Types of Stars
advertisement

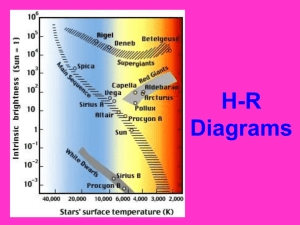
Stars Distances To The Stars • Stars are separated by vast distances. • Astronomers use units called light years to measure the distance of stars • A light-year is the distance that light travels in a vacuum in a year • Proxima Centauri, is the closest star to the sun. Measuring_Distance_in_Space__The_Light_Year Parallax • Astronomers have developed various methods of determining the distance of stars. • The change in position of an object with respect to a distant background is called parallax. • As Earth moves in its orbit, astronomers are able to observe stars from two different positions. • Astronomers measure the parallax of nearby stars to determine their distance from Earth Properties of Stars • Astronomers classify stars by their color, size, and brightness. Other properties of stars are chemical composition and mass. • Color and Temperature – a stars color indicates the temperature of its’ surface. • The hottest stars appear blue • The cooler stars appear red • The spectrum of color in a star is from blues to greens to yellows and reds. The_Color_of_Stars Brightness • • • • The brightness of a star as viewed from Earth is dependent on many factors such as color intensity and distance. Apparent Brightness – is the brightness of a star as it appears from Earth. The apparent brightness decreases as its distance from you increases Absolute Brightness – is how bright a star really is. The absolute brightness is a characteristic of the star and is not dependent on its distance from Earth. Composition • Each star has its own spectrum. • Most stars have a chemical makeup that is similar to the sun, with hydrogen and helium together making up to 96 to 99.9 % of a star’s mass. How Stars Form • A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust spread out over a large volume of space. • Some nebulas are glowing clouds lit from within by bright stars. • A star is formed when a contacting cloud of gas and dust becomes so dense and hot that nuclear fusion begins. How_Stars_Form Life Cycles of Stars • Adult Stars – A star’s mass determines the star’s place on the main sequence and how long it will stay. • The amount of gas and dust available when a star forms determines the mass of each young star. • The larger the star the more energy produce. • Since blue stars burn brightly, they use up their fuel quickly and are short lived. The_Life_Cycle_of_Stars.asf The Death of a Star • The dwindling supply of fuel in a star’s core leads to the star’s death as a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole. Dying_Stars_and_Conclusion .asf Groups of Stars • Astronomers have determined that more than half of all stars are members of star systems. • There are three basic kinds of star clusters: open clusters, associations, and globular clusters. • Astronomers classify galaxies into four main types: spiral, barred-spiral, elliptical, and irregular. Expanding Universe • The observed red shift in the spectra of galaxies shows that the universe is expanding. • Astronomers theorize that the universe came into being in an event called the big bang. • Dark matter can only be detected by observing its gravitational effects on visible matter. Beyond_the_Milky_Way_and_Back_Into_Time.asf Spin_Around_the_Solar_System__A__Look_to_the_Stars