Star Classification
advertisement

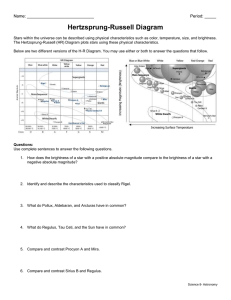
Chapter 11: Characterizing Stars WHAT DO YOU THINK? How near is the closest star other than the Sun? Is the Sun brighter than other stars, or just closer? What colors are stars? Are brighter stars hotter? What sizes are stars? Are most stars isolated from other stars, as the Sun is? Apparent Magnitude Scale – brightness of a star as seen from Earth Several stars in and around the constellation Orion labeled with their names and apparent magnitudes Astronomers give the brightness of objects in the sky by apparent magnitudes. Stars visible to the naked eye have magnitudes between m = –1.44 and about m = +6. The Inverse-Square Law The farther a star is from Earth, the dimmer it looks to us. Doubling the distance makes the star look one-fourth as bright. Tripling the distance decreases the star’s brightness by a factor of 9. Absolute Magnitude – the actual brightness of a star Absolute magnitude tells how bright a star really is, no matter how far from Earth it is. Are the car lights actually dimmer as the car moves away? No. Their actual brightness (absolute magnitude) is the same no matter the distance. But they look dimmer (apparent magnitude) to us when the car is farther away. Temperature and Color (review) Hottest = blue color Medium = orange/yellow color Coolest = red color Spectral Classes (Color and Temperature) “Oh, Be A Fine Guy/Girl, Kiss Me!” HertzsprungRussell (HR) Diagram (Textbook page 305) Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) Diagram Star brightness is plotted against star spectral types (color / temperature). Brightness and spectral type are related. Main-sequence stars (fusing hydrogen to helium) fall along the red curve. Giants are to the upper right and super-giants are on the top. White dwarfs are below the main sequence. HR Diagram Basics Thanks to Dan Enriquez Star Size Is Also Important Hotter stars are brighter than cooler stars (of the same size). Bigger stars are brighter than smaller stars (of the same temperature). So the brightest stars are the biggest, hottest ones. L = R2T4 (L = brightness, R = radius, T = temperature) Mass-Temperature-Brightness Each dot = a mainsequence star. The dot’s number is the mass of that star in solar masses (Sun = 1). Mass, brightness, and temperature of main-sequence stars increase from lower right to upper left. WHAT DID YOU THINK? How near is the closest star other than the Sun? Proxima Centauri is about 40 trillion kilometers (25 trillion miles) away. It takes light about 4 years to reach the Earth from there. How luminous is the Sun compared with other stars? The most luminous stars are about a million times brighter and the least luminous stars are about a hundred thousand times dimmer than the Sun. What colors are stars? Stars are found in a wide range of colors, from red through violet, as well as white. WHAT DID YOU THINK? Are brighter stars hotter than dimmer stars? Not necessarily. Many brighter stars, such as red giants, are cooler but larger than hotter, dimmer stars, such as white dwarfs. What sizes are stars? Stars range from more than 1000 times the Sun’s diameter to less than 1/100 the Sun’s diameter. Are most stars isolated from other stars, as the Sun is? No. In the vicinity of the Sun, two-thirds of the stars are found in pairs or larger groups.