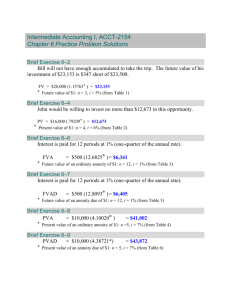
Document
advertisement

Attention! In Even weeks lecture starts earlier!!! At 16.00 – 18.00 in room EF. 13-15 In odd weeks at 18.10 -19.40 Midterm exam: 26. October 2010. Topic: present value calculations 1 Investment decisions and time value of money „Res tantum valet quantum vendi protest” A thing is worth only what someone else will pay for it. (unknown) 2 Learning goals 1. Discuss the role of time value in finance 2. Understand the concepts of future and present value 3. Find the future and present value of ordinary annuity 4. Find the present value of a perpetuity 3 Materials to learn from Lawrence J. Gitman: Principles of Managerial Finance, Addison - Wesley 10th Edition – see sharepoint: CH4 + web – http://wps.aw.com/aw_gitman_pmf_11 Brealey and Myers: Principles of corporate Finance, West Publishing Company www.mhhe.com/business/finance Lecture material 4 Basic principles of finance Time value of money - a dollar today worth more than a dollar tomorrow A safe dollar is worth more than a risky one 5 Basic idea and theories 1. Theory of Present Value 2. Castle-in-the –air Theory 6 Castle-in-the-air Theory Baloon theory by Lord Keynes (1936) Investor psychology Follow others Succesful investor: identify timepoint of building castle in the air, and buy before that point „Tronics prosperity” 7 Theory of Present Value Theory by John B. Williams Based on : dividends and assumes long-term decisions Compares actual value and real value 8 Basics Yield – Rate of return – Rate of interest – Income Maturity Nominal/ par/face value-the principal Future and present value Simple interest Compound interest 9 Concept of time value of money postulate All operations with money must be compared between alternatives to find the best result. Interest rate is a simple but prominent equivalent of any change of time value of money. 10 Rate of return rule We accept investments that offer rates of return in excess of their opportunity cost of capital Cost of capital invested: the return forgone by NOT INVESTING in other securities 11 Future value and present value Changing in time value of money gets future and present nomination Getting from present value to future value is called compounding. Getting from future value to present value is called discounting. 12 PV and FV PV – cash in hand today FV – cash received at given future date Time line – can be used to depict the cash flows in time 13 Simple interest Present value = discount future value by an appropriate interest rate Interest rate – opportunity cost of capital PRINCIPAL – AMOUNT OF MONEY ON WHICH INTEREST IS PAID Up to 1 year PV= FV / (1+ r) FV = PV ( 1+ r) 14 Where to use simple interest Money market instruments – – – – – – Treasury bills (T-bill) Local authority/ public utility bills Certificate of deposit (CD) Commercial paper (CP) Bill of exchange Bankers` acceptance (BA) 15 Money market Short term instruments Pure discount securities Contracts up to 1 year Huge volume and vigorous competition No physical place Essentially for professionals ( banks,institutional investors, brokerage firms, companies) Liquidity ( fine spreads based on interest rate of lending and borrowing) Creditworthiness 16 Money market securities T-bills – Domestic instruments issued by governments to raise short term finance balancing cashflow – Non-interest bearing and interest-bearing, sold at discount in auction – Negotiable – Generally 13,26,52 weeks Certificate of deposit - CD – – – – – Usually issued by banks, is simple the evidence of time deposit Negotiable not as time deposit Sold at discount or pay coupon Interest payed at maturity 30 days to 3 month or could be longer 17 Money market securities 2 Commercial paper- CP – Issued by large, safe and well-known companies bypassing banks to achieve lower borrowing rates (sometimes below the bank’s prime rate) – Very short term (max 270 days, most 60days or less) – Issued at discount – Unsecured security 18 Money market securities 3 Trade bill, bills of exchange, bankers’acceptance – Used by companies for trade purposes – The seller draws up a bill to the buyer to pay and asks to sign it – Could be sold at a discount to the bank – Bank’s signature is a guaranty ( eligible bills in UK the Bank of England is the guarantor) 19 HELP!!! Computational tools for finding PV and FV: – Financial tables – Financial Calculators – Computers and spreadsheets 20 FV FV = PV ( 1+ r)t r = interest rate PV = recent cashflow FV = future cashflow t = time period FVIF= (1 + r)t FV = PV ( FVIF) PV = $100 r = 10% FV = ? t = 1 year t = 3 years FV = 100 (1 + 0.10) = 110 FV = 100 (1.10)3 = 133. 21 Future value and present value (1 + r)ⁿ is a future value factor (FVF) To simplify calculations of FV use table of FVF. Years 1% 2% 3% 4% 5% 6% 7% 8% 9% 10% 1 1,01 1,02 1,03 1,04 1,05 1,06 1,07 1,08 1,09 1,1 2 1,02 1,04 1,06 1,08 1,10 1,12 1,14 1,17 1,19 1,21 3 1,03 1,06 1,09 1,12 1,16 1,19 1,23 1,26 1,295 1,33 4 1,04 1,08 1,13 1,17 1,22 1,26 1,31 1,36 1,41 1,46 5 1,05 1,1 1,16 1,22 1,28 1,34 1,40 1,47 1,54 1,61 6 1,06 1,13 1,19 1,27 1,34 1,42 1,50 1,59 1,68 1,77 7 1,07 1,15 1,23 1,32 1,41 1,50 1,61 1,71 1,83 1,94 8 1,08 1,17 1,27 1,37 1,48 1,59 1,72 1,85 1,99 2,14 9 1,09 1,20 1,30 1,42 1,55 1,69 1,84 1,999 2,17 2,36 10 1,1 1,22 1,34 1,48 1,63 1,79 1,97 2,16 2,37 2,59 22 Nominal and Effective Annual Rate of Interest (EAR) EAR = (1+ r/t )t - 1 EAR …?…. with increasing compounding frequency 23 Compound Interest 1 Invetments for more than 1 year Contracts in the capital markets 24 Capital market Instruments – Bonds – Government bonds – Local authority papers – Mortgage or other assets backed bonds – Corporate – Foreign – Junk – Shares – Preferred – Normal Innovations – Convertibles – Variables Investment notes 25 Present Value PV = $125 FV = $132 r=? PV = FV / DF DF = discount factor DF = 1 / 1 + r DF = PV / FV DF = 125: 132 = 0.899 26 2. Future value and present value Table of present value factor Years 1% 2% 3% 4% 5% 6% 7% 8% 9% 10% 1 0,99 0,98 0,97 0,96 0,95 0,94 0,935 0,93 0,92 0,91 2 0,98 0,96 0,94 0,92 0,91 0,89 0,87 0,86 0,84 0,83 3 0,97 0,94 0,92 0,89 0,86 0,84 