Deoxyribose nucleic acid
advertisement
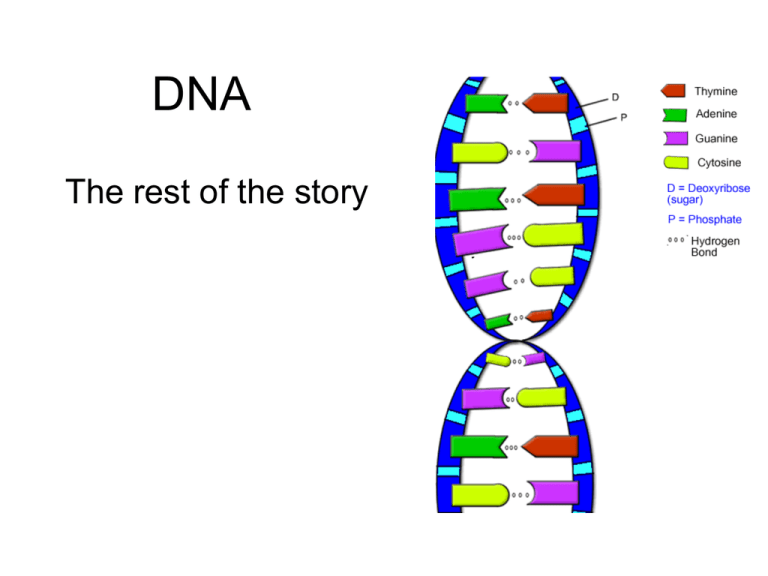
DNA The rest of the story Discovering the structure of DNA • DNA = Deoxyribose nucleic acid • Made out of sugars (deoxyribose), phosphates and nitrogen bases Discovering the structure of DNA • Structure was discovered in 1953 by James Watson and Francis Crick Discovering the structure of DNA Rosalind Franklin’s DNA image “Chargoff’s rule” A=T & C=G Cell division and DNA replication • Cells divide (a process called mitosis) Why divide? Growth, Repair, Replacement of cells • Before cells divide they must first copy the DNA so both cells will have a copy. DNA replication: When the cell copies the DNA 2 daughter cells are both identical to the parent cell Steps to DNA replication 1. DNA helicase (an enzyme) unwinds and unzips the DNA 2. DNA polymerase (another enzyme) reads the two DNA strands and lays down the new DNA 3. DNA polyermase checks the base pairs and makes sure there are no mistakes 4. DNA helicase zips the half old/ half new strands of DNA back up and winds it back into a helix DNA replication occurs at the replication fork * Replication occurs from 5’ to 3’ * One strand is the leading strand, one is the lagging strand. The Okazaki fragments are fused together by DNA ligase, an enzyme. DNA replication Replication results in 2 identical strands of DNA. Each strand is half old, half new. mistakes, or changes in the DNA are called mutations. Transcription of DNA •DNA is in the nucleus, right? •DNA cannot leave the nucleus •So DNA must send a messenger to carry its code outside of the nucleus, so the cell machinery in the cytoplasm can read the message and use it to make a protein •DNA codes for PROTEIN!!! •The messenger that DNA sends is called mRNA. •Transcription is the process by which DNA makes RNA. It has 4 steps. Transcription of DNA 1. DNA helicase unwinds and unzips the DNA 2. RNA polymerase reads the DNA code and lays down the mRNA strand. 3. There is no Thymine in mRNA, use Uracil instead! 4. DNA helicase winds the DNA strand back up 5. The mRNA gets a cap and a tail, and leaves the nucleus Translation: translating the code into protein Translation steps: Codon = three bases on the mRNA strand 1. Enzymes “read” the message three bases at a time on the mRNA and attach amino acids into a chain, corresponding to the code. The start codon on mRNA is always AUG. 2. The amino acid chain grows until it comes to a stop codon... Then it is snipped off and is a finished protein. So DNA codes for Protein! The genetic code Translate this code: AUGAAAGCUGACUCAGGGCCGACUGCAUAA



