Test Review for Astronomy Unit
advertisement

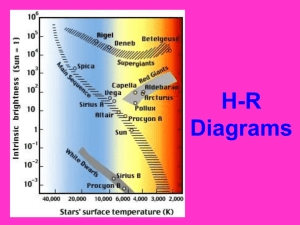
Name ________________________________________________ Class Period _______ Test Date:_________________ Test Review for Astronomy Unit 1. Which telescope did scientists use to show that most galaxies have black holes in their centers? _________The Hubble Telescope_________________________________________ 2. What is a light year? ___ distance light travels in one year_____________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. Is a light year a measure of time or distance? ____distance___________________________________ 4. Why do we use light years instead of km to measure the distance to stars? The distances to stars are so large that km is not a very practical unit. Light years is easier to calculate. 5. What is a spectrograph? A spectrograph breaks the light from an object into colors and photographs the resulting spectrum. It helps us to get information about stars. 6. A scientist was looking at a star that was 20 light years away. All of a sudden the star went dark. When did the star stop glowing? ____20 years ago___________________________ 7. What are the three ways in which we classify stars? __size_______, _____temperature__________, and ______brightness________ 8. What are the largest stars called? _____super-giants_____________________________ 9. What size star is the Sun? _____medium-sized star_______________________________ 10. Compare absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude. Absolute magnitude is the brightness the star would have if it were a standard distance from Earth and apparent magnitude is how bright a star appears to be when seen from Earth. 11. Number the star colors from coolest to hottest (1 means coldest and 4 means hottest): __3__ yellow __2__ orange ___4__ blue-white ___1__ red 12. After a white dwarf stops glowing, it becomes a ___black dwarf________. 13. How bright a star looks from Earth depends upon its ___distance from Earth______ and __its actual brightness________. 14. According to the Big Bang Theory, the universe is ___expanding________ Because galaxies are moving ____away_______ from each other. 15. What evidence is used to support the Big Bang Theory? The shifting of light from galaxies to the red end of the spectrum, the cosmic background radiation left over from the explosion, and the abundance of the light elements (H and He) found in the universe. 16. Our solar system is located in the Milky Way galaxy, which is what type of galaxy? __spiral galaxy_____. Draw a picture of what it looks like: 17. Which type of galaxy has little gas and dust? ____Elliptical________ 18. Which type of galaxy has a lot of gas and dust? ____Spiral____________ 19. At what point in the life cycle of a star, do we consider it “born?” when nuclear fusion starts ____________________________________________ 20. All stars begin as a mass of gas and dust called a _ nebula (gravity holds it together _. 21. When the most massive stars explode, they form _Black__ __holes__. 22. An explosion of a giant or super-giant star is called a __Supernova__, and the material left behind can form a ____neutron_____ star. 23. The lifetime of a star depends upon the star’s ___mass___. The larger the star, the ___shorter____ the lifespan; the smaller the star, the ____longer________________________ the lifespan. Use the diagram to the right To answer questions 24-27. 24. I’m thinking of a star that is blue-white, very bright, and a Supergiant. Which star am I thinking of? _______Rigel__________________ 25. Name all the yellow stars that are also Main sequence stars: Procyon, Sun, Alpha Centuri A, Tau Ceti 26. Compare the North Star (Polaris) and Betelgeuse in terms of temperature, brightness, and size. North Star is hotter, Betelguese is a little brighter, both stars are supergiants 27. What pattern do you see in temperature and brightness among main sequence stars? As the temperature of the main sequence star increases, its brightness increases. 28. I have a telescope that detects wavelengths up to 1.41 x 10-9 Hz. What type of waves can this telecope see? ______Ultraviolet_______________________________________________________________ 29. I have another telescope that detects wavelengths only up to 3.2 x 10-7 Hz. What type of wave can this telescope see? ________Visible______________________________________________________________