admin-parsons-IEEEITU-joint-workshop-summary
advertisement

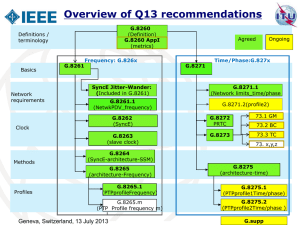
Joint IEEE-SA and ITU Workshop on Ethernet Protection and Packet Synchronization http://www.itu.int/en/ITU-T/Workshops-andSeminars/ethernet/201307/Pages/default.aspx Geneva, Switzerland, 13 July 2013 Joint IEEE-SA and ITU Workshop on Ethernet Moderator Summary Ethernet Protection Summary Ghani Abbas, Ericsson – ITU-T SG15 vice chair Steve Haddock – IEEE 802.1 Interworking chair Glenn Parsons, Ericsson – IEEE 802.1 vice chair Geneva, Switzerland, 13 July 2013 Summary ….. 1/2 IEEE 802.1AX LAG is being revised to provide node and link redundancy, address dual-homed interconnects, and congruent per-service traffic distribution. Expected Standards 1H2014 New Project p802.1CB started to identify and replicate frames and eliminate these frames in seamless protection scheme New project p802.1 Qca -Path Control and Reservation (PCR) started. It leverages SPB for explicit Path establishment as well as reservation and redundancy Geneva, Switzerland, 2 13 July 2013 3 Summary …..2/2 G.Supplement 52 for G.8032 was approved. It provides scenarios for: - Ethernet services support - Ring interconnections - Network applications and use cases New work G.mdsp provides protection interworking for UNI/NNI network scenarios using ITU approved protection schemes (OTN and Ethernet) MECP is under study. It addresses protection of single rooted-multipoint (RMP) Ethernet connections in Ethernet transport networks. Geneva, Switzerland, 13 July 2013 4 Joint IEEE-SA and ITU Workshop on Ethernet Moderator Summary Packet Synchronization Jean-Loup Farrant – ITU-T SG15 Q13 rapporteur Michael Johas Teener – IEEE 802.1 TSN chair Geneva, Switzerland, 13 July 2013 Overview of Q13 recommendations G.8260 (Definition) G.8260 AppI (metrics) Definitions / terminology Basics Network requirements G.8261 Frequency: G.826x Time/Phase:G.827x G.8271.1 (Network limits_time/phase G.8261.1 (NetwkPDV_frequency) G.8271.2(profile2) G.8262 (SyncE) G.8272 PRTC 73.1 GM G.8263 (slave clock) G.8273 73.3 TC 73.2 BC 73. x,y,z G.8264 (SyncE-architecture-SSM) G.8265 (architecture-Frequency) Profiles G.8271 Ongoing SyncE Jitter-Wander: (Included in G.8261) Clock Methods Agreed G.8275 (architecture-time) G.8265.1 (PTPprofileFrequency) G.8275.1 (PTPprofile1Time/phase) G.8265.m (PTP Profile frequency m) 6 G.8275.2 (PTPprofile2Time/phase ) Geneva, Switzerland, 13 July 2013 G.supp Summary of the Synchronization sessions -1 IEEE 1588 Revision Fix existing problems, remove inconsistancies Improve accuracy, security, configuration and MIBs Layered architecture, but backwards compatible Backward compatibility is very important for operators IEEE 802.1AS Revision Additional link types, link aggregation Redundancy and faster reconfiguration Architectural convergence with 1588 Geneva, Switzerland,13 July 2013 7 Summary of the 3 Synchronization sessions -2 IEEE Issue One step clock One-step clock implies the implementation of hardware that greatly reduces the processor requirements for synch and delay processing Backwards compatibility a requirement IEEE 1588 simulations for G.827x 802.1AS & The proposed G.827x and 802.1AS profiles will meet their goals Partial support still to be performed in ITU Geneva, Switzerland,13 July 2013 8 Summary of the Synchronization sessions -3 Network limits-Asymmetry Asymmetry remains one of the main issues in the transport of time. Partial support might add new sources of asymmetry Synchronization network architecture Key aspects of NGN synchronization Packet network infrastructure New synchronization requirements New methods New clock structures Architecture helps see how all pieces fit together Geneva, Switzerland,13 July 2013 9 Summary of the Synchronization sessions - 4 802.1Q Stream reservation protocol deterministic operation requires that resources are available based on 802.1Q Multiple Registration Protocol talkers advertise the streams that they can source Important side-effect sets up a reservation « domain » listeners register for streams New work under way static reservations, faster startup, big reduction in packet traffic, support for new shapers, more management Geneva, Switzerland,13 July 2013 10 Summary of the Synchronization sessions - 5 802.1Qbv scheduled traffic Scheduling stream transmission can greatly reduce delays through switches Cut-through makes sense Management of schedule is not a plugand-play operation, it will require intelligence Geneva, Switzerland,13 July 2013 11 Summary of the Synchronization sessions -6 G.8275.x profiles G.8275.x time PTP telecom profiles are designed to support the needs of current and future mobile technologies G.8275.1 (full timing suport) will be finalized soon, G.8275.2 (partial timing support) is just starting Geneva, Switzerland,13 July 2013 12