Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life
advertisement
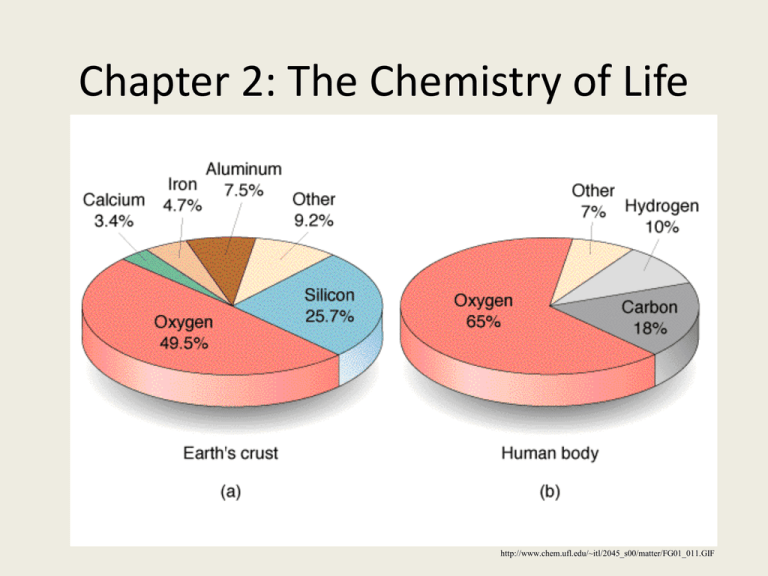
Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life http://www.chem.ufl.edu/~itl/2045_s00/matter/FG01_011.GIF Chapter 2 Vocab 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Reactant Product Activation energy Substrate Enzyme Carbohydrate Nucleic acid Nucleotide 9. Protein 10. Amino acid 11. Lipid 12. pH scale 13. Acid 14. Base 15. Ionic bond 16. Covalent bond 2-1 Objectives • 1. Use a periodic table to give atomic number and mass. • 2. Name simple ionic and covalently bonded compounds. Atom: the smallest unit of matter • Subatomic particles – 1. neutron • a. In nucleus • b. No charge • c. Weight 1dalton – 2. proton • a. In nucleus • b. + charge • c.Weight 1 dalton – 3. electron • • • • a. Outside nucleus b. Move at speed of light c. Have a negative charge d. Weight1/2000 of a dalton http://www.wjcc.k12.va.us/ROBB/Atom%20Animation%20Resources_files/image003.gif If you are not able, use the table! http://www.corrosionsource.com/handbook/periodic/periodic_table.gif Atomic Number and Weight • 1. atomic number- number of protons in nucleus • 2. atomic weight- number of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus of the atom (a.k.a. mass number) http://www.wisegorilla.com/images/chemstry/PeriodicTable.gif How many neutrons are in an atom? Subtract the number of protons from the mass number (which = p+n) to get the number of neutrons Mass number – atomic number = # of neutrons Find the atomic number, atomic mass, and # of protons, electrons and neutrons of the following elements. Atomic Mass # # # # # protons electrons neutrons Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Isotopes of Carbon Isotopes of Carbon Electron Shells • 1. Energy Shells – a. first level can only have 2 electrons. – b. second level can have 8 electrons. – c. all other levels have 8. • 2. The chemical behavior of the atom is determined by the atom’s electron shell. • 3. Valance Electronsoutermost shell http://static.howstuffworks.com/gif/atom-h-he-li-na.gif Problem? All atoms want to have their valance electron shells full! I wish I could be a noble gas! http://www.csupomona.edu/~egoldstein/121/IMAGES/Periodic_noble.gif Why does everyone want to be a noble gas? Hindenburg Video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F54rqDh2mWA Hindenburg Video 2 http://dsc.discovery.com/videos/mythbusters-burnblimp-burn.html Chemical Bonds • 1. Making of chemcial bonds Stores Energy. • 2. The breaking of chemical bonds Releases Energy Blah blah balh Sdf http://faculty.clintoncc.suny.edu/faculty/michael.gregory/files/Bio%20101/Bio%20101%20Lectures/energy/energy12.gif Chemical Bonds • 1. Covalent bond -The sharing of a pair of valance electrons by two atoms. Caring is sharing! http://www.school-for-champions.com/chemistry/images/bonding_types-water.gif http://www.roboimages.com/image/ri33813/Care_Bears_Easter.jpg Methane: covalent bonds http://sixthsense.osfc.ac.uk/chemistry/bonding/GRAPHICS/gif15.CH4bp.gif 2. All non-metals form covalent bonds • 1. glucose • 2. water • 3. carbon dioxide • 4. sucrose http://www.peoriaendocrine.com/images/diabetes_lecture/glucose.GIF http://www.brooklyn.cuny.edu/bc/ahp/SDgraphics/PSgraphics/WaterMolecule.GIF Common Prefixes • • • • • 1 — mono 2 — di 3 — tri 4 — tetra 5 — penta • • • • • 6 — hexa 7 — hepta 8 — octa 9 — nona 10 — deca Naming Covalent Compounds Prefix + First element + Prefix + Second Element + -ide Example: CO2 becomes Carbon dioxide Unless! the element is bonded to itself (Ex: Cl2 = chlorine) What is Dihydrogen Monoxide? • Name the following covalent compounds: a) SiF4 a) b) silicon tetrafluoride N2S3 b) dinitrogen trisulfide c) HBr c) hydrogen bromide (or hydrobromic acid) d) Br2 d) bromine Ionic Bonds • 1.One atom “steals” electrons from another to complete its outer shell. • Example: NaCl – Because one atom has lost an electron (Na) it has now has an overall charge of +1 – Because the atom that took the electron (Cl) now has an extra electron, its overall charge is -1 http://www.sci.sdsu.edu/classes/biology/bio100/truesdale/Lectures%2005/lec2/Image6.gif 4. Ionic Bonding: all metals http://gcserevision101.files.wordpress.com/2009/02/halogen-ionic-bond.jpg Name the following Ionic Compounds • NaOH • Sodium hydroxide • KCl • Potassium chloride • H2 S • Hydrogen sulfide Naming Ionic Compounds Example: Magnesium iodide • Step 1: What chemical symbols do you need? • Step 1: • Step 2: How many atoms of each element are needed to make the bond? • Step 2: a. Find the charges for each ion using the periodic table Mg and I a. Mg = +2 I = -1 b. Mg(1)I(2) => MgI2 b. “Cross the charges” 2-2 Objectives • 1. Analyze the properties of water. • 2. Distinguish between acids and bases. Water is a Major Components of Cells 1. 2/3 of all molecules in the body (all your cells are surrounded by water) 2. Water stores heat efficiently. a. sweating- helps release heat b. helps maintain homeostasis by regulating temperature http://www.bigbrandwaterfilter.com/water_filter_images/waterdrop_embossed.gif Water bonds to itself and other surfaces • Adhesion- between different substances *includes capillary action Cohesion-between similar substances nce/sp/en/syllabus/unit5/images/roots%26soil1.jpg&imgrefurl=http://resources.ed.gov.hk/~s1sci/R_S1Science/sp/en/syllabus/unit5/article-ce.htm&h=150&w=150&sz=6&tbnid=_euQe4K3sE8J:&tbnh=90&tbnw=90&hl=en& Water Dissolves Many Substances • Solution- mixture in which one or more substances is evenly distributed. • Many important substances are dissolved in blood. http://www.elmhurst.edu/~chm/demos/images/bluebottle.GIF Polarity-molecules with an electrical charge • Water is a polar molecule • Only polar molecules will dissolve in water • Nonpolar molecules will not dissolve in water – oil Polarity Video! http://colossus.chem.umass.edu/genchem/whelan/class_images/Structure_of_Water.jpg http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VhWQ-r1LYXY&feature=player_embedded Water molecules adhere to other polar molecules. + Hydrogen Bonds - water molecule + + + + - - + + + - - HCl hydrogen bond + + + Acids and Bases • Water can be broken down into acids and bases • Acids1) high concentration of hydrogen ions. 2) pH less than 7 http://www.epa.gov/acidrain/site_students/images/phscale.gif Acids and Bases Bases – 1) Low concentration of hydrogen ions 2) pH is greater than 7 7 is neutral-pure water http://www.btinternet.com/~chemistry.diagrams/ph_scale.gif pH (2) More H+ More OH- Review Question • 1. What type of molecules will dissolve in water? • 2. What is a pH scale? • 3. What is an acid and a base? • 4. What is neutral on the pH scale. • 5.Will oil dissolve in water? • 6. Which has more hydrogen ions, an acid or a base? 2-3 Objectives • 1. Summarize the characteristics of organic compounds. • 2. Distinguish between carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. • 3. Describe the structure and function of nucleic acids and ATP. Organic Compounds • Contain carbon usually bonded to oxygen, hydrogen, and other carbon atoms. • Most of the matter in your body is organic! • These are compounds that usually come from organisms http://www.chemistryland.com/ElementarySchool/BuildingBlocks/Jungle500.jpg Carbohydrates