The Ear - TeacherWeb
advertisement
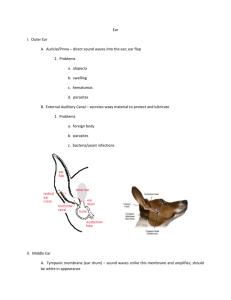
The Ear Terminology chapter 13 Function • To hear • To provide the sense of balance Structure of the Ear • External ear – Auricle (pinna) to the eardrum – Directs sound waves into the ear Structure of the Ear • Middle ear – Eardrum (tympanic membrane) – Eustachian tube connects middle ear to pharynx • Equalizes air pressure on both sides of eardrum – Ossicles • Carry sound vibrations • 3 small bones Structure of the Ear • Inner ear – Bony space in skull – Cochlea • Contains organ of hearing – Semicircular canals and vestibule • Sense of balance is maintained here • Equilibrium Word Parts • Combining forms – acou/o, audi/o…………hearing – aur/i, aur/o, ot/o……….ear – labyrinth/o…………….. inner ear – myring/o………………..eardrum, tympanic membrane Medical Terms • Otomycosis – fungus in the ear – usually affects the outer ear canal Medical Terms • Tympanitis – inflammation of the middle ear – commonly called otitis media (OM) – Bulging, perforated, or reddened tympanic membrane are signs – Common in children Disease and Disorder Terms • Meniere’s disease – Chronic disorder – affects the inner ear – Dizziness, ringing in the ears, and hearing loss are the symptoms Normal Abnormal Disease and Disorder Terms • Tinnitus – Ringing in the ears – Can be caused by Aspirin Disease and Disorder Terms • Vertigo – sense that one’s own body or the environment is revolving – may indicate inner ear disease Surgical Terms • Myringotomy – Incision into the eardrum to release pus or fluid and relieve pressure in the middle ear Diagnostic Terms • Otoscope – instrument used for visual examination of the ear Complementary Terms • Audiologist – one who studies and specializes in hearing • Audiology – study of hearing Common Abbreviations • • • • • EENT……..eyes, ears, nose, and throat OM………..otitis media AD…………right ear AS…………left ear AU…………both ears