Case- control
advertisement

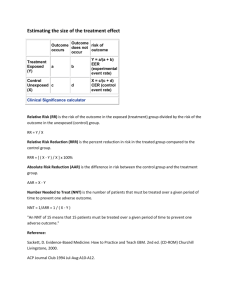
Introduction to Study Design and RCTs Simon Thornley That sugar movie… http://gameauland.com/that-sugar-film-teaser-trailer/ Cohort Participants Exposure Outcomes By measurement Exposed Exposed Disease Exposed no disease Participants Unexposed Unexposed Unexposed Disease No disease Cohort study eg Framingham Patients without disease Group by exposure Can use a variety of exposures Follow until disease develops Cohort advantages Exposure precedes disease Disease status does not influence selection Several outcomes possible Good for rare exposures Control group obvious (compare case-control) Cohort disadvantages Prospective costly Inefficient for rare diseases with long latency Several outcomes possible Exposed followed more closely than unexposed? Loss to follow up causes bias Do computer screens cause spontaneous abortions? 1991 Participants Female telephone operators Exposure Computer screens Exposed Outcomes abortion No abortion 54 Exposed Disease 312 Exposed no disease Participants Unexposed No computers Time 82 434 Unexposed Unexposed Disease No disease Do computer screens cause spontaneous abortions? Incidence in exposed Relative risk =---------------------------Incidence in unexposed 54/(54+312) = ------------------- = 0.93 82/(82+434) In pictures - Actual Null hypothesis; No effect 800 600 400 200 0 Frequency 1000 1200 1400 Effect of Monitors on abortion 0 1 2 3 Risk ratio 4 5 Cross sectional Participants sampled at one point or short duration Exposures and outcomes assessed at same point in time Participants Exposure Outcomes By measurement Exposed Exposed Disease Exposed no disease Participants Unexposed Unexposed Unexposed Disease No disease Cross-sectional Advantages Describes pattern of disease Variety of outcomes and exposures Cheap Inexpensive Disadvantages Prevalent rather than incident cases Can not distinguish cause and effect Must survive long enough to be included in study Short duration diseases under-represented (e.g. Influenza) Cross-Sectional study - bias Imagine... People with disease that are sedentary die early Cross-sectional study of disease (outcome) and exercise (exposure) Only sample survivors, so find high proportion of people who exercise with disease What would you infer about causal relationships? Does wearing fluoro gear protect you from bike crashes? Participants Cyclists Taupo bike race Exposure Outcomes Bike crash No bike crash Fluoro colours 162 323 Exposed Exposed Disease Exposed no disease 588 1343 Participants Unexposed No fluoro colours Unexposed Unexposed Disease No disease Do computer screens cause spontaneous abortions? Cum. Incidence in exposed Relative risk = ---------------------------Cum. Incidence in unexposed 162/(162+323) = ------------------- = 1.10 588/(588+1343) In pictures- Actual Independent Case-control Investigator selects cases and controls based on disease status Carefully defined population (cases = control population) Exposure history examined Derive P(exposure | case status) Case-control study: Cases Ideally, pcase=pdisease Prevalent From survey people with disease at particular point in time selection bias/favours long lived, chronic cases Incident from population registry exposure and disease tied only to development of disease, not duration or prognosis. Case control study: Controls Ideally, pcontrol=pundiseased Population vs. hospital controls Hospital controls likely to have disease related to exposure, even if not disease of interest. Population controls, from source of cases, generally better approach, but $$ can be prohibitive Electoral rolls Random digit dialling Reality More complex; rarely have matches, but frequency matching more common. E.g. Cot death study Cases – infants who died from cot death (area) Method Sampling frame – all births in geographic area Frequency matched Control randomly allocated age for interview similar to age distribution to cot deaths from previous years (about 3 months old) DOB calculated and adjusted to fit day of week (weekends higher chance of becoming cases) Obstetric hospital randomly chosen in proportion to number of births in previous financial year CC - advantages Good for long latency/ rare diseases Look at many exposures Smaller sample size CC - disadvantages Only one disease Can't estimate disease risk, because work backwards from disease to exposure* More susceptible to selection bias as exposure has already occurred. More susceptible to information bias Not efficient for rare exposures (Why?) Case-Control study -example Fenoterol study, Neil Pearce (guest lecturer) Participants Exposure Fenoterol Exposed Outcomes Cases Controls 60 Exposed Disease 189 Exposed no disease Participants Adults in hospital with asthma Unexposed Ventolin/other 57 279 Unexposed Unexposed Disease No disease Effect measure Odds ratio= odds of exposure in cases ---------------------------odds of exposure in controls 60/57 = -------------= 1.55 189/279 Actual Null hypothesis; No effect Questions Which study design is best for assessing causation, assuming no other limitations are present? A) Cross-sectional study B) Randomised controlled trial C) Case-control study D) Cohort study E) Case-series Questions In a cross sectional study of risk factors for angina, a random sample of elderly subjects were asked the question “Do you smoke cigarettes?” Answers were used to classify respondents as smokers or non-smokers. Further, subjects were classified as positive for angina if they had, at some time in the past, been told by a doctor that they suffered from this condition. When the data from the study was analysed, no statistically significant association was found between cigarette smoking status and angina status. Has the study measured incidence or prevalence of angina? Explain your answer. A considerable body of past evidence suggests that the risk of angina increases with increasing tobacco consumption. Suggest reasons why the study described here failed to find an association. Suggest an alternative design of study that would be more suitable for investigating whether smoking causes angina. Consider the question(s) that you would ask the chosen subjects about their smoking habits. Summary Characteristic Crosssectional Case-control Cohort RCT Selection bias Medium High Low Low Recall bias High High Low Low Loss to follow up NA NA High High Confounding Medium Medium Medium Low Time required Low Medium High High Cost Medium Medium High High Summary Observational Experimental Cohort Many outcomes, exposures limited Case- control One outcome, many exposures Cross – sectional Many exposure, many outcomes; Temporality limits causal inference Randomised controlled trial Ethical constraints Ideal design