0,82 0,79 0,77 0,75 4 0,96 0,92 0,89 0,85 0,82 0,79 0,76 0,74 0,71 0,68 5 0,95 0,91 0,87 0,82 0,78 0,75 0,71 0,68 0,65 0,62 6 0,94 0,89 0,84 0,79 0,75 0,70 0,67 0,63 0,596 0,56 7 0,93 0,87 0,81 0,76 0,71 0,67 0,62 0,58 0,55 0,51 8 0,92 0,85 0,79 0,73 0,68 0,63 0,58 0,54 0,50 0,47 9 0,914 0,84 0,77 0,70 0,64 0,59 0,54 0,50 0,46 0,42 10 0,905 0,82 0,74 0,68 0,61 0,56 0,51 0,46 0,42 0,39 27 Compound Interest 2 28 Compound Interest 3 DF8 = 0.285 FV8 =CF8 = $ 596 PV = ? PV = FV (DF) = 596 X 0.285 = $170 29 Valuing more assets We have plenty of investments: PV = PV1 + PV2 + PV3 + ….+ PVn 30 Basic patterns of cash flow Single amount : a lump sum amount Annuity : A level periodic stream –fixed amount for fixed period of time Mixed stream: stream of CF that reflects no particular pattern Perpetuity: fixed amount of payments forever 31 Annuities Asset that pays a fixed sum each year over a specified period of time Outflows or inflows Expl: house mortgage, Installment credit, bond Types: – annuity due ( CF at the begining) – Ordinary annuity ( CF at the end of each period) 32 Annuities 2 End of year 1 2 3 4 5 CF 100 100 100 100 100 33 Annuities 3 The model of annuities present value calculation is: PVa = cf / (1 + r)¹ + cf / (1 + r)² + cf / (1+ r)³ + … + cf / (1+ r)ⁿ-1; Matematical expression: PVIFAr, t = 1 / r X ( 1 - 1/ (1 + r)t Pva = CF X PVIFA 34 Calculating The Future Value of an Annuity Fred wishes to determine how much money he will have at the end of 5 years, if he puts $1000 at the end of each year. The saving account pays 7% interest per annum 35 Future and present value of stream of cash flow Table of future value factor of annuity Years 1% 2% 3% 4% 5% 6% 7% 8% 9% 10% 1 1,00 1,00 1,00 1,00 1,00 1,00 1,00 1,00 1,00 1,00 2 2,01 2,02 2,03 2,04 2,05 2,06 2,07 2,08 2,09 2,1 3 3,03 3,06 3,09 3,12 3,15 3,18 3,22 3,25 3,28 3,31 4 4,06 4,12 4,2 4,25 4,31 4,38 4,44 4,51 4,57 4,64 5 5,1 5,2 5,3 5,42 5,53 5,64 5,75 5,87 5,99 6,11 6 6,2 6,3 6,5 6,63 6,8 6,98 7,15 7,34 7,52 7,72 7 7,2 7,4 7,7 7,898 8,14 8,39 8,65 8,92 9,2 9,49 8 8,3 8,6 8,9 9,21 9,55 9,897 10,26 10,64 11,03 11,45 9 9,4 9,8 10,16 10,58 11,03 11,49 11,98 12,49 13,02 13,58 10 10,5 10,95 11,46 12,01 12,58 13,18 13,82 14,49 15,19 15,94 36 Calculating The Future Value of an Annuity CF = $1000 t = 5 years r = 7% FVa = CF X FVIFA FVa = CF X ∑ (1 + r )t-1 Years amount PV 1. 2. 3 4. 5. 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1311 1225 1145 1070 1000 ? 5000 5751 37 Table of present value annuity factor Years 1% 2% 3% 4% 5% 6% 7% 8% 9% 10% 1 0,99 0,98 0,97 0,96 0,95 0,94 0,93 0,925 0,917 0,91 2 1,97 1,94 1,91 1,89 1,86 1,83 1,81 1,78 1,76 1,74 3 2,94 2,88 2,83 2,76 2,72 2,67 2,62 2,58 2,53 2,49 4 3,90 3,81 3,72 3,63 3,55 3,47 3,39 3,31 3,24 3,17 5 4,85 4,71 4,58 4,45 4,33 4,21 4,10 3,99 3,89 3,79 6 5,796 5,60 5,42 5,24 5,08 4,91 4,77 4,62 4,49 4,36 7 6,73 6,47 6,23 6,00 5,79 5,58 5,39 5,21 5,03 4,87 8 7,65 7,33 7,02 6,73 6,46 6,21 5,97 5,75 5,53 5,33 9 8,57 8,16 7,79 7,44 7,11 6,8 6,52 6,25 5,99 5,76 10 9,47 8,98 8,73 8,11 7,72 7,36 7,02 6,71 6,42 6,14 38 Thank you 39