Early American Civilization - Baltimore City Public School System
advertisement

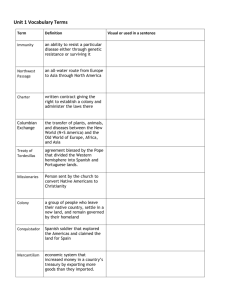
United States History Mr. Novak Warm-up- (1) Examine the image carefully. Record in your notebook any information that you see while looking at the picture. Look in the foreground and background of the picture. Pueblo Camp Ojibwa Camp The First Americans • Native Americans have many stories explaining the origin of their people. • Do you know any stories about the origin of people? The First Americans • Some groups believe they were created by gods. • Some believe they were created by Mother Earth. The First Americans • Scientists today believe that Native Americans migrated to North America from Asia. • Scientists think that during the last Ice Age a land bridge called Beringia opened up allowing people to cross from Asia to North America. • Scientists believe that this crossing occurred between 30,000-12,000 years ago. The First Americans • Until about 5,000 years ago most Native American groups were huntergatherers. • Around 5,000 years ago groups in Mexico became agriculturists and domesticated animals. Early American Civilizations • The earliest civilizations in the Americas arose in central Mexico and stretched down to where Nicaragua is today. Early American Civilizations • The Olmec civilization lasted from about 1200 B.C.E to about 400 B.C.E. • The Olmec built earthen mounds, built great cities, and traded with groups around them. Early American Civilizations • Around 650 years after the Olmec the Maya built a great civilization in southern Mexico. • The Maya had an accurate calendar, built pyramids and temples, and where the first in the Americas to use a system of numbers that included zero. Early American Civilization • Between 1200 and 1535 AD, the Inca population lived in the part of South America extending from the Equator to the Pacific coast of Chile. Early American Civilization • Polytheistic religion- Pantheon headed by Inti-the sun god • offered food, clothing, and drink • rituals included forms of divination, sacrifice of humans and animals Early American Civilization Economic Developments • constructed aquaducts, cities, temples, fortresses, short rock tunnels, suspension bridges, 2250mi road system • metal works of alloy, copper, tin, bronze, silver gold • developed important medical practices- surgery on human skull, anesthesia • resources-corn, potatoes, coffee, grain • created woven baskets, woodwinds • Upon the arrival of Europeans, Native Americans lived throughout the continents of North and South America. • Each group had a distinct culture, language and history. Jig Saw Activity • In groups of three you will research one Native American region and the groups that lived there • You will create a short presentation related to the geography region and the culture of this region • You will teach your classmates about this region • Assessment will be based on your presentation and the knowledge gained by your classmates PREVIEW 1/WARM-UP 1 Carefully EXAMINE the transparency of the coastal plain. IMAGINE you have suddenly been placed in this environment, and you must survive there for a year. In the space below, DESCRIBE the shelter you would build, the clothing you would make to protect yourself from the elements, and the tools you would create to acquire food. TELL why you designed the items the way you did. MENTION the natural resources you would use. History Alive! Text • Open your textbook to page v. • Active Instruction, multiple intelligences, cooperative, builds background knowledge • Reader friendly textbook and short chapters • Graphic organizers • Turn to the Table of Contents Analyzing Native American Artifacts Turn to Reading Notes 1 in their Interactive Student Notebooks. Review the directions for the activity. • Each pair goes to a station and examines the artifacts shown on the placard. • Using the four maps on pages 4 and 5 in History Alive! The United States Through Industrialism, pairs try to determine the Native American cultural region from which the artifact came. They write the letter of the placard in the appropriate box on their Reading Notes and have you check their answers. • Pairs then fill in three features of the environment of that cultural region, using only the artifacts as clues. • Students read the corresponding section in their books. They correct any misinformation they filled in concerning the environment. Then they write a short journal entry that mentions the three artifacts on the placard and three features of the environment. California H •Cone shaped houses of bark or leaves •Wild plants, animals, seeds, berries, and nuts •Plant materials Today my mother woke me up to go pick berries, while my brothers went fishing. I came to our dome house and had some berry soup and nuts. I had to repair my grass skirt because I fell while playing in the woods. Warm-Up Create a glossary of terms in your notebook for the following: Use pages 2-3 in your textbook. 