Web Design I - Technical Slides
advertisement

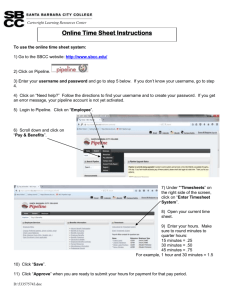
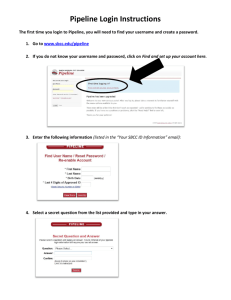
Web Design I Technical Slides Internet Friend or Foe What is the Internet? • A single computer • A Network connects workstations to a Server • Servers – File and Print – Application – Web • A Local Area Network (LAN) • A Wide Area Network (WAN) • A network of networks Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 3 How did the Internet start? • Advanced Research Projects Agency Network, was started in the 1960's by the U.S. Defense Department. ARPANet is the predecessor to the Internet. • De-centralized • No single network administrator • Runs on TCP/IP Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 4 Network Models • Network Interface Layer • Transport Layer – Transfer Control Protocol (TCP) – Physical – Datalink • Application Layer • Network Layer – Internet Protocol (IP) Updated 8/17/2008 – Presentation – Session – Application Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 5 HTTP • HTTP Hypertext Transfer Protocol • Hyperlink • Hypertext Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 6 Internet Protocols • • • • HTTP (Port 80) HTTPS (Port 433) E-mail (Port 25) FTP File Transfer Protocol (Port 21) • Gopher (Port 70) • RTSP Real Time Stream Control Protocol (Port 554) • Telnet (Port 23) Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 7 ASCII/HTML • ASCII American Standard Code for Information Interchange • HTML Hypertext Markup Language Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 8 XHTML and XML • XHTML Extensible HTML • XML Extensible Markup Language Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 9 The Web Browser • • • • Internet Explorer Firefox Netscape Safari 2007 July June May April March February January • Opera • AOL • Google?!??! Source: http://www.w3schools.com/browsers/browsers_ stats.asp IE7 IE6 IE5 Fx Moz S 20.10% 36.90% 1.50% 34.50% 1.40% 19.70% 37.30% 1.50% 34.00% 1.40% 19.20% 38.10% 1.60% 33.70% 1.30% 19.10% 38.40% 1.70% 32.90% 1.30% 18.00% 38.70% 2.00% 31.80% 1.30% 16.40% 39.80% 2.50% 31.20% 1.40% 13.30% 42.30% 3.00% 31.00% 1.50% Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu O 1.50% 1.50% 1.50% 1.50% 1.60% 1.70% 1.70% 1.90% 1.80% 1.70% 1.60% 1.60% 1.50% 1.50% 10 Browser plug-ins • • • • • • • Adobe Flash Adobe Acrobat Adobe Shockwave Apple QuickTime Microsoft SilverLight Real Player Sun Java Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 11 Music • Ghetto Gospel, by Tupac Shakur, is inspired by which Elton John / Bernie Taupin song? Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 12 Music • Ghetto Gospel, by Tupac Shakur, is inspired by which Elton John / Bernie Taupin song? • Indian Sunset – From Mad Man Across the Water Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 13 XHTML Extensible Formatting Language of the Web What Happened to HTML • • • • • • eXtensible Hypertext Markup Language Combines of HTML and XML XHTML is an adopted standard Support is universal among current browsers Allows support for mobile devices More strict code formatting than HTML Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 15 Example Page • This is how a basic XHTML page is displayed in Internet Explorer • Looks like any HTML page Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 16 Viewing Source • Click on View, Source Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 17 XHTML Source Code • This is the information that causes the page to be rendered Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 18 XHTML Structure • All XHTML documents have two sections – Head This information is not seen on the web page Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 19 XHTML Structure – Body This information is displayed on the web page Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 20 XHTML Tags • Tags are denoted and surrounded by the less-than and greater-than signs < > • Tags MUST be lowercase • Tags may have attributes • Attributes may have a value – Attribute values MUST always be enclosed in double-quotation marks " " (not “”) Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 21 XHTML Tags • Attributes are separated by a single space • Some tags have opening and closing tags – Closing tags are denotes by the preceding forward slash / in the tag Example: </body> – Tags that do not have a separate closing tag are closed with a forward slash before the closing greater-than sign Example: <br /> Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 22 XHTML Tags • Nested tags MUST be closed in the opposite order in which they were opened – Example: <td><div>Content</div></td> Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 23 Astronomy • How many planets are in our solar system? Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 24 Astronomy • How many planets are in our solar system? • Eight. Pluto was demoted in August 2006 by the International Astronomical Union. Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 25 Definitions Let’s Get on the Same Page Definitions Computer Stuff Client, Workstation • A single computer on the network • Web site visitor • Customer Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 28 Server • A computer provides services to a network • Common types of servers – – – – Web File and Print Application Authentication Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 29 Credentials • Username, I.D., Logon Name • Password Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 30 WebDAV • Web-based Distributed Authoring and Versioning • It is a set of extensions to the HTTP protocol which allows users to collaboratively edit and manage files on remote web servers • Using HTTPS, is more secure than FTP Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 31 FTP • • • • File Transfer Protocol Universal Less secure than WebDAV Comes in FTPS flavor which encrypts transmission Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 32 Definitions Browser Stuff Title Bar Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 34 Browser Window Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 35 Status Bar Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 36 URL • • • • Uniform Resource Locator Uniform Resource Indicator (URI) Address Web Address http://www.WebDesignSB.com/Information/MAT153/ Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 37 Domain • In the web address: http://www.WebDesignSB.com/information/MAT153/ • WebDesignSB.com is the Domain Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 38 Definitions Graphic Stuff