Making it Work: The Volatile 1790's
advertisement

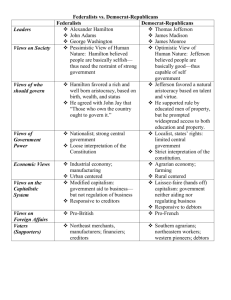
Lecture 3: Making it Work – the Volatile 1790’s The Early Republic (1789-1820) Problems: Internal: Uneducated masses Monarchy Legislature External: Spain, Great Britain, France The Early Republic (1789-1820) Tremendous growth: Population: 1790 - 3.9 mil; 1820 - 9.6 mil Cotton export: 1794 - 2 mil; 1820 - 128 mil Total US export: 1791 - $19 mil; 1807 - $108 mil Geographic expansion Washington’s Presidency Washington’s election Setting precedents Title 1st lady Cabinet: State: Jefferson Treasury: Hamilton War: Knox VP: Adams Chief Justice: Jay Rivalry in the Cabinet Jefferson vs. Hamilton Jefferson vs. Hamilton Jefferson: French Rev. Contradictions “Republican” States Ties to France Agrarian, expansive nation Hamilton: Illegitimate, immigrant Aide to GW “Federalist” National govt. Ties to England Urban, industrial nation Conflict between order and liberty Washington’s Presidency The 1st party system: Federalists and Republicans The volatile 1790s: Yellow fever Financial panics Taxpayer revolts Violent protest Sedition act Fights in congress The Duel Parties: Principled, yet compromise The Presidency Washington’s Presidency Republican party first Washington’s presence House of Representatives Federalist rule Hamilton’s winning streak: Fund debt,; taxes; national bank Shades of British system Repay war debt (Madison system rejected) Assumption of state debt (Madison rejected) Whiskey tax National bank How to fight back? Rally public opinion! Washington’s Presidency The newspaper war Freneau, National Gazette Fenno, Gazette of the United States The 1792 campaign Media Letters Pamphlets Madison’s reversal Hamilton’s attacks The 1792 election Washington’s Presidency Foreign affairs: France or Britain? “Independent Internationalism” Commercial alliances Stay out of war Westward expansion 1793 Proclamation of Neutrality Treaties with England and Spain (Jay’s Treaty and Pinckney’s Treaty) Washington’s Presidency Election of 1796 Farewell Address No entangling alliances John Adams as President Conflict with France “X,Y,Z Affair” The Federalists unravel: Immigration Alien & Sedition Acts Standing army Taxes The Sedition law The Virginia and Kentucky Resolutions Jefferson as President The Election of 1800 The “Revolution of 1801” Marbury v. Madison Judicial review Louisiana Purchase Haitian slave rebellion Embargo Act Mr. Madison’s War Causes of the War of 1812 Impressment Leopard/Chesapeake Economic warfare Indian attacks Canada? Mr. Madison’s War War of 1812 Treaty of Ghent Results of the war: National pride Westward expansion Military growth Transportation