Propaganda & Persuasive Techniques - MissDianaMiller-
advertisement

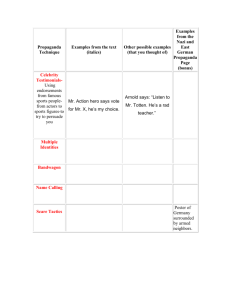
Propaganda & Persuasive Techniques CPEnglish 10 A famous example of propaganda…What do you know about this poster? Uncle Sam… •Originally published as July 6, 1916 magazine cover with the title "What Are You Doing for Preparedness?” •Went on to become--according to its creator, James Montgomery Flagg--"the most famous poster in the world." •Over four million copies printed between 1917 and 1918, as the US entered WWI and began sending troops and materials into war zones. •The image was later adapted for use in World War II. What is propaganda and what is its purpose? Definition - Information that is spread to support a cause Purpose – To create an emotional connection between the message and the reader Where do we find propaganda every day?? • Television • Magazines • Public Speeches • Political Campaigns • Can you think of more? Types of Propaganda Bandwagon “Everybody else is doing it.” Verizon Wireless Testimonial “It worked for me and it will work for you.” Bieber is Proactiv! Plain Folks The candidate or cause is identified with common people from everyday walks of life. Examples: Dress, Speech, Actions Political Ad *Don't get worked up about the politics. I am in no way imposing any views, nor am I revealing my stance on the election. I am simply being relevant. Transfer Symbols, quotes or images of other people or ideas that convey a message not necessarily associated with them. Ideas of religion, science, etc. can be used in transfer propaganda as well. Darth Vader Kid Self-Review : What is bandwagon propaganda? 1. 2. 3. 4. “Follow the crowd” “It worked for me; it’ll work for you!” “I’m just like you!” Image that stands for a message Self-Review : What is plain folks propaganda? 1. 2. 3. 4. “Follow the crowd” “It worked for me; it’ll work for you!” “I’m just like you!” Image that stands for a message Self-Review : What is testimonial propaganda? 1. 2. 3. 4. “Follow the crowd” “It worked for me; it’ll work for you!” “I’m just like you!” Image that stands for a message Self-Review: What is transfer propaganda? 1. 2. 3. 4. “Follow the crowd” “It worked for me; it’ll work for you!” “I’m just like you!” Image that stands for a message Logical Fallacies • • A logical fallacy is, roughly speaking, an error of reasoning. When someone adopts a position, or tries to persuade someone else to adopt a position, based on a bad piece of reasoning, they commit a fallacy. EXAMPLE: • Premise 1: Greg supports gun control. • Premise 2: Communist regimes have always supported gun control. • Conclusion: Greg is a communist. Banned Political Ad Glittering Generalities • A generally accepted virtue is usually employed to stir up favorable emotions. U.S. Marines Name-Calling It is the use of derogatory language or words that carry a negative connotation when describing an enemy. Attempts to arouse prejudice among the public by labeling the target something that the public dislikes. Often, name calling is employed using sarcasm and ridicule, and shows up often in political cartoons or writings. Orbit Gum Card Stacking “One-sidedness” or leaving out the opposite side of the argument or only showing the good sides of the propagandist’s argument. Blockbuster: No More Late Fees Self-Review :What is a logical fallicy? 1. 2. 3. 4. An error of reasoning One-sidedness Derogatory language that carry a negative connotation A virtue accepted to stir emotions Self-Review :What is a glittering generality? 1. 2. 3. 4. An error of reasoning One-sidedness Derogatory language that carry a negative connotation A virtue accepted to stir emotions Self-Review :What is namecalling? 1. 2. 3. 4. An error of reasoning One-sidedness Derogatory language that carry a negative connotation A virtue accepted to stir emotions Self-Review :What is cardstacking? 1. 2. 3. 4. An error of reasoning One-sidedness Derogatory language that carry a negative connotation A virtue accepted to stir emotions Why do we care? • Understanding propaganda helps us make educated decisions. • Understanding propaganda helps us create it ourselves. • We use propaganda to PERSUADE. Persuasive Techniques (As seen on the OGT) 1. State the facts. 2. State the benefits. 3. State the author’s expertise. 4. Connect emotionally with the reader. The Greeks and Persuasion The Greek philosopher Aristotle divided the means of persuasion, appeals, into three categories--Ethos, Pathos, Logos. Ethos (ethical appeal) •Ethos (Credibility) means convincing by the character of the author •We tend to believe people whom we respect •Project an impression to the reader that you are someone worth listening to Pathos (emotional appeal) •Pathos (Emotional) means persuading by appealing to the reader's emotions. •Language choice affects the audience's emotional response •Emotional appeal can effectively be used to enhance an argument. Logos (logical appeal) •Logos means persuading by the use of reasoning. •Aristotle's favorite. •Deductive and inductive reasoning •Avoid common logical fallacies Persuasive Language Techniques •Rhetorical Questions- Sometimes a writer/speaker will ask a question to which no answer is required. The writer implies that the answer is obvious; the reader has no choice but to agree with the writer's point. •Example: teacher? Am I not your favorite English Geico Word Choice/Diction •Writers/speakers tend to reinforce their arguments by choosing words which will influence their reader's perception of an item or issue. Diction may also help to establish a writer's "Voice" or "Tone." •“Mask” or “Guise”? •“Disperse” or “Scatter”? Repetition/Parallelism Overly repetitive writing can become tiresome. However, when used sparingly for effect, it can reinforce the writer's/speaker's message. Writers/speakers may repeat a word, a phrase or an entire sentence for emphasis. Parallelism is the repetition of structure in sentences. Noble vs. Different ways of saying so Irony •Irony is present if the writer's/speaker's words contain more than one meaning. This may be in the form of sarcasm, gentle irony, or a pun (play on words). It can be used to add humor or to emphasize an implied meaning under the surface. Figurative Language •Language used to create a special effect or feeling •More than likely compares or exaggerates Hyperbole This is one of the more enjoyable persuasive techniques. It involves completely overstating and exaggerating your point for effect. (Like when I say, "I must have told you a million times how to setup MLA on your written assignments.”) If for some reason the videos would not play on the “movie screen” the links are provided below: Verizon Wireless http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=14CKzskjn4s&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode=1&safe=active Bieber’s Proactiv http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-fb5K7FOjI&feature=relmfu&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode=1&safe=active Political Ad http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7QSIIzbYRdo Darth Vader Kid http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R55e-uHQna0&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode=1&safe=active Banned Political Ad http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9Q8M-b7dOgk US Marines http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UwY67LYzH7Q&feature=related&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode=1 &safe=active Orbit Gum http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WEJJUGJZxpU&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode=1&safe=active Blockbuster http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=92S-S9vJ0PA&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode=1&safe=active Geico http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hxRoXuPjAKc