triplebeambalance.jpg Measuring Mass – Triple-Beam Balance 1st – Place the film canister on the scale. 2nd – Slide the large weight to the right until the arm drops below the line. Move the rider back one groove. Make sure it “locks” into place. 3rd – Repeat this process with the top weight. When the arm moves below the line, back it up one groove. 4th – Slide the small weight on the front beam until the lines match up. 5th – Add the amounts on each beam to find the total mass to the nearest tenth of a gram. Beaker • Measures liquids (but not very accurately) • May be heated • Used to hold or mix chemicals Stirring Rod • Glass rod used for stirring • BE CAREFUL! They break easily Erlenmeyer Flask • Measures liquids (but not accurately) • May be heated • Used for mixing • Has a cone-shaped container with neck, so you can hold the flask (to stir) or attach a clamp or use a stopper. Graduated Cylinder • Measures volumes of liquids accurately Test Tube/Test Tube Rack Test Tube: May be heated Mix chemicals Holding small amounts of chemicals Test Tube Rack: Holds test tubes in a vertical position. Allows for clear sight. Drying rack Test tube holder: It holds a test tube Wire Gauze/Funnel/Loop • Wire Gauze: Spreads out the heat produced by a Bunsen burner Inoculation Loop: A tool used to transfer and spread microorganisms to a petri dish. Funnel: Holds filter paper for filtering solutions. Transferring liquids to smaller narrow necked containers Mortar and Pestle/ Plastic Wash Bottle/Forceps/Crucible Tongs Mortar and Pestle: • Used for grinding crystals Plastic Wash Bottle: • Dispenses water for rinsing equipment Forceps: • Used to pick up small items. Crucible Tongs: Pick up and hold small hot items like a crucible. Bunsen Burner (& Striker) • Controls release of natural gas for burning. • Surgical tubing connects to gas source. • Striker with flint is used to ignite the burner Rubber Stopper/Scoopula/Test Tube Brushes/Pipette Test Tube Rubber Stopper: • Covers test tube for mixing Scoopula: Used to transfer solids from one container to another Brushes: Used to clean out the test tubes Pipette: A narrow tube into which small amounts of liquid are suctioned for transfer or measurement. Petri Dish, Microscope slide and cover slips, and Microscope Petri Dish: A shallow circular dish with a loosefitting cover, used to culture bacteria or other microorganisms. Cover Slip: A very thin piece of glass placed over a specimen on a glass slide that is to be examined under a microscope. Microscope: Microscope slide: A small, flat rectangular piece of glass on which specimens can be mounted for microscopic study. An instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye.