myostatin mutation
advertisement

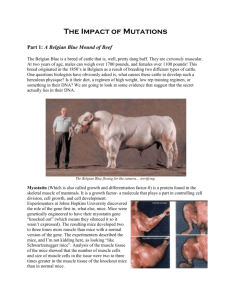
Molecular Exercise Physiology Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy Presentation 8 Henning Wackerhage Learning outcomes At the end of this presentation you should be able to: • Explain the effects of myostatin knockout on muscle growth. • Explain how myostatin signalling may inhibit muscle growth TGF-b signalling The TGFb superfamily is a large group of proteins that regulate growth, differentiation and apoptosis. One subclass within the TGFb superfamily are growth and differentiation factors (GDFs). Myostatin is a GDF whose knockout in mice resulted in skeletal muscle hypertrophy and hyperplasia (McPherron et al., 1997). The muscles of myostatin knockout mice are shown on the next slide. Myostatin knockout mice Wildtype Myostatin knockout McPherron et al. (1997) knocked out growth and development factor 8 (gdf-8) which was later termed myostatin. The absence of myostatin leads to muscle hypertrophy (e) compared to the wildtype (d). Figure from Lee et al. (1999) Myostatin also affects fibre type Myostatin knockout (MSTN-/-) also leads to a reduction in type I fibres when compared to the wildtype Girgenrath et al. (2005). Myostatin Discovery of myostatin (GDF-8): • Myostatin is almost only expressed in skeletal muscle. • Myostatin could first be detected at day 9.5 post-coitum. • Myostatin knock-out mice muscles weigh 2-3 times more than those of wild type animals. • Hyperplasia (more fibres) and hypertrophy (larger fibres); more DNA. (McPherron et al. 1997) Myostatin is a negative growth factor. If you have lots of it, you’re small. If you don’t have it, you’re musculous. Natural myostatin mutations occur Natural myostatin mutations can occur as well: McPherron et al. (1997) found in Belgian Blue and Piedmontese cattle a natural myostatin mutation resulting in non-functional myostatin and increased muscle size. An article reporting a toddler with a natural myostatin mutation is on the website. Figure: A fullblood Belgian Blue bull showing the double muscling phenotype (McPherron et al. 1997). Natural myostatin mutation in cattle Belgian blue deletion Piedmontese GA mutation Myostatin protein structure and effect of mutation Myostatin mutations (mut) in Belgian Blue and Piedmontese cattle compared with wild-type (wt) Holstein cattle. These mutations lead to a large increase in muscle mass, known as double-muscling (McPherron et al. 1997) Flex Wheeler: a mutant? Flex Wheeler has a website where someone states that Flex has a special genotype linked to his muscle grwoth: “Flex was one of only nine extreme responders that had the very rare "myostatin mutation." Myostatin is the gene that "limits muscle growth." Specifically, Flex had the rarest form of myostatin mutation at the "exon 2" position on the gene. This simply means Flex has a much larger number of muscle fibers compared to the other subjects or the normal population.” Flex Wheeler: It’s all natural!? Task: Search for scientific literature on this SNP/mutation. Does it exist? Flex Wheeler: a mutant – hang on… The gentleman who has written the letter for Flex is Victor Conte. This is what the BBC says (23.10.2004): “Victor Conte is founder and president of Bay Area Laboratory Co-operative (Balco), the San Francisco-based company which the United States AntiDoping Agency says developed the banned steroid THG (tetrahydrogestrinone)”. So, Flex is all natural? Victor Conte How is myostatin expression regulated? Myostatin expression is regulated via DNA binding elements for glucocorticoid (GC), androgen (Tes), thyroid hormone (Thy), myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs), MEF2, PPARg (Ma et al., 2001). Only the glucocorticoid binding site has been experimentally verified (Ma et al., 2003). Resistance Other Tes training regulators Myostatin GC Does myostatin regulate the response to exercise? If myostatin has such a dramatic effect on muscle mass, is it involved in mediating hypertrophy in response to resistance training? The story is not clear at the moment: Some reports suggest that myostatin mRNA or circulating myostatin does decrease after resistance training (Roth et al., 2003;Zambon et al., 2003;Walker et al., 2004) whereas others suggest it does not (Willoughby, 2004). The jury is still out and a high-resolution time course needs to be obtained after human resistance training in order to see whether there is a regulatory myostatin expression change in response to resistance training. Some data are shown on the following slide. Myostatin response to resistance training Figure. Myostatin expression levels (arbitrary units) for before ST (n = 15) versus after ST (n = 15) for each individual. •, males; , females. A significant decrease in myostatin expression was observed in response to ST, P < 0.05, with no group differences. (Roth et al. 2003) How does myostatin inhibit growth? Myostatin is like IGF-1 a protein that is secreted by muscle cells and myostatin dimers bind so-called activin receptors. These receptors then phosphorylate and activate the transcription factor Smad2/3. A simplified version of the events is shown below. Myostatin dimer Activin type I and II receptors P SMAD2,3 P SMAD2,3 P Growth inhibition Myostatin inhibitors (or not?) Obviously, bodybuilders are very keen to inhibit myostatin in order to promote muscle growth further. “Champion Nutrition” already managed to develop a myostatin inhibitor (or not?): “After extensive research, Champion Nutrition found a scientist that had isolated a naturally occurring fraction of a sea vegetable. It binds strongly to myostatin, thereby deactivating it. This discovery made it possible for Champion to begin work on the first product ever specifically designed to bind myostatin in humans”. See: www.bodybuilding.com/store/cn/myostim.html Myostatin inhibitors Researchers have identified natural the receptor binding of myostatin proteins form so-called myostatin are myostatin propeptide, follistatin Myostatin homodimer can bind receptor myostatin inhibitors that regulate in the organism. These bindingheterodimers. Inhibitor proteins and GASP-1. Myostatin-gasp1 or myostatin-follistatin heterodimers can not bind receptor Activin type I and II receptors P Myostatin inhibition can improve muscular dystrophy Bogdanovich et al. (2003) treated mdx mice (model for muscular dystrophy) with a monoclonal antibody against myostatin which inhibited myostatin. Control mdx mice (a) had significantly greater pathological changes (arrowheads) in the diaphragm than treated mice (b), as evidenced by a lack of cellular infiltration and fibrosis. Myostatin is an ideal treatment target Myostatin is probably a very good target for improving muscle mass in various conditions for the following reasons: a) Myostatin is secreted and thus treatments do not need to cross membranes; b) Myostatin needs to be inhibited which usually is easier than activation; c) Natural inhibitors (follistatin, gasp-1) exist which can be copied; d) Myostatin expression is largely limited to muscle and thus side effects should be limited. A myostatin-related therapy via antibodies, peptides or other drugs seems a realistic prospect. Summary Myostatin is a muscle-specific muscle growth inhibitor whose expression is probably controlled by glucocorticoids and anabolic steroids among other. Myostatin binds activin receptors as a dimer. Myostatin binding to specific inhibitory proteins (follistatin, gasp-1) can prevent myostatin binding to its receptor. Myostatin binding to the receptor activates the kinase bit of the receptor which causes phosphorylation of Smad2/3. Smad2/3 transport to the nucleus and DNA binding can be modulated by inhibitory and co-Smads. Smad2/3 probably regulates genes that inhibit muscle growth. The events mentioned above are shown on the next slide. Myostatin-gasp1 or myostatin-follistatin heterodimer Summary Myostatin homodimer Activin type I and II receptors P Myostatin modification Androgens, Glucocorticoids, thyroid hormones, MRFs, MEF2 I-SMAD SMAD2,3 Co-SMAD P SMAD2,3 P Co-SMAD Growth inhibition Enhancers and silencers Nucleus Skeletal muscle fibre The End