Structural proteins
advertisement

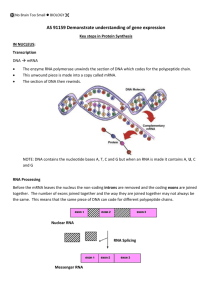
Jan 2006 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS THE LINK BETWEEN GENES AND PROTEINS 1. Jan 2006 2. Gene -portion of DNA that codes for a protein that controls a trait Two types of proteins a. Structural proteins: determine how we look EX: Hair & skin pigments; ear lobe shape b. Enzymes: determine how we function Control every chemical reaction in the body EX: Sucrase breaks down sucrose (table sugar) Detached ear lobes Attached ear lobes OVERVIEW Sequence of bases determines the “genetic code” 2. DNA NEVER leaves the nucleus 3. RNA copies DNA code of a gene. a. RNA carries the copied code out of the nucleus to the ribosome where protein is made 1. DNA code Jan 2006 TYPES OF RNA Messenger RNA = mRNA a. Copies instructions from DNA code; carries code out of nucleus to ribosome 2. Ribosomal RNA = rRNA a. Ribosomes are made of protein and RNA 3. Transfer RNA = tRNA a. Carries and transfers a specific amino acid to the ribosome b. T-shape 1. mRNA rRNA tRNA Step 1: Transcription 1. Transcription: a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA in the nucleus a. DNA unwinds – helicase b. RNA polymerase uses DNA template to make mRNA strand If DNA is TACCAGTTT mRNA will be AUGGUCAAA c. mRNA is removed and DNA strands will join & recoil Slide # 8 Step 2: mRNA editing 1. 2. 3. mRNA editing: cutting and splicing mRNA before it leaves the nucleus a. Introns- (interfere) are cut out by enzymes b. Exons- (expressed) are left spliced together to create an edited version Poly-A tail added to end Edited mRNA is sent to ribosome Introns are removed and exons are spliced together. This is the message that is translated. Slide # 9 Step 3: Translation 1. How the mRNA is read: a. Every 3 bases on mRNA represents a code for an amino acid (codon) b. Amino acids are abbreviated (usually first 3 letters). Met = methonine (start) Leu = leucine Slide # 11 Step 3: Translation 4. Occurs at a ribosome 5. Codon on mRNA specifies which tRNA brings the designated amino acid Anticodon on tRNA “reads” the codon on mRNA Ribosome joins the amino acids together with peptide bonds to build a polypeptide (protein) 6. DNA (gene) RNA Protein Trait Slide # 12 TRANSLATION Lysine Phenylalanine t RNA Methionine Anticodon Ribosome mRNA Start codon Go to Section: Jan 2006 Nucleus mRNA TRANSLATION Slide # 13 Jan 2006 Growing polypeptide chain The Polypeptide “Assembly Line” Ribosome tRNA Lysine tRNA mRNA Completing the Polypeptide mRNA Ribosome Go to Section: Translation direction Slide # 10 READING THE CODON CHART Examples: AUG = Methionine CAU = Histidine UAG = Stop First Position Try these: Answers: GCU: Alanine UAC: Tyrosine CUG: Leucine UUA: Leucine Jan 2006 Third Position This chart only works for mRNA codons. Jan 2006