1. Migrate2. Environment3. Natural Resources4. Culture5. Cultural RegionHomework- Write a short story using the five terms. (One paragraph) Warm-UP 1.2 Answer the following questions in your notebook How do scientists think people first migrated to the Americas a. They walked from Asia across the Beringia land bridge. b. They sailed from Polynesia in large canoes. c. They paddled across the Bering Strait from Siberia in Kayaks. d. They rowed from Iceland in sturdy wooden boats. Native Americans of the Southeast built a. adobe villages on desert mesas. b. towns clustered around large earth mounds. c. villages of longhouses in the forest near streams. d. underground pit houses beside major rivers. Native Americans living on the Northwest Coast got most of their food from a. buffalo herds. b. desert plants. c. their own farms. d. rivers and the sea. Native Americans of the Southwest adapted to a desert climate by building a. thick walled adobe houses. b. wooden houses out of cedar logs. c. movable tipis made of buffalo skins. d. homes clustered around mounds. Great Basin Northwest Coast Eastern Woodlands California Plateau Southwest Great Plains Southeast • Low region between the Sierra Nevada Mountains and the Rocky Mountains • Dry desert climate • Homes made of poles and covered with grasses • Ate ducks, duck eggs, snakes, seeds and berries The Great Basin • Land includes mountains, canyons, deserts, and rivers • Hot and dry climate • Used adobe bricks to build massive houses • Ate corn, squash and beans • Wore clothing made of cotton The Southwest • • • • • • Cold winters and wet, warm summers Forests, lakes and streams Ate deer, beaver, birds and fish Grew corn Used canoes for transportation Built log homes with the wood from the forest The Eastern Woodlands • Treeless grasslands • Area stretches from the Rocky Mountains to the Mississippi River • Part of this region has good soil • Part of this region is dry grassland • Hunted buffalo • Used buffalo hides for clothing and blankets • Built tipis with poles and buffalo skins The Great Plains • Flatlands, hills, steep valleys and large rivers • Long cold winters, and mild summers • People built villages along major rivers • Built pit houses partly underground • Hunted deer and used hides for clothing and blankets • Fished and gathered wild plants The Plateau • Coastal plains, river valleys, mountains and swamps • Long warm summers and mild winters • Farming was a major activity • Men hunted using blowguns • Wore short deerskins skirts • Part of this region is dry grassland • Built large earth mounds for burial • Built rectangular wood houses and pointed roof The Southeast • Ocean storms, winter rains, and hot dry summers • Deserts, large forests and ocean coast • Ate salmon and shellfish • Some groups hunted deer with bows and arrows • Gathered berries and nuts • Wore skirts made of grass and animal hides in the colder months • Wove thick grass mats and made cone shaped houses California • • • • • • Thick forests and mountains Heavy rain most of the year Cold winters and cool summers Ate mostly seafood and hunted using harpoons Used thin boards to build large homes Used bark from trees to make clothing and blankets • Built tools from bones and stone The Northwest Coast PROCESSING 1 Create an annotated diagram showing the climate, land, and adaptations made by Native Americans in one cultural region. Use textbook pages 8-13 as a guide. In your diagram, use words and pictures to describe the land, climate, and adaptations of the Native Americans. See the example in your handout. Seating Chart Shakierra Jacob Myeshia Asia, Bobbi Eric S., Curtis Michael Eric , Raqua Karol, Maria Cortez, Dara Eric, Oscar Claudia, Erin Richard, Rogelio Dimit, Noun Che PREVIEW 2 Historical Connection (Age of Exploration 1490’s) Classroom Experience • groups of students • You Drew a map to help you navigate the classroom • European nations, such as England, France, the Netherlands, and Spain claimed land in North and South America • • Students walked around the classroom to CLAIM furniture. • Students CLAIMED furniture with sticky notes. • One group had directions that allowed them to begin labeling furniture sooner. • Other groups rushed to catch up with the first group. • The first group had 30 sticky notes and could claim more pieces of furniture. European nations used maps to explore the world • European explorers sailed across the Atlantic Ocean to the Americas. • European explorers used national flags to stake territorial claims for the countries they sailed for. • Spain was the first European country to claim land in the Americas. • Portugal, England, France, and the Netherlands later competed with Spain for land in the Americas. • Spain sent many explorers to the New World and claimed an enormous amount of territory in North and South America. European Territories in the Americas 1. Which European countries claimed territories in the Americas? 