Gas Laws: Boyle*s and Charles* Law At the
advertisement
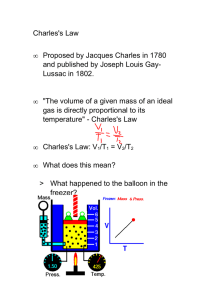
Gas Laws: Boyle’s and Charles’ Law At the conclusion of our time together, you should be able to: 1. Describe Charles’ Law with a formula. 2. Use Charles’ Law to determine either a temperature or volume Charles’ Law – Page 11 If n and P are constant, then V α T V and T are directly proportional. V1 V2 T1 T2 If one temperature goes up, the volume goes up! Jacques Charles (1746-1823). Isolated boron and studied gases. Balloonist. Charles’s Original Balloon Modern LongDistance Balloon Charles’ Law Summary The volume of a gas is directly proportional to temperature, and extrapolates to zero at zero Kelvin. (P = constant) V1 V2 T1 T2 Charles’ Law – Page 11 Example – Page 12 V1 V2 T1 T2 Charles’ Law Practice – Page 12 #2 V1 V2 T1 T2