Endocrine/Lymphatic Jeopardy Review
advertisement

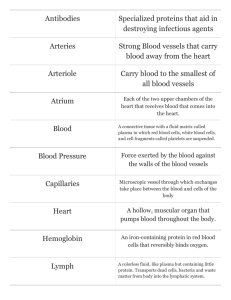
THIS IS With Your Host... Mastergland Hormonal Influence 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Lymphatic Anatomy Immunity 100 100 100 200 200 300 Lymphatic System Endocrine System The watery, clear fluid inside lymphatic vessels is called? A 100 lymph A 100 What are the specialized white cells that protect the body against antigens like viruses and bacteria? A 200 Lymphocytes A 200 What prevents the lymph fluid from flowing backwards? A 300 semilunar valves A 300 What force moves the lymph fluid through the lymphatic vessels? A 400 muscle contractions A 400 What is the back up of extra fluid in tissue called? A 500 Edema A 500 What are the two functions of the lymphatic system? B 100 1 – pick up leaky fluid 2 – protection (immunity) B 100 Movement of substances into the lymphatic vessels is caused by what force? B 200 pressure B 200 What type of cells make up the membranes of the lymphatic vessels? B 300 Simple, squamous epithelium B 300 What two molecules are moved through the lymphatic vessels because they are too big for the blood capillaries? B 400 proteins and fat B 400 What vein does all filtered lymph empty into? B 500 Subclavian Vein B 500 What structure in the lymphatic system filters lymph fluid and makes lymphocytes used for protection? C 100 Lymph Nodes C 100 Lymphatic vessels are structurally most similar to? C 200 Veins C 200 What is the body largest lymphatic organ? C 300 Spleen C 300 DAILY Place A Wager DOUBLE C 400 Which gland is located behind the sternum, shrinks with age and helps mature lymphocytes into T cells? C 400 Thymus Gland C 400 Lymph drains unevenly in the body. Which duct drains lymph from most of the body? C 500 Thoracic Duct C 500 What term describes how hormones are directly dumped into the bloodstream? D 100 Endocrine D 100 What molecules deliver messages to the body? D 200 Hormones D 200 What type of cells have specific receptors that recognize certain hormones? D 300 Target Cells D 300 What term describes the changes that our bodies go through in adolescence that is primarily influenced by hormones? D 400 puberty D 400 Hormones are made of what type of molecule? Be specific. D 500 lipid based steroids D 500 Which gland is commonly referred to as the “mastergland?” E 100 Pituitary Gland E 100 Which area of the brain controls the pituitary gland? E 200 Hypothalamus E 200 Which hormone stimulates milk production in mammals? E 300 Prolactin E 300 Which hormone stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth? E 400 Oxytocin E 400 Which hormone produced by the pituitary controls stress by stimulating the adrenal cortex? E 500 Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone (ACTH) E 500 Which hormone causes gigantism and dwarfism? F 100 Human Growth Hormone F 100 Which gland is located in the front of the next and on top of the trachea? F 200 Thyroid gland F 200 Which hormone needs iodine and ultimately stimulates your metabolism? F 300 Thyroid Hormone F 300 Which hormone increases calcium, phosphate, and magnesium absorption in the intestines? F 400 Parathyroid Hormone F 400 Which hormone commonly called adrenaline is responsible for creating fear under stress? F 500 Epinephrine F 500 The Final Jeopardy Category is: Endocrine System Please record your wager. Click on screen to begin Which hormone signals the liver to release glucose? Click on screen to continue Glucagon Click on screen to continue Thank You for Playing Jeopardy!