2. Which European country claimed the most territory on the map? Read Section 2.2 in the History Alive textbook pages 18-21. Complete Reading Notes 2.2 after reading Section 2.2 in your textbook. 2.2 Spain Starts an Empire did Spain establish How did Spain establishHow territorial claims in the territorial claims in the Caribbean and South America? Caribbean and South America such as Spain sent explorers Christopher Columbus, Hernan Cortes, and Francisco Pizarro to discover and claim lands for Spain. 2.2 Spain Starts an Empire What was life like in Spanish settlements in the Caribbean and South America? Most Spanish settlers were interested in finding gold, and some started sugar plantations. At first, settlers forced Native Americans to work for them as slaves. When the native people began to die from European diseases and over work, slave traders provided enslaved Africans as workers. 2.2 Spain Starts an Empire What type of relationship existed between the Spanish and Native Americans living in the Caribbean and South America? The Spanish treated Native Americans living in the Caribbean and South America harshly. Cortes attacked the Aztecs in Mexico. Pizarro conquered the Incas in Peru and killed their leader Atahulpa, even though the Incas had given Pizarro the gold he demanded. Explorers also brought diseases such as smallpox that killed many natives. 2.3 The Spanish Borderlands How did Spain establish territorial claims in North America? Several explorers established Spanish territories in North America. Ponce de Leon explored Florida. Francisco Coronado traveled as far north as the Great Plains in search of cities of gold (Cibola). All he found were seven pueblos, or villages. 2.3 The Spanish Borderlands What types of permanent settlements did the Spanish establish in North America? Spanish soldiers established forts called presidios to protect Spanish lands. Catholic priests, anxious to convert Native Americans, established missions. 2.3 The Spanish Borderlands What type of relationship existed between the Spanish and Native Americans living in North America? The Spanish and Native Americans learned many things from each other. Pueblo people learned how to use new tools, grow new foods, and raise sheep for wool. Many Native Americans converted to Christianity. From the Native Americans, the Spanish learned new ways to farm. Many Native Americans were made slaves by the Spanish. The Spanish brought deadly diseases. Native Americans sometimes attacked the Spanish. Act it Out Columbus, Soldier, Priest • Where are you from? • What do you think of these people you have found here? • Where do you think you have landed? • What did you expect to find? • Why are you carrying swords? • Why have you brought a priest? Act it Out Taino Indian • Who are you? • Why do you think these men have come? • What do you find most unusual about these new people? • Will you treat these men as friends or enemies? Why or why not? Act-it-Out Rubric Team Planning Students planned well together. The entire team was part of the planning process. 20 Presentation Creativity Students did not work well together. Only a few of the team members worked on the assignment. 10 Students were prepared to answer the interview questions. All students demonstrated knowledge of the topic. Students were not prepared to answer the interview questions, and did not demonstrate knowledge of the topic. 20 10 Students used props, and other materials to bring the act-it-out to life. Students did not use props or other objects to create a realistic act-itout. 