Chapter 5
advertisement

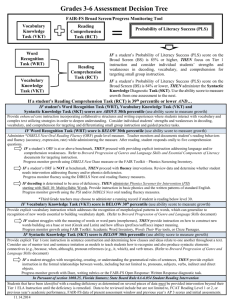
Chapter 5 Informal Assessment: Progress Monitoring Introduction • The Assessment Continuum • Reliability and Validity • Criterion-Referenced Assessment • Progress Monitoring • Computer-based Assessment of Reading • Special Considerations for Young, Adult and English Language Learners The Assessment Continuum Figure 5.1 Reliability and Validity Types of Reliability and Validity • Tables 5.1 and 5.2 Reliability • Reliability=Consistency • Correlation: Positive, Negative, No Relationship • Correlation Coefficient Ranges from +1.00 to – 1.00 • Measures of Reliability: Pearson’s R, KuderRichardson, Split-Half, Coefficient Alpha, TestRetest, Equivalent Forms, Interrater • Standard Error of Measure • Obtained Score= True Score+Error • Estimated True Score Types of Reliability • Inter-Rater • %age agreement • Intra-Rater • %age agreement • Alternate Form • Pearson r • Internal Consistency • Spearman Brown, Cronbach’s alpha • Test-Retest • Pearson r • Consistency between 2 or more raters • 1 rater’s consistency across assessments • Consistency of scores over equivalent forms • Consistency of scores on items within same test • Consistency of scores from one testing to another Validity • Validity=Accuracy • Types of Validity: Criterion-Related, Concurrent, Predictive, Content, Construct • Reliability versus Validity • Can a Test Be Valid without Being Reliable? Types of Validity • How well do items assess desired • Expert review, test blueprint (Figure 5.2) content? • How well do items • Construct assess a particular • Correlations with similar measures domain, skill, etc.? • Concurrent vs • Same time vs Predictive future • Treatment • Analysis of gain • Prediction of student scores after learning gains instruction • Content Criterion-Referenced Assessment Criterion-Referenced Assessment • • • • • Assess mastery of specific objectives Determine present levels of performance Establish future educational objective Determine IEP objectives Monitor progress Brigance Inventories • Brigance Diagnostic Inventory of Early Development-III • Brigance Diagnostic Comprehensive Inventory of Basic Skills-III • Criterion-Referenced but yields some standard scores • Gives grade placement information • Assess a wide range of reading and other skills • Can be used to monitor progress, set IEP goals Linkages Between Brigance and Common Core State Standards • Table 5.3 Examples from Brigance CIBS-III • Figures 5.3, 5.4, 5.5 Figure 5.3 Figure 5.4 Figure 5.5 Progress Monitoring Trends in Progress Monitoring • National Center on Student Progress Monitoring • http://www.studentprogress.org/ • National Center on Response to Intervention • http://www.rti4success.org/ • National Center on Intensive Intervention • http://www.intensiveintervention.org/ • Hybrids • Computerized Assessment “Hybrid” Assessments • Assessments that combine aspects of both formal and informal assessment • Standardization Sample (Formal) • Curriculum-like tasks (Informal) • Ability to monitor progress (Informal) • Dynamic Indicators of Basic Early Literacy Skills (DIBELS) & AIMSWeb progress monitoring system • http://dibels.uoregon.edu • www.aimsweb.com AIMSweb • • • • • • • • Reading Fluency Comprehension Early Literacy Measures Spanish Early Literacy Early Numeracy Math Computation Spelling Written Expression AIMSweb Reading • Reading Fluency • Measures Oral Reading Fluency • Reading Comprehension (MAZE) • Measures Reading Comprehension AIMSweb Early Literacy Measures • • • • Letter Naming Letter Sound Fluency Phoneme Segmentation Nonsense Word Fluency AIMSweb Spanish Early Literacy Measures • • • • • • Letter Naming Fluency Letter Sound Fluency Syllable Sound Fluency Syllable Reading Fluency Syllable and Word Spelling Oral Reading Fluency Example: DIBELS (Good & Kaminski, 2002) • Brief, standardized, individually administered measures • • • • • Initial/First Sound Fluency Letter Naming Fluency Phoneme Segment. Fluency Nonsense Word Fluency Daze (DIBELS Next only) - Oral Reading Fluency - Oral Retelling Fluency - Word Use Fluency • Assess development of pre-reading and early reading skills • Includes DIBELS Data System What DIBELS Purports to Assess Area of Reading DIBELS Assessment • Phonics • Initial Sound/First Sound • Phoneme Segmentation • Phonemic Awareness • Nonsense Word • Fluency • Letter Naming • Oral Reading • Comprehension • Retell • Daze (DIBELS Next) • Vocabulary • Word Use Overview of DIBELS Measures Initial Sounds Fluency (First Sound Fluency in DIBELS Next) • Grade administered: Kindergarten • Measures: a student’s ability to recognize and produce the beginning sound(s) in an orally presented word • Students performing below expectations will benefit from instruction in phonological awareness Overview of DIBELS Measures Letter Naming Fluency • Grades administered: Kindergarten through fall of first grade • Measures: A student’s proficiency in naming upper and lower case letters • Students identified at risk should be instructed in phonological awareness and alphabetic principle Probe 1 c c N u Q M u h S i n b e N F f o a K k g p k p a H C e G D b w F i h O x j I K x t Y q L d f T g v T V Q o w P J t B X Z v U P R l V C l W R J m O z D G y U Y Z y A m X z H S M E q n j s W r d s B r A E L c c N u Q M I Total: ____/110 Overview of DIBELS Measures