Alias, Anti-Alias • Alias is an abrupt change between two colors in an image • Anti-Alias is a smooth change between two colors in an image Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 40 JPEG • • • • Joint Photographic Experts Group Millions of Colors Lossy Compression One of two Web-Ready image formats Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 41 GIF • • • • • • Graphics Interchange Format 256 Indexed Color Loss-less Compression Transparency Animation One of two Web-Ready image formats Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 42 PNG • • • • • Portable Network Graphics Millions of colors Loss-less compression Rapidly gaining acceptance Not universal enough yet to recommend Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 43 Flat Color • A single smooth expanse of a single color Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 44 Dither • The combining of several colors in an image to trick the eye into seeing a single color that is other than the colors in the image Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 45 Feather-Edged • A smooth or fuzzy transition between two composited images or an image and the background • Opposite of Hard-Edged Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 46 Hard-Edged • A sharp distinct transition between a composited image and the background or another image Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 47 Raster, Rasterize • Raster is a bit map image • Each pixel in the image is stored as a byte of information • The number of bits in the byte determines the color depth Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 48 Vector • Images that are represented by points and lines, rather than by individual pixel values • Vector image file size a generally very small as compared to Raster images • Flash uses vector images to animate quickly with a relatively small file size Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 49 Web-Safe Color • Also know as Browser-Safe colors • One of 216 colors that are a part of the color pallets of Mac/OS, Unix and Windows • Not really an issue any more! Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 50 Tile • Tiles are used for background images on Web pages http://www.scottandtammy.com/mat122/seamless_graphics/ Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 51 Tile Example Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 52 Definitions Monitor Stuff Pixel • Picture Element • A single dot on a computer or television screen Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 54 PPI • • • • Pixels Per Inch Used to define monitor resolution 72 PPI is typical monitor resolution 2540 PPI is typical for print publishing Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 55 DPI • • • • • Dots Per Inch Defines the sharpness of the image 72 DPI is for the Web 600 DPI is most home printers 1200 and greater is for professional printing Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 56 Resolution • The X and Y coordinates of the number of pixels displayed on a computer monitor • Typical resolutions are: – 640 x 480 - Universally Compatible – 800 x 600 - Good current minimum standard – 1024 x 768 - Good minimum for production houses Updated 8/17/2008 – 1280 x 1024 - Maximum Standard Desktop Size – 1680 x 1050 - Apple Cinema Display – 1920 x 1200 - Apple Cinema HD Display – 2048 x 1280 - Apple Cinema HD Display – 2560 x 1600 - Apple Cinema HD Displayer Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 57 CMYK • Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black • Used in print media Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 58 RGB • Red, Green Blue • Used for screen delivery • These three colors sum together to display all of the millions (16.7) of color you see on your computer monitor Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 59 Definitions XHTML and Dreamweaver Stuff XHTML • Extensible Hyper-Text Markup Language Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 61 XHTML Text • Text that is displayed in the browser windows that has been typed directly into the XHTML code Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 62 Mouseover, Rollover, Image Swap • Terms used interchangeably to describe a change in image when the mouse pointer hovers over an image Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 63 Table • Like a spreadsheet • Tables used to be used to format pages and hold sliced images together • This is fallen out of favor Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 64 Nested Table • An HTML table that is inside the cell of another HTML table Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 65 CSS • Cascading Style Sheet Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 66 Divisions and Spans • <DIV> – Div’s are used in CSS layouts to apply a style to an area or element • <SPAN> – Span’s are used in CSS layouts to apply a style to an area or element – Span’s can be applied in mid-sentence without a line break Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 67 The File System Know Your Enemy Folder and Filenames • Adopt the 8.3 (MS DOS convention) nomenclature when you will be converting between Windows OS and Mac OS/9 and older • For Mac OS/9 compatibility, filenames should be 31 total characters or less • Use all lowercase letters – Unix, Linux and Apple servers are case-sensitive – Windows servers are not case-sensitive Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 69 Characters to Use • • • • Letters a - z Numbers 0 - 9 Dash or Hyphen Underscore _ Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 70 Characters Not to Use • • • • • • • Space Forward slash / Back slash \ Colon : Asterisk or star * Question mark ? Double Quotation “ Updated 8/17/2008 • Greater than and less than signs >< • Pipe | • Pound or number sign # • Percent sign % • At sign @ • Comma , • Apostrophe ‘ Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 71 Special File Names • First page of a web site must be one of these file names – index.htm (most universally compatible) – index.html (not supported IIS by default) – Default.htm – Default.asp – Default.aspx Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 72 Zoology • What is a pregnant gold fish called? Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 73 Zoology • What is a pregnant gold fish called? • A twit Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 74 Questions and Answers Updated 8/17/2008 Scott Nelson, Instructor SANelson@Pipeline.SBCC.Edu 75 Thank You! That wraps it for tonight. Thanks for your attention!