Modern Evolutionary Classification

Modern Evolutionary
Classification
Section 18-2
Which Similarities are Most
Important?
Taxonomic groups above species were
“invented” to distinguish between one family, phylum, etc., and another
Taxonomists have always tried to group organisms according to biologically important characteristics
Grouping organisms based on visible similarities and differences has its drawbacks
Ex. Dolphins
Fish? - live in water, have finlike limbs
Mammal? - breathe air and feed young
Evolutionary Classification
Phylogeny - study of evolutionary relationships among organisms
Prompted by Darwin and his descent with modification
Organisms grouped into categories that represent evolutionary descent
Evolutionary classification
What this means…
Species in a genus are more closely related to each other than they are with species of another genus
Reasoning: all members of a genus share a common ancestor
What this means…
All genera in a family share a common ancestor
Ancestor is further in past than ancestor of any genus in family
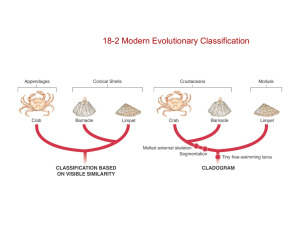
Crustacean or Mollusks?
Limpets and barnacles first classified on visible similarities
Similar shells, hole in shell, attached to rocks
Crustacean or Mollusks?
Barnacles - molt (shed exoskeleton), have joined limbs, body segments
Limpets - internal anatomy like snails, don’t molt
Barnacles are crustaceans, limpets are mollusks
Classification Using Cladograms
Shift made from evolutionary classification to cladistic analysis
Uses characteristics that are “evolutionary innovations” or new characteristics that arose as lineages evolve over time
called derived characteristics - not found in older lineages
Classification Using Cladograms
Can use derived characteristics to construct a cladogram
Diagram that shows evolutionary relationships
Shows how one lineage branched into others
Similarities in DNA and RNA
Because DNA and RNA are so similar across all forms of life, these molecules provide an excellent way of comparing organism
Similarities in DNA and RNA
Genes show important similarities at the molecular level
DNA similarities can be used the help determine classification and evolutionary relationships
Similarities in DNA and RNA
Scientists can compare DNA sequences to trace history of genes over millions of years
DNA evidence can show evolutionary relationships of species and how species have changed
More similar DNA sequences - more recently shared common ancestor
Molecular Clocks
Comparisons of DNA can be used to mark the passage of evolutionary time
Done with molecular clocks
Uses DNA comparisons to estimate length of time two species have been evolving independently
Molecular Clocks
By analyzing neutral gene mutations, and looking for dissimilarities, one can tell how long ago they shared a common ancestor