http://www.exploratorium.edu/cookng/candy/images/sugar-molecule-1.gif • 1.Made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. • 2. Key source of energy-Found in fruits and vegetables. • 3. Monosaccharidessingle sugars, – A. the building blocks of carbs – B. Ends in-ose • Examples: glucose, fructose, maltose http://vienna-doctor.com/images/Pictures/carbohydrates.jpg Disaccharides and Polysaccharides • 4. Disaccharides- two sugars glucose + fructose = sucrose 5. Polysaccharides -a. macromolecule made of many sugars. -b. storehouse for energy Excess Energy is stored as: -c. starch-in plants d. glycogen- in animals e. cellulose-found in plant cell walls http://www.pecanbread.com/new/saccharides.jpg Let’s Draw a Glucose molecule! • 1. Draw the carbon ring – It has 6 sides • 2. Number the carbons 16 • 3. Label # 6 carbon • 4. carbons 1, 2, 4 are the same, have OH on the bottom. • 5. # 4 carbon is a HO! • 6. # 3 carbon is odd, OH on top http://www.thefreshloaf.com/files/u12441/alpha-D-glucose%20ring.gif http://kentsimmons.uwinnipeg.ca/cm1504/Image71.gif Dehydrations synthesis: making carbohydrates Taking water away to join molecules • 1. Dehydrate means to take water away. • 2. #1 and #4 carbon will form a bond by removing water. • 3. What is left? http://www.uq.edu.au/_School_Science_Lessons/16.3.1.4ach.GIF Lipids- are nonpolar • Fats, phospholipids, steroids(cholesterol) and waxes. • Found in plant pigments such as chlorophyll. • Fats are lipids that store energy – Saturated fat- animal fat, solid at room temp. – Unsaturated fat-plant oils, liquid at room http://www.bodybuilding.com/fun/crisco1k.jpg http://cwx.prenhall.com/bookbind/pubbooks/hillchem3/medialib/media_portfolio/text_images/CH09/FG09_16-05Box.JPG http://www.healingtouchwebhelp.net/image/heart31.jpg http://www.chemistryland.com/ElementarySchool/BuildingBlocks/Lipids.jpg Lipids are made by combining two types of molecules • 1. glycerol – A three carbon alcohol • 2. 3 fatty acids – Long hydrocarbon chains. – Non polar http://faculty.clintoncc.suny.edu/faculty/michael.gregory/files/Bio%20101/Bio%20101%20Lectures/Biochemistry/glycerol,%20fatty%20acids,%20triglyceride.gif Dehydration Synthesis: lipids Lipids: Fats Saturated vs. Unsaturated Structural formula of a saturated fat molecule Stearic acid, a saturated fatty acid Structural formula of an unsaturated fat molecule Oleic acid, an unsaturated fatty acid (a) Saturated fat (b) Unsaturated fat cis double bond causes bending Proteins • Made of chains of amino acids • There are 20 known amino acids • These 20 amino acids are found in all biological species. • Collagen-protein found in skin • Hemoglobin, blood clots, and muscles. http://images.apple.com/science/profiles/proteinfolding/images/proteins.jpg http://www.cybered.net/library/Teaching_Resources/Biology/Genetic_Engineering/Image_Gallery/GeneticEng-Proteins.jpg All Amino Acids have the same basic structure • 1. alpha carbon- makes center of amino acid • 2. amino group • 3. Carboxyl group- this is an acid • 4. a single hydrogen • 5 . Variable group-R – There are 20 R groups – Therefore there are 20 different amino acids in all living things http://www.contexo.info/DNA_Basics/images/aminoacidsweb.gif Let’s draw an amino acid • 1. draw the alpha carbon • 2. put in amino group. • 3. put in carboxyl group • 4. Hydrogen • 5. R group (variable) http://www.aloeveraibs.com/wp-content/uploads/2008/08/aminoacidstruc.jpg Amino Acids form bonds • • • • 1. forms peptide bond. 2. Oxygen is taken from the carboxyl group 3. Hydrogen is taken from the Amino group 4. Called Dehydration Synthesis Peptide Bonds: dehydration synthesis http://bill.srnr.arizona.edu/classes/182/PeptideBond-HiRes.JPEG