File
advertisement
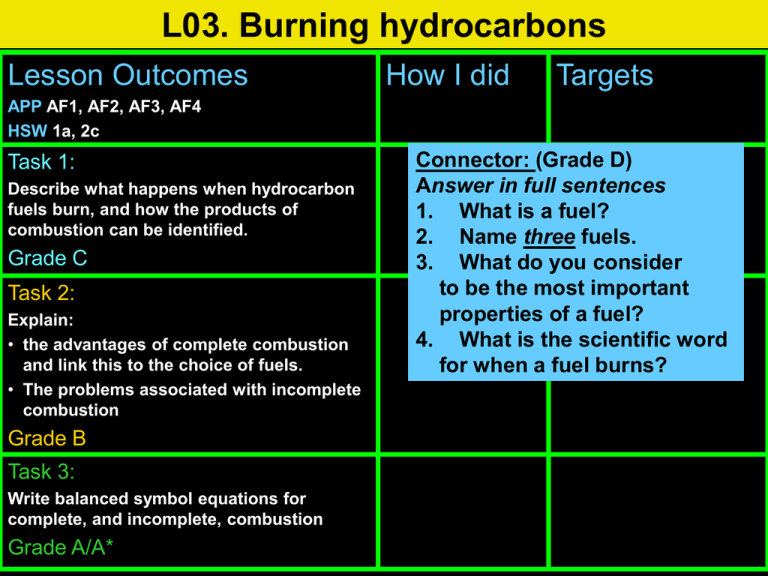
L03. Burning hydrocarbons Lesson Outcomes How I did Targets APP AF1, AF2, AF3, AF4 HSW 1a, 2c Task 1: Describe what happens when hydrocarbon fuels burn, and how the products of combustion can be identified. Grade C Task 2: Explain: • the advantages of complete combustion and link this to the choice of fuels. • The problems associated with incomplete combustion Grade B Task 3: Write balanced symbol equations for complete, and incomplete, combustion Grade A/A* Connector: (Grade D) Answer in full sentences 1. What is a fuel? 2. Name three fuels. 3. What do you consider to be the most important properties of a fuel? 4. What is the scientific word for when a fuel burns? 1. A fuel is a substance that contains stored chemical energy. When fuels are burned in the air (with oxygen) they release heat and light energy. 2. petrol, wood, ethanol, coal, macaroni, sugar, etc. 3. A good fuel would release a lot of heat energy with little or no polluting or harmful by-products. 4. Combustion BIG picture • What skills will you be developing this lesson? • • • • • • • • • ICT Numeracy Literacy Team work Self management Creative thinking Independent enquiry Participation Reflection • How is this lesson relevant to every day life? (WRL/CIT) Task 1 (Grade C) • Task 1: Describe what happens when hydrocarbon fuels burn, and how the products of combustion can be identified. Keywords for Task 1: Combustion, Complete combustion Fuel Compounds containing H and C are called? Combustion fuel Many fuels like coal, oil, petrol, candle wax, and natural gas are called HYDROCARBONS The products of burning a hydrocarbon to pump water water and ice and ice limewater anhydrous cobalt chloride paper Hydrocarbons are compounds of carbon and hydrogen ONLY. When pure carbon is burned, carbon dioxide is formed and when hydrogen is burned, water is produced. 1. What happens to the anhydrous cobalt chloride paper? 2. What happens to the limewater? 3. Explain the significance of the above observations. Task 1: Review Go back to your lesson outcome grid and fill out the ‘How I did’ and the ‘Targets’ column. Lesson Outcomes Task 1: Describe what happens when hydrocarbon fuels burn, and how the products of combustion can be identified. Grade C How I did Met? Partly met? Not met? Targets How can I improve on task 1? Task 2 (Grade B) • Task 2: Explain: – the advantages of complete combustion and link this to the choice of fuels. – The problems associated with incomplete combustion • Task 2: Extension Keywords for Task 2: • • • • • • • • Combustion, Complete combustion, Fuel Carbon monoxide, Incomplete combustion, Pollution, Soot, Toxicity From the pictures below,achoose best fuel. What makes good the fuel? Explain your choice. Yellow flame, soot Blue flame, no soot Yellow flame, soot, ash (residue) Summary exercise energy • Fuels contain stored __________ . When fuels oxygen burn they react with __________ in the air and heat give out __________ energy. This is called a combustion reaction. Most fuels contain carbon __________ hydrogen and __________ atoms. When the fuel burns these atoms react with oxygen to make carbon water __________ dioxide and __________ . carbon combustion energy heat hydrogen oxygen water Lots of oxygen: Complete and incomplete combustion Methane + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + Water Carbon + monoxide Water This is called Complete combustion Some oxygen: Methane + Oxygen This is called Incomplete combustion Little oxygen: Methane + Oxygen Carbon + Water (soot) This is also called Incomplete combustion To get complete combustion the fuel must be burned in EXCESS O2. The hazard of incomplete combustion Why did the man die? Less amount of available oxygen caused the release of colourless, odourless, poisonous carbon monoxide. Incomplete combustion Carbon monoxide Edexcel video Question Homework • Homework task: • Due date: • Criteria for Grade C: • Criteria for Grade B Summary oxygen • When a fuel burns with a good supply of __________ to complete form carbon dioxide and water it is called __________ combustion. When a fuel burns without a good enough monoxide supply of oxygen and forms deadly carbon __________ incomplete combustion. (and/or soot) and water it is called __________ Incomplete combustion can happen in faulty gas boilers if intake their air __________ vent is blocked. Carbon monoxide is a odourless colourless , toxic gas. It kills because it __________ , __________ oxygen stops your blood from carrying __________ . colourless complete incomplete intake monoxide odourless oxygen oxygen Task 2: Review Go back to your lesson outcome grid and fill out the ‘How I did’ and the ‘Targets’ column. Lesson Outcomes Task 2: Explain: • the advantages of complete combustion and link this to the choice of fuels. • The problems associated with incomplete combustion Grade B How I did Met? Partly met? Not met? Targets How can I improve on task 2? Task 3: (Grade A/A*) • Task 3: Write balanced symbol equations for complete, and incomplete, combustion • Task 3: Extension Keywords for Task 3: • incomplete combustion • complete combustion Combustion of methane 1. 2. Write the word equation for combustion of methane. Write a balanced symbol equation for the combustion of methane. Write the balanced symbol equations for these reactions: + Extension task • Some camping gas stoves run on propane gas. Propane molecules have the formula C3H8. • (a) What new chemicals are produced when you burn propane? • (b) Write a word equation for the combustion reaction of propane. • (c) Write a balanced formula equation for this reaction. (Hint: you will need five oxygen molecules for every propane molecule.) Task 3: Review Go back to your lesson outcome grid and fill out the ‘How I did’ and the ‘Targets’ column. Lesson Outcomes Task 3: Write balanced symbol equations for complete, and incomplete, combustion Grade A/A* How I did Met? Partly met? Not met? Targets How can I improve on task 3? Review of lesson – a selection of past paper questions Question Can you explain these key words? Combustion, complete combustion, Fuel Carbon monoxide, incomplete combustion, pollution, soot, toxicity Technicians’ list Demonstration 1 Eye protection Two gas jars of oxygen Deflagrating spoon Two stoppered boiling tubes of hydrogen Dry cobalt chloride paper (blue) Forceps Splints Limewater (corrosive) Charcoal Demonstration 2 Combustion rig







