File
advertisement

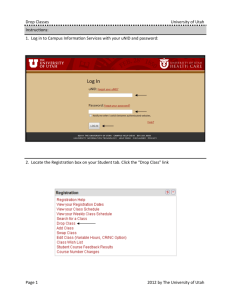
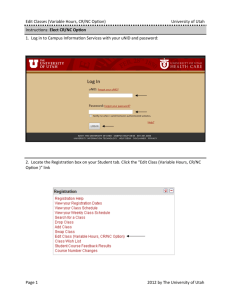
Utah’s statehood Packet Name__________________________ Period_________________________ Anti-Polygamy Acts Chapter 9 Use the yellow box on Pg.173 to complete these notes of federal laws passed. 1. Morrill Anti-Bigamy Act ( ): Stated that no one could be time. No church in the territories could earn more than to more than one person at a worth of property. This bill was not heavily enforced. 2. Poland Bill ( ): Gave jurisdiction to This reduced the influence of local 3. Edmunds Act ( _________________,or even 4. Edmunds-Tucker Act ( appointed judges. courts. ): Stated that imprisonment and a away the _______ courts with was punishable by fine. Convicted polygamists could not hold years of office, serve on a in elections. ): Required wives to testify against their husbands, and took from Utah women. Abolished the militia, and confiscated the property of the LDS Church. 5. Do you feel that Mormon polygamists had their rights protected by the government? Why? Federal Laws Timeline: Fill in the federal law that was passed in this year. 1862 1874 1882 1887 Statehood at Last : Chapter 10 For help with answers see page 182 Political Parties 1. The two original political parties in Utah were the Mormon “_____________ _____________” and the non-Mormon “ ______________ _______________”. The Newspapers took sides too. The _______________ ______________________ was usually the voice of the People’s Party, while The ____________ ____________________ ________________ leaned toward the Liberal Party. National Parties 1. In an effort to comply with the national two-party system, the LDS church dropped the ________________ ____________________ and encouraged its members to join one of the national parties. The _____________________Party and the _________________________Party were the two choices. The Liberal Party became less powerful. Democrat Joseph Rawlins introduced a ______________ to the U. S. ________________ for Utah’s admission to the union. It _____________________, with only ______________ opposing votes. Writing Utah’s Constitution: 1. U.S. President Cleveland finally authorized the draft a _____________ of Utah’s delegates to a convention. Their job was to for the new state. John Henry Smith was chosen as president of the convention . The________ delegates met at noon on _____________________ _______________ to write a constitution for Utah. Women’s Suffrage: 1. One of the most debated issues during the convention regarded who could ________________for _________________ and who could _______________________. 2. In Utah , women had ______________the right to vote in ______________but it was taken away in ________________________by the Edmunds-Tucker Act. Regaining the _________________to _______________ was an important aim of Utah _________________, many of whom had been involved in the national _______________________movement for many years. 3. The debate over __________________________ ____________________________was the longest debate in the convention . Women gain the right to vote! Prohibition 1. Many of Utah’s religious and civic groups pushed for a __________________________ section in the new Utah Constitution…..meaning they wanted to ____________ 2. making, selling, and drinking of _____________ in Utah. After much debate, the delegates decided to leave the _______________ alone. The Task Completed: 1. voters supported the constitution. 2. voters were against it. 3. The U.S. __________ and ___________________in Washington then reviewed it. 4. Utah became a state on January ____________, __________________. “Now therefore, I, Grover Cleveland, President of the United States of America…do hereby declare and proclaim that the terms of and conditions prescribed by the Congress of the United States to entitle the State of Utah to admission in to the Union have been duly complied with, and that the creation of said State and its admission into the Union on an equal footing with the original States is now accomplished.” -President Grover Cleveland, January 4, 1896 Utah’s Executive Branch Governor: Directs_________________government, Is the in chief of the National Guard, may present bills to ___________________, may call _________________sessions of legislature, signs(approves) or________________bills. Can pardon(_____________________________) people convicted of . Lieutenant Governor: Keeps of the legislature, performs other duties, and acts as _____________________when the governor is _____________or the _________________________. State Treasurer: Directs the of state . State Auditor: Looks after the state’s records. Attorney General: Performs duties for the governor and other offices. State Boards, Departments, and Commissions: Look after things such as safety, agriculture, land use and ___________________________,water, _______________,etc. Utah’s Judicial Branch Courts ____________________________the Law-----they determine if the law is ______________________________, and if a _______________has been broken. The job of the ________________________is to ensure the accused of a _________________trial. Federal, ____________________, county and _____________________courts operate in _________________. Utah state courts include the ________________________court, court of __________________________, district________________________, _______________________courts (for people under age 18), __________________courts and ___________________courts. Utah’s courts handle both __________________and _____________________cases. A __________________case is on ewhich involves_____________, contracts or ___________________rights. An example of a criminal case would be a _______________________, such as a bank robbery, or a ______________________(a lesser crime), such as disturbing the peace. ___________________also play an important role. They are made up of ________________________citizens who are called to _______________________for a short time. Juries listen to the witnesses and ____________________________, then ____________________on whether they believe a person is ____________________________or __________________________________. If the person on trial receives a “guilty” decision , he or she may _____________________ to a higher court for a new trial. Local Government What are the responsibilities of a County Government? What are the responsibilities of a City Government? How A Bill Becomes A Law! How does a bill become a law? (In 5 to 10 sentences)