20 10 This flag belongs to which country? France France is on which of the seven continents? Europe What language do they speak in France? French What places in North America do people speak French? Parts of Canada New Orleans Haiti The West Indies How did the French establish territorial claims in North America? Explorers established French claims in North America. Jacques Cartier claimed Canada. Samuel de Champlain established a trading port in Quebec. Father Marquette and Louis Joliet explored the Mississippi River. Robert de La Salle claimed Louisiana. What was life like in French settlements in North America? Fur trappers, or coureurs de bois, and missionaries came to New France. The colony failed to attract many settlers because of the harsh climate and the colony’s policy of giving the best land to wealthy nobles. What type of relationship existed between the French and Native Americans living in North America? The French made the Native Americans their trading partners. A friendly relationship existed between the French and the Huron. European disease killed many Native Americans. VSC 8.5.B BCR 1 Explain the reasons why the following groups began settling the Americas? (2 Paragraphs) • The Spanish • The French How did this settlement affect Native Americans? (1 Paragraph) How did England establish territorial claims in North America? John Cabot’s brief landing in New foundland established English claims in North America. The English also established settlements in Virginia. What was life like in Jamestown? Life was difficult for the settlers in Jamestown. Their settlement was located in a swap were disease carrying mosquitoes bred. Settlers were not able to provide for their needs. Captain John Smith took over leadership, and conditions improved. The settlers went through a starving time, and Native Americans would not trade with them. What type of relationship existed between the English and the Native Americans living around Jamestown? Captain John Smith became friends with the Native Americans. The daughter of the chief, Pocahontas, helped the colonists avoid starvation. Although the Native Americans refused to trade with settlers during the Starving Time, relations improved when John Rolfe married Pocahontas. New Spain After Columbus’ lAnding in north AmeriCA mAny spAnish explorers like Hernan Cortes, and francisco pizarro followed and claimed land for spain. The spanish claimed land from modern day florida, down into south america. The spanish searched for cibola, and the fountain of youth. While seeking riches in north america they enslaved native americans, and conquistadors conquered native american land. As a result of the spanish arrival more than ninety percent of native americans died in some areas. New spain flourished. The gold they found and the sugar plantations provided wealth for spain. Title and Visuals Student’s work contains a title and visuals for each point Student’s work does not contain a title and/or visuals Summary Student has answered all three questions Student did not answer all three questions Grammar and Spelling Student’s writing is free of spelling and grammatical errors Student’s work contains spelling and grammatical errors Chapter Three Vocabulary • • • • • • Indentured Servant Cash Crops Assembly Democratic Puritans Slave Trade Vocabulary Assessment on 12/3/2008 Complete the following in your notebook. 8 13 3 10 12 6 5 1. Into what three regions were the 13 English Colonies divided? 2. Label the 13 English Colonies. 9 4 1. 7 1 11 2. North Carolina Georgia 3. Connecticut 4. Delaware 5. New Jersey 6. Rhode Island 7. Virginia New Hampshire 8. 2 9. Maryland 10. 11. New York South Carolina 12. Pennsylvania 13. Massachusetts 13 Colonies Game!!! Massachusetts is the place to be, God fearing folk keep you company. Life by the sea, a good economy. Keep your tropical breeze give me Massachusetts please. Political Cartoon Analysis • Analyze the political cartoon on page 3 in your Current Events magazine. • Write down what point you think the cartoonist is trying to make. Colonial Fair Walk-About • Two Students from the group will man the booth and present their colony to visitors • Two students from each group will visit all of the other booths and complete the Reading Notes for each colony • Groups will have 15 minutes to make it to each of the booths Closing Activity • Go back to your Reading Notes and complete the scale for each Colony. • Rank each Colony with 1 being the Colony you would most like to settle in. • If you had your choice, which colony would you settle? Which colony would you not settle in? What factors contributed to your choice? Complete the following in your notebook. 8 13 3 10 12 2. Which European country controlled the 13 Colonies? 6 5 2. Label the 13 English Colonies. 9 4 7 1. Into what three regions were the 13 English Colonies divided? 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 5. Delaware New Jersey 6. Rhode Island 7. 11 8. 9. 10. 2 North Carolina Georgia Connecticut Virginia New Hampshire Maryland 11. New York South Carolina 12. Pennsylvania 13. Massachusetts