Phoneme Segmentation Fluency • Grades Administered: Midkindergarten to end of first grade • Measures: A student’s ability to segment three- and fourphoneme words into their individual phonemes • Students performing below expectations in this measure will benefit from instruction in phonological awareness activities Overview of DIBELS Measures Nonsense Word Fluency • Grades administered: midkindergarten through first grade • Measures: the student’s knowledge of letter-sound correspondence and ability to blend letters into words • Students performing below expectations will benefit from activities focusing on decoding kik kaj lan yuf bub wuv nif suv yaj tig woj fek nul pos dij nij vec yig zof mak sig av zem vok sij pik al dit um sog faj zin og viv vus nok boj tum vim wot yis zez nom feg tos mot nen joj vel sav Overview of DIBELS Measures Oral Reading Fluency • Grades administered: Mid year first grade through third grade There was a robin’s nest outside our kitchen window. The nest was in a tall bush. The mother robin sat in the nest all day long. One day when I was watching, the mother bird flew away. I saw the eggs she was sitting on. There were four blue eggs. • Measures: fluency in oral reading of connected text I watched and watched. The eggs moved. I watched some more. The eggs started to crack. Finally, the eggs hatched. I saw four baby birds. The • Students at risk will often have difficulty in comprehension baby birds opened their beaks wide. I heard them peeping. Soon the mother bird came back. Then the mother robin put worms in their mouths. Every day I watched the baby birds and their mother. Pretty soon the babies were so fat there was no room for the mother. Then one morning the nest was gone from the bush. Overview of DIBELS Measures Oral Retelling Fluency • Grades administered: mid-year first to third grade • Measures: Comprehension of the passage read orally • Children generally use about half the number of words in their retell that they read aloud in a 1minute passage Overview of DIBELS Measures Word Use Fluency • Grades Administered: Kindergarten through Third grade • Measures: Vocabulary knowledge and expressive language Overview of DIBELS Measures Daze • Grades Administered: Third through sixth grade • Measures: Comprehension Strengths & Weaknesses • • Strengths • • • Progress monitoring Assesses all NRP areas Relatively brief • Pressley, Hilden, & Shankland (2005) Weaknesses • • • • Predictive Power Emphasis on speed vs. comprehension Cost The Truth About DIBELS: What It Is, What It Does (Goodman, 2006) • “Barking at print?” (Samuels, 2007) Computer-Based Assessment of Reading Computerized Assessment • Star Reading • http://www.renaissance.com/Products/StarAssessments/STAR-Reading • Linked to Accelerated Reader • Read 180 • http://www.scholastic.com/read180/index.htm • DORA and DOMA • http://www.letsgolearn.com/lglsite/products/ • Total Reader • www.totalreader.com/index.php?fuseaction=home.faq Lexiles • Computer-generated • Sophisticated but user-friendly system to track student progress over time and to link students to appropriate level texts • Ranges from 200 (beginning reading) to 1700+ (advanced readers) • Students and books can be matched along the continuum of Lexile scores • Common Core State Standard Lexile bands define expected levels (in Lexile scores) of reading for each grade level Special Considerations for Young, Adult and English Language Learners Special Considerations in the Informal Assessment of Young Children • May want to use portfolios to keep track of student progress • 8 essential literacy skills for Kindergarteners • • • • • • • • Letter/sound associations Phonological awareness skills Print concepts Phonemic segmentation/representation Word reading Word writing Text reading Text writing Special Considerations in the Informal Assessment of Adults • Text Box 5.1 • Adults learning to read are typically sensitive, and in some cases, ashamed • Take time to establish rapport • Assessment materials should be based on adult themes (e.g., work, family life) • Assess various areas of reading, rather than assuming possession of basic word analysis skills • Assess oral reading rate; if 125 wept or less, further assessment is needed • Use stronger vocabulary acquired through life experiences as a building block of reading Special Considerations in the Informal Assessment of English Language Learners • Text Box 5.2 • 4 categories of ELLs • • • • Newly arrived students with limited formal schooling Newly arrived students with adequate formal schooling Students exposed to two languages simultaneously Long-term English-language learners • Assessments should match the literacy background and knowledge base of the student • Ensure assessments conform to the general assessment standards set by the Teachers of English to Speakers of Other Languages (TESOL; www.tesol.org/) Assessment at a Glance: Criterion Referenced and Progress Monitoring • Tables 5.5 and 5.6 • Characteristics of Informal Assessment and Progress Monitoring Measures • Psychometric Properties of Informal Assessment and Progress Monitoring Measures Summary • The Assessment Continuum • Reliability and Validity • Criterion-Referenced Assessment • Progress Monitoring • Computer-based Assessment of Reading • Special Considerations for Young, Adult and English Language Learners