Nucleic Acids http://www.duke.edu/web/MAT/jennifer_sohn/unit/images/what_is_rna1.gif • Made of nucleotides. • Nucleotides contain a sugar, phosphate and a nitrogen base. • DNA-double stranded and makes up chromosomes • RNA-single stranded, used in making proteins. DNA and RNA http://images2.clinicaltools.com/images/gene/dna_versus_rna_reversed.jpg ATP-Adenosine Triphosphate • Energy currency for the cells. • Cells need a constant supply of ATP to function. http://www.colorado.edu/epob/academics/web_resources/cartoons/atp.gif Review Questions • 7. In what ratio is carbon, hydrogen and oxygen found in carbohydrates? • 8. All sugars end in what? • 9. What is the difference between a polysaccharides, disaccharide, and a monosaccharide? • 10. Give and example of 2 polysaccharides. • 11. What are the two types of fats? • 12. What are proteins made up of ? • 13. Name two types of nucleic acids. Objective 2-4 • 1. Describe the role of enzymes in chemical reactions. • 2. Explain how enzymes work. Organisms Need Energy for Life Processes • Energy- the ability to move or change matter. • A. Energy is stored and released by chemical reactions. • B.Reactants and products • Chemical reaction absorb and release energy – 1.Freezing water releases energy – 2.Melting ice absorbs energy http://www.windows.ucar.edu/teacher_resources/activities_3x3.jpeg Energy is needed to start a chemical reaction. • 1. Activation energythe energy needed to start a chemical reaction. • 2. Chemical push! http://www.colorado.edu/intphys/Class/IPHY3430-200/image/04-3.jpg Enzymes help biochemical reactions occur. • A. allows reactions to occur quickly and at low temperatures. • B. increases the speed of chemical reactions. • C. most are proteins. • D. act as catalysts-reduce the amount of activation energy required. • E. helps maintain homeostasis. http://w3.dwm.ks.edu.tw/bio/activelearner/06/images/ch06c1.jpg Enzymes End in ase https://www.google.com/search?q=lactose+and+lactase+reaction&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ei=Mkc 3UufDMtPH4AP6goEY&ved=0CAcQ_AUoAQ&biw=1440&bih=805&dpr=1#facrc=_&imgdii=_&imgrc =_W7J_yOT05rFmM%3A%3BO8f3SM6l45zgtM%3Bhttp%253A%252F%252Fwww.chemicalconnection .org.uk%252Fchemistry%252Ftopics%252Fimages%252Fpp8.jpg%3Bhttp%253A%252F%252Fwww.che micalconnection.org.uk%252Fchemistry%252Ftopics%252Fview.php%253Ftopic%253D5%2526headingn o%253D8%3B400%3B240 Enzymes affect specific substances. http://library.thinkquest.org/3659/orgchem/lock-key-enzyme.gif http://www.blc.arizona.edu/courses/181summer/graphics/graphics%20lect7/Life7e-Fig-06-10-0%203D%20fit%20of%20enzyme%20and%20substrate.jpg • 1.Substrate-substance on which an enzyme acts. – A. amylase- breaks starch down into glucose • 2.Active Site – A deep folds in the surface of the enzyme. – B. substrate fits into the active site Enzymes are Biological Catalysts http://www.staff.uni-mainz.de/lieb/tierphys/enzyme.gif Three things that effect enzyme action. • 1. amount of enzyme concentration • 2. Temperature • 3. pH https://www.google.com/search?q=lactose+and+lactase+reaction&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ei=Mkc3UufDMtPH4A P6goEY&ved=0CAcQ_AUoAQ&biw=1440&bih=805&dpr=1#facrc=_&imgdii=_&imgrc=19PXmfPEXBeumM%3A%3B nTw62t7ir_X6M%3Bhttp%253A%252F%252Fweb.mit.edu%252Fkevles%252Fwww%252Flactose.gif%3Bhttp%253A%252F%252 Fweb.mit.edu%252Fkevles%252Fwww%252Fnomilk.html%3B677%3B233 Review Questions • • • • 14. What is activation energy? 15. What is a catalyst? 16. Why are enzymes important? 17. Where does the substrate bind to on the enzyme? • 18. What do all enzymes end in? • 19. What three thing can effect